Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Space Active Opto-ElectronicsTechnology, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200083, China
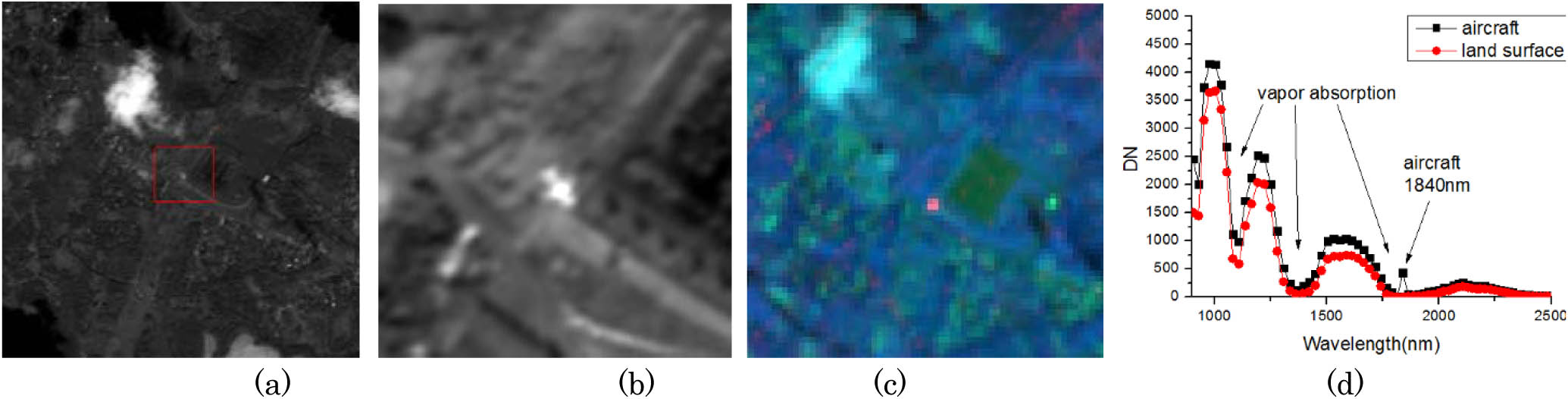
Infrared signatures of aircraft are the basis for detection and monitoring. In past years, most of the studies focused on the aircraft’s infrared signature in the mid-wave spectral region and long-wave spectral region for missile guidance or aircraft survivability studies. For the security of civil aviation, methods and instruments that can detect and monitor aircrafts from space are expected to be developed in the coming years. A short-wave infrared hyperspectral imager aboard the Tiangong-1 spacecraft acquired some civil aircraft’s spectral data. The differences between the aircraft and the background in their spectral signatures are analyzed and discussed. Less absorption in the vapor absorption bands and a reflection spike is discovered at the 1.84 μm spectral band. The result shows that 1.84 μm and other vapor absorption bands can make contributions to aircraft detection in the daytime.
280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors 100.4145 Motion, hyperspectral image processing Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(12): 122801
哈尔滨工程大学 信息与通信工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
提出了一种基于LKRX检测器的实时异常检测算法.利用局部因果滑动阵列窗, 使检测系统保持因果性.根据卡尔曼滤波器的递归思想, 利用Hermitian矩阵分块求逆引理和Woodbury引理, 将LKRX算法中核协方差矩阵以及其逆矩阵以递归方式更新, 避免了数据的重复计算和逆矩阵的求解, 大大降低了算法复杂度.通过真实数据进行实验, 结果表明, 与LKRX算法相比, 实时LKRX算法在保持相同检测精度的同时, 消耗更少的计算时间; 而与实时RX算法相比, 实时LKRX算法能够检测到更多的异常目标.
高光谱图像处理 多项式KRX算法 实时异常检测 Hermitian矩阵分块求逆引理 Woodbury引理 hyperspectral image processing polynomial KRX algorithm real-time anomaly detection Hermitian lemma Woodbury’s identity
1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所光学成像重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710119
2 西安石油大学计算机学院, 陕西 西安 710065
3 中国人民武装警察部队工程大学, 陕西 西安 710086
4 中国科学院软件研究所, 北京 100080
5 华东交通大学信息工程学院, 江西 南昌 330013
传统的高光谱遥感影像分类算法侧重于光谱信息的应用。 随着高光谱遥感影像的空间分辨率的增加, 高光谱影像中相同类别的地物在空间分布上呈现聚类特性, 将空间特性有效地应用于高光谱遥感影像分类算法对分类精度的提升非常关键。 但是, 高光谱影像的高分辨率提供空间聚类特性的同时, 在不同地物边缘处表现出的差异性更加明显, 若不对空间邻域像素进行甄选, 直接将邻域光谱信息引入, 设计空谱联合稀疏表示进行图像分割, 则分类误差较大, 收敛速度大大降低。 将光谱角引入空谱联合稀疏表示图像分类理论中, 提出了一种基于邻域分割的空谱联合稀疏表示分类算法。 该算法利用光谱角计算相邻像素的空间相似度, 剥离相似度较低的邻域像素, 将相似度高的邻域像素定义为同类地物, 引入空谱联合稀疏表示模型中, 采用子联合空间追踪算子和联合正交匹配追踪算子对其优化求解, 以最小重构误差为准则进行分类。 选取AVIRIS及ROSIS典型光谱影像数据进行实验仿真, 从中可以看出, 随着光谱角分割阈值的提高, 复杂的高光谱影像分类精度和平滑区域的高光谱影像分类精度均逐步提高, 表明邻域分割在空谱联合稀疏表示分类中的必要性。
高光谱影像处理 稀疏表示 邻域聚类 邻域分割 最小重构误差 Hyperspectral image processing Sparse representation Neighborhood clustering Neighborhood segmentation Minimum reconstruction error 光谱学与光谱分析
2016, 36(9): 2919
1 中国科学院西安光学精密机械研究所光学成像重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710119
2 西安石油大学计算机学院, 陕西 西安 710065
3 中国人民武装警察部队工程大学, 陕西 西安 710086
4 中国科学院软件研究所, 北京 100080
5 华东交通大学信息工程学院, 江苏 南昌 330013
高光谱遥感影像不但具有高分辨率的空间信息还包含连续的光谱信息, 因此在目标探测领域具有独特的应用优势。 传统的高光谱遥感影像目标探测侧重于光谱信息的应用, 形成了确定性算法和统计学算法。 确定性算法通过计算目标光谱与待检测光谱之间的距离来查找目标, 不能检测亚像素目标, 而且容易受到噪声的影响; 统计学目标检测计算背景统计特性, 通过探测异常点来检测目标, 可以检测亚像素目标和小目标, 但容易受到目标尺寸的影响, 不能很好的检测大目标。 随着高光谱遥感影像的空间分辨率的增加, 探测目标已有亚像素目标逐步转换为单像素及多像素目标, 此时, 在高光谱图像中, 相同类别的地物在空间分布上呈现聚类特性, 因此, 在利用高光谱遥感影像进行目标探测时, 需要将其空间信息融入算法中。 将空间特征引入传统目标探测算法。 提出了一种新的空谱结合的高光谱目标探测算法, 将传统的基于统计的目标探测算子与空域邻域聚类算法相结合, 首先利用目标探测算子将影像划分为潜在目标区域与背景区域; 通过计算潜在目标区域的质心, 以质心为中心进行邻域聚类, 剔除潜在目标区域中的背景区域, 通过迭代计算获取最终目标探测结果。 传统的基于统计的目标探测算子, 将整个探测区域定义为背景区域, 实现对背景区域的统计特征提取, 而该方法将背景区域与潜在目标区域分离, 剔除了目标区域对背景区域的统计干扰。 将本算子与传统的约束能量最小化算子和自适应余弦探测算子进行分析比较可知, 该算子的大目标探测性能优于传统的统计算子。
目标探测 空谱联合算子 高光谱影像处理 邻域聚类 统计学算子 Target detection Spatial-spectral algorithm Hyperspectral image processing Neighborhood clustering Statistical operators 光谱学与光谱分析
2016, 36(4): 1163
1 哈尔滨工程大学 信息与通信工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150001
2 德州理工大学, 计算机科学系, 拉伯克 德克萨斯州 79409
高光谱图像分类是高光谱数据分析的重要研究内容.相关向量机由于不受梅西定理的限制、不需要设置惩罚因子等优势受到广泛关注.由于高光谱数据具有较高的维数, 当训练样本较少时, 高光谱数据的分类精度受到严重的影响.通常解决这种现象的办法是对原数据进行特征降维处理, 然而多数基于filter模型的特征选择算法无法直接给出最优特征选择个数.为此提出利用蒙特卡罗随机实验可以对特征参量进行统计估计的特性, 计算高光谱图像的最优降维特征数, 并与相关向量机结合, 对降维后的数据进行分类.实验结果表明了使用蒙特卡罗算法求解降维波段数的可靠性.相比较原始未降维数据, 降维后的高光谱图像分类精度有较大幅度的提高.
高光谱图像处理 蒙特卡罗特征降维算法 相关向量机 最优降维波段数 hyperspectral image processing Mote Carlo feature reduction method relevance vector machine optimal feature reduction number
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Oil microleakage can cause the land surface vegetation to be abnormal. An oil and gas exploration method based on the vegetation information in the hyperspectral remote sensing images is proposed. It's used to probe the effectiveness of extracting the oil and gas microleakage information, with the vegetation anomalies in the remote sensing images. A decision tree based on the vegetation index is taken to extract the anomalies areas of vegetation in the CASI images. It's shown by the experiment that there are some potential for the exploration of oil and gas in the areas covered by sparse vegetations.
100.0100 Image processing 100.4145 Motion, hyperspectral image processing Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(s1): s11004
1 杭州电子科技大学计算机应用技术研究所, 浙江 杭州 310018
2 浙江大学电气工程学院, 浙江 杭州 310027
针对非线性混合的高光谱图像目标检测问题,在核信号空间正交投影法(KSSP)的基础上,提出了一种光谱和空间信息结合的组合核信号空间正交投影方法(CKSSP)。分别基于边缘序和像元距离为序尺度函数的导出序将灰度形态变换扩展到多值图像空间中的形态变换,利用多结构元素组合的扩展数学形态学方法提取高光谱图像的空间信息。根据核函数定义,结合光谱信息和空间信息构造出组合核函数并加以证明,通过组合核信号空间正交投影实现目标检测。该方法在充分利用光谱信息的同时,合理利用了空间信息。仿真数据实验结果表明CKSSP的均方根误差比KSSP小0.03,真实高光谱图像数据实验和ROC曲线均表明CKSSP目标检测结果优于KSSP。
遥感 高光谱图像处理 数学形态学 核信号空间正交投影 目标检测 光学学报
2011, 31(12): 1228003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Land Environment and Disaster Monitoring of State Bureau of Surveying and Mapping of China, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, China
2 Hebei Bureau of Surveying and Mapping, Shijiazhuang 050031, China
To apply decision level fusion to hyperspectral remote sensing (HRS) image classification, three decision level fusion strategies are experimented on and compared, namely, linear consensus algorithm, improved evidence theory, and the proposed support vector machine (SVM) combiner. To evaluate the effects of the input features on classification performance, four schemes are used to organize input features for member classifiers. In the experiment, by using the operational modular imaging spectrometer (OMIS) II HRS image, the decision level fusion is shown as an effective way for improving the classification accuracy of the HRS image, and the proposed SVM combiner is especially suitable for decision level fusion. The results also indicate that the optimization of input features can improve the classification performance.
决策级融合 高光谱遥感 支持向量机 图象分类 100.4145 Motion, hyperspectral image processing 280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(3): 031002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Land Environment and Disaster Monitoring of State Bureau of Surveying and Mapping of China, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou 221116, China
Many remote sensing image classifiers are limited in their ability to combine spectral features with spatial features. Multi-kernel classifiers, however, are capable of integrating spectral features with spatial or structural features using multiple kernels and summing them for final outputs. Using a support vector machine (SVM) as classifier, different multi-kernel classifiers are constructed and tested using 64-band Operational Modular Imaging Spectrometer II hyperspectral image of Changping Area, Beijing City. Results show that by integrating spectral and wavelet texture information, multi-kernel SVM classifiers can obtain more accurate classification results than sole-kernel SVM classifiers and cross-information SVM kernel classifiers. Moreover, when the multi-kernel SVM classifier is used, the combination of the first four principal components from principal component analysis and wavelet texture provides the highest accuracy (97.06%). Multi-kernel SVM is therefore an effective approach to improve the accuracy of hyperspectral image classification and to expand possibilities for remote sensing image interpretation and application.
核函数 多核 支持向量机 小波变换 高光谱影像分类 100.4145 Motion, hyperspectral image processing 100.5010 Pattern recognition 100.7410 Wavelets Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(1): 011003
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electronic Engineering and Information Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230027, China
Technology used to automatically assess video quality plays a significant role in video processing areas. Because of the complexity of video media, there are great limitations to assess video quality with only one factor. We propose a new method using artificial random neural networks (RNNs) with motion evaluation as an estimation of perceived visual distortion. The results are obtained through a nonlinear fitting procedure and well correlated with human perception. Compared with other methods, the proposed method performs more adaptable and accurate predictions.
视频质量评价 人眼视觉 随机神经网络 运动矢量 120.3940 Metrology 110.3000 Image quality assessment 330.5020 Perception psychology 330.5000 Vision - patterns and recognition 100.2960 Image analysis 100.4145 Motion, hyperspectral image processing Chinese Optics Letters
2009, 7(11): 1004





