1 佛山科学技术学院材料科学与氢能学院, 广东 佛山 528000
2 广东省氢能技术重点实验室, 广东 佛山 528000
3 佛山市无机微纳米发光材料工程技术研究中心, 广东 佛山 528000
4 佛山科学技术学院物理与光电工程学院, 广东 佛山 528225
5 粤港澳智能微纳光电技术联合实验室, 广东 佛山 528225
传统的商用白光LED由于缺乏红光成分, 造成显色指数较低。为了提升白光LED的显色性能, 可以在荧光粉中加入Sm3+, 以提升橙红光的发射能力。采用传统的高温固相法制备了Ca2YNbO6:Sm3+新型双钙钛矿氧化物荧光粉, 并详细研究了荧光粉末的晶体结构、元素组成、发射光谱、激发光谱、热稳定性和荧光寿命等性质。研究表明, 该荧光粉为纯相化合物, 粒径约5 μm。在408 nm的激发下, Sm3+在650 nm附近有强烈的红光发射。数据拟合表明, 荧光粉的发光属于Sm3+的电偶极子-偶极子相互作用过程。高温测试表明, 该氧化物荧光粉具有较高的热稳定性。将商用蓝粉、绿粉与Ca2Y0.96NbO6:0.04Sm3+粉体混合, 并利用365 nm的InGaN芯片激发, 可制备出色坐标为(0.344, 0.350), 色温为4 989 K, 显色指数为81的暖白光LED。
稀土掺杂材料 光致发光 荧光粉 红光发射 白光LED rare-earth-doped materials photoluminescence phosphors red emission white LED
1 华东师范大学物理与电子科学学院极端光机电实验室,上海 200241
2 华东师范大学纳光电集成与先进装备教育部工程研究中心,上海 200241
3 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强场激光物理国家重点实验室,上海 201800
光子集成器件以极低的成本和功耗实现覆盖从光源、调制、非线性频率转换、光放大到光探测的全功能单片集成,对光电信息处理系统产生显著而深远的影响,并推动一系列诸如高速通信、人工智能、量子信息,以及精密测量等重大应用领域的持续发展。近年来,铌酸锂薄膜光子器件得益于离子揭膜技术和微纳刻蚀工艺的进步,以宽的工作窗口、低的传输损耗、大的调制带宽、高的非线性光学转换效率和兼容大规模光子集成等优点,在集成光子学领域占据重要一席之地。本文介绍了利用超快激光光刻结合化学机械抛光技术在掺杂有源发光稀土离子的铌酸锂薄膜衬底上实现片上激光与光放大的最新进展,包括在波导放大器中实现了超过20 dB的最大内部净增益,并且在高品质铌酸锂微盘中演示了具有454.7 Hz窄线宽的电光可调谐单频激光器,演示了单片集成的电驱动微环激光器,以及连续光刻方式实现的无源/有源混合集成器件。
集成光学 超快激光加工 铌酸锂 光放大器 光源 稀土掺杂材料 光学学报
2023, 43(16): 1623014

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Laboratory of Micro-Nano Optoelectronic Materials and Devices, Key Laboratory of Materials for High-Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 University of Michigan-Shanghai Jiao Tong University Joint Institute, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
4 CAS Center for Excellence in Ultra-intense Laser Science (CEULS), Shanghai 201800, China
5 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
The idea of a slot waveguide amplifier based on erbium-doped tellurite glass is first theoretically discussed in this work. Choosing the horizontal slot for low propagation loss, the TM mode profile compressed in the insertion layer was simulated, and the gain characteristics of the slot waveguide amplifier were calculated. Combining the capacity to confine light locally and the merits of tellurite glass as an emission host, this optimized amplifier shows enhanced interactions between the electric field and erbium ions and achieves a net gain of 15.21 dB for the 0.01 mW input light at 1530 nm, implying great promise of a high-performance device.
guided waves optical amplifiers rare-earth-doped materials Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(1): 011404
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Heat Fluid Flow Technology and Energy Application, School of Mathematics and Physics, Suzhou University of Science and Technology, Suzhou 215009, China
2 Suzhou Institute of Nano-Tech and Nano-Bionics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou 215123, China
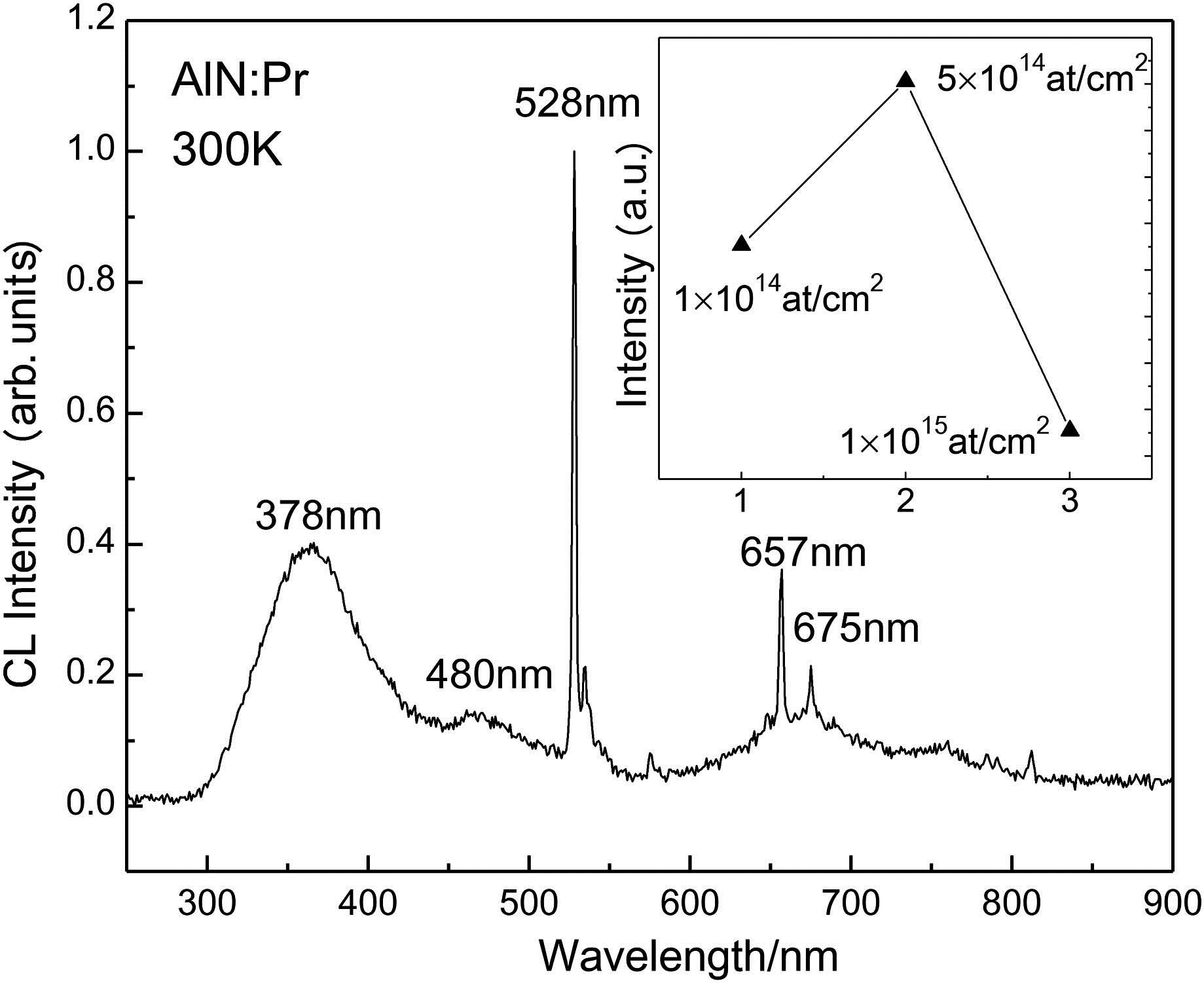
In this work, Er-doped aluminum nitride (AlN), Pr-doped AlN, and Er, Pr co-doped AlN thin films were prepared by ion implantation. After annealing, the luminescence properties were investigated by cathodoluminescence. Some new and interesting phenomena were observed. The peak at 480 nm was observed only for Er-doped AlN. However, for Er, Pr co-doped AlN, it disappeared. At the same time, a new peak at 494 nm was observed, although it was not observed for Er-doped AlN or Pr-doped AlN before. Therefore, the energy transfer mechanism between Er3+ and Pr3+ in AlN thin films was investigated in detail. Through optimizing the dose ratio of Er3+ with respect to Pr3+, white light emission with an International Commission on Illumination chromaticity coordinate (0.332, 0.332) was obtained. This work may provide a new strategy for realizing white light emission based on nitride semiconductors.
160.4760 Optical properties 160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 160.6000 Semiconductor materials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 111602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Materials Science and Engineering, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
Ho3+/Yb3+: BaMoO4 phosphors with different concentrations were fabricated by a gel combustion method. The upconversion (UC) luminescence, intrinsic optical bistability, and the corresponding mechanisms were reported for the present system. The optical thermometric properties based on red (5F5→5I8) and green (5F4/5S2→5I8) emissions were studied. The sensing sensitivities could be tuned by manipulating the cooperative energy transfer process. The highest absolute sensitivity was 99 × 10 4 K 1 at 573 K, which is larger than that of many previous UC materials.
160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 120.6780 Temperature 280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(11): 111601
吉林大学电子科学与工程学院集成光电子学国家重点实验室, 吉林 长春 130012
中红外波段光纤激光光源在基础科学研究、光通信、生物医疗、环境监测以及**安全领域有着重要应用。超连续谱(SC)激光光源和稀土离子掺杂光纤激光器是目前研究得较多的两类中红外波段激光光源。面向该类光源的应用需求,笔者研究组经过大量实验探索,筛选出一种具有较高稳定性和较高损伤阈值的氟碲酸盐玻璃光纤,并利用其作为非线性介质研制出了光谱范围覆盖0.6~5.4 μm宽带的SC激光光源和平均功率约为20 W、光谱范围覆盖1~4 μm的SC激光光源;制备出具有较强抗潮解能力的Ho
3+离子掺杂AlF3基玻璃光纤,并利用其作为增益介质,获得了波长约为2868 nm的激光输出;研制出具有较低声子能量的Ho
3+离子掺杂InF3基玻璃光纤,并利用其作为增益介质,获得了波长约为2875 nm的激光输出。总结了氟碲酸盐玻璃光纤、AlF3基玻璃光纤和InF3基玻璃光纤的特点及相应激光器的研究进展。
光纤光学 激光材料 中红外激光 超连续谱产生 稀土掺杂材料 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170604
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
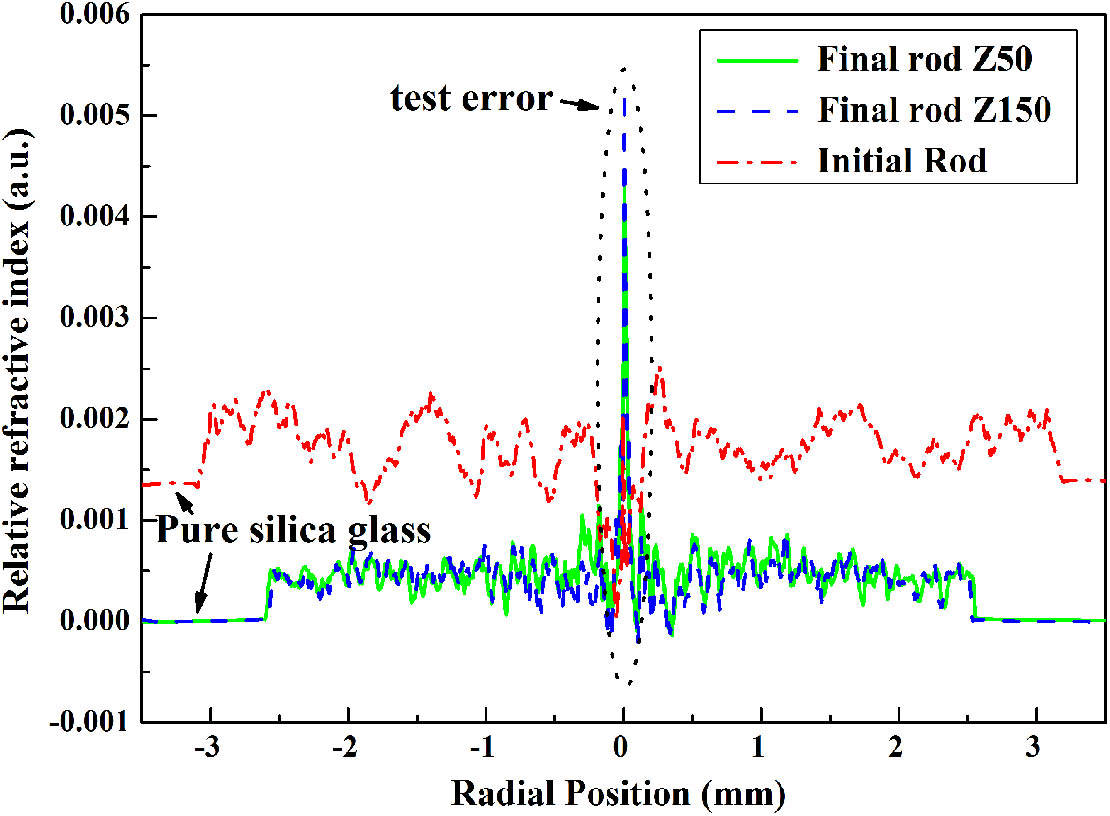
A large-mode-area (LMA) ytterbium-doped photonic crystal fiber (PCF) with core NA of 0.034 and core diameter of 50 μm was made by the stack-and-draw technique. The core is formed by Yb3+/Al3+/F /P5+ co-doped silica glass containing 0.09 mol% Yb2O3 with an absorption coefficient at 976 nm up to 3.2 dB/m. The core glass with homogeneous distribution of Yb3+ ions and refractive index difference of 4 × 10 4 compared with pure silica was prepared by the sol-gel method and heat homogenization at 2000°C. Laser power amplification of this LMA PCF was studied using a seed source of 21 ps pulse duration and 48.7 MHz repetition rate at 1030 nm wavelength. With pump power of 520 W, a maximum 272 W (266 kW peak power) quasi-single-mode laser output with M2 of 2.2 was achieved in a 4.7 m fiber length bent at a diameter of 47 cm with slope efficiency of 52%, and no obvious mode instability, stimulated Raman scattering, or thermal damage on the end facet of the fiber were observed.
140.3538 Lasers, pulsed 140.3615 Lasers, ytterbium 140.3510 Lasers, fiber 160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 071401

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Ningbo University of Finance and Economics, Ningbo 315175, China
2 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 201804, China
3 School of Material Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang 212013, China
4 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, College of Optical Science and Engineering, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
We report on the elemental redistribution behavior in oxyfluoride glasses with a high repetition rate near-infrared femtosecond laser. Elemental analysis by an electro-probe microanalyzer demonstrates that the redistributions of Ca2+ and Yb3+ ions change dramatically with pulse energy, which are quite different compared with previous reported results. Confocal fluorescence spectra of Yb3+ ions demonstrate that the luminescence intensity changes obviously with the elemental redistribution. The mechanism of the observed phenomenon is discussed. This observation may have potential applications in the fabrication of micro-optical devices.
160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 160.2750 Glass and other amorphous materials 160.4760 Optical properties 350.3390 Laser materials processing Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 061601
唐山学院 智能与信息工程学院, 河北 唐山 063000
为了对存在于石英玻璃中的非桥氧空穴缺陷的特性进行研究, 采用高频等离子体法对掺Yb3+石英玻璃进行了制备。首先介绍了玻璃样品的制备过程, 然后对所制备的掺Yb3+石英玻璃样品的吸收特性、发射特性以及傅里叶变换红外吸收光谱进行了分析。结果表明, 所制备的玻璃样品具有Yb3+离子典型的吸收特性。位于260 nm波长的吸收峰以及200 nm激发波长下产生的位于630 nm波长的发射峰都表明所制备的玻璃样品中存在非桥氧空穴缺陷。并且不同激发波长所产生的发射峰以及红外吸收光谱都说明玻璃样品中的非桥氧空穴缺陷是由≡Si-O↑和≡Si-O↑…H-O-Si≡两类空穴中心构成, Yb3+离子对合作发光与非桥氧空穴缺陷间存在能量转移过程。
稀土掺杂材料 掺Yb3+石英玻璃 高频等离子体 非桥氧空穴缺陷 rare earth doped materials Yb3+-doped silica glass high frequency plasma NBOHC defects
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Materials Science and Engineering, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
2 Institute of Optoelectronic Technology, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
3 e-mail: sxucjlu@163.com
Er/Ho co-doped oxyfluoride germanosilicate glass and glass ceramics are prepared and compared. The results indicate that the glass consists of SiO4 and GeO4 structural units, while the network of the glass ceramics consists of SiO4, GeO4, and GeO6 units together with NaYF4 nanocrystals. The presence of multiple local structures in glass ceramics creates a range of dipole environments, which is beneficial to the broadening of 2.7 μm emission. Two other reasons are attributed to the broadening of 2.7 μm emission in glass ceramics: the energy-level splitting of Er3+ and the enhancement of the Ho3+:I65→I75 transition in NaYF4 nanocrystals.
Rare-earth-doped materials Laser materials Glass and other amorphous materials Spectroscopy, infrared Photonics Research
2018, 6(4): 04000339





