1 北京理工大学物理学院,北京 100081
2 北京理工大学先进光电量子结构设计与测量教育部重点实验室,北京 100081
单像素成像使用一系列空间光调制掩模对目标场景进行单像素亚采样,再根据掩模与测量值之间的关联重构出物体图像。这种间接获取图像的方式之所以能保证重建质量,除了有重构算法的功劳,更关键的是测量掩模的构造。随着压缩感知理论的引入,随机掩模进入人们视野,但它让测量变得盲目,缺乏针对性,而且这种掩模不便于存储和计算,极大限制了空间像素分辨率。哈达玛基掩模因其结构化特征使快速计算成为可能,且方便存储和提取,近年来得到广泛关注,已发展出诸多哈达玛基掩模优化排序方法,这些方法已被证明能大幅降低采样率。本综述系统地梳理了这类方法的设计框架和前沿进展,展望了确定性掩模构造的未来发展趋势,可为后续的研究工作提供有益的借鉴和指导。
计算成像 图像检测系统 成像理论 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(4): 0400006
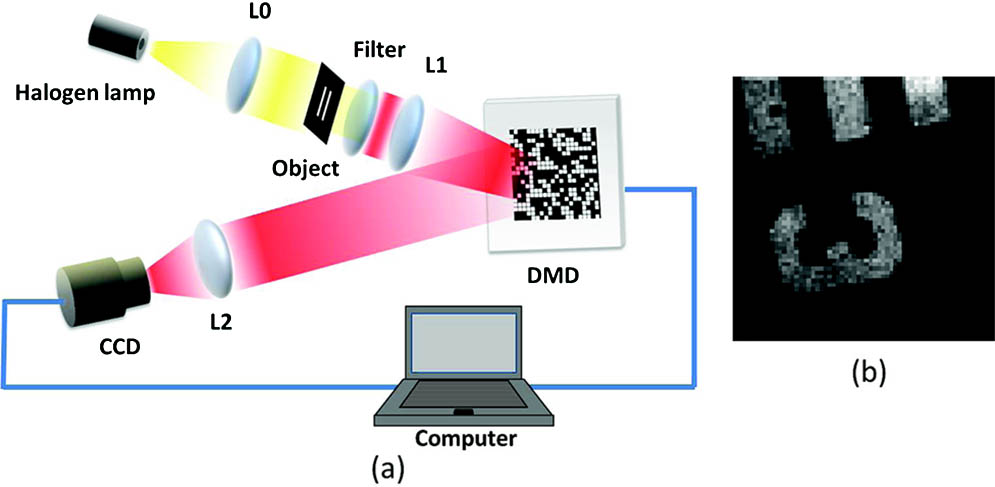
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center for Quantum Technology Research, School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
3 Key Laboratory of Electronics and Information Technology for Space Systems, National Space Science Center, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
Single-pixel cameras, which employ either structured illumination or image modulation and compressive sensing algorithms, provide an alternative approach to imaging in scenarios where the use of a detector array is restricted or difficult because of cost or technological constraints. In this work, we present a robust imaging method based on compressive imaging that sets two thresholds to select the measurement data for image reconstruction. The experimental and numerical simulation results show that the proposed double-threshold compressive imaging protocol provides better image quality than previous compressive imaging schemes. Faster imaging speeds can be attained using this scheme because it requires less data storage space and computing time. Thus, this denoising method offers a very effective approach to promote the implementation of compressive imaging in real-time practical applications.
110.0110 Imaging systems 110.2990 Image formation theory Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(12): 121101

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics and Center for Cold Atom Physics of CAS, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The effect of background light on the imaging quality of three typical ghost imaging (GI) lidar systems (namely narrow pulsed GI lidar, heterodyne GI lidar, and pulse-compression GI lidar via coherent detection) is investigated. By computing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of fluctuation-correlation GI, our analytical results, which are backed up by numerical simulations, demonstrate that pulse-compression GI lidar via coherent detection has the strongest capacity against background light, whereas the reconstruction quality of narrow pulsed GI lidar is the most vulnerable to background light. The relationship between the peak SNR of the reconstruction image and σ (namely, the signal power to background power ratio) for the three GI lidar systems is also presented, and the results accord with the curve of SNR-σ.
(110.0110) Imaging systems (110.2990) Image formation theory (110.1758) Computational imaging. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000431
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Physics, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
We show how quantum entangled biphoton states can be used to realize ghost scattering, a nonlocal scheme to obtain scattering information of an unknown object through the correlation measurement of the scattering photons in two different optical paths. We present a framework to describe the biphoton ghost scattering process from the T-matrix formula of the scattering theory. We find the scattering information of a test object can be retrieved from either the test arm or the reference arm. By adjusting the biphoton states, the ghost scattering patterns may be varied from the scattering pattern of the object in the test arm to the object in the reference arm.
Quantum optics Quantum optics Scattering theory Scattering theory Image formation theory Image formation theory Photonics Research
2017, 5(1): 01000041
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics and Center for Cold Atom Physics of CAS, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
For a Hanbury Brown and Twiss system, the influence of relative motion between the object and the detection plane on the resolution of second-order intensity-correlated imaging is investigated. The analytical results, which are backed up by experiments, demonstrate that the amplitude and mode of the object’s motion have no effect on the second-order intensity-correlated imaging and that high-resolution imaging can be always achieved by using a phase-retrieval method from the diffraction patterns. The use of motion de-blurring imaging for this approach is also discussed.
030.6600 Statistical optics 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 110.2990 Image formation theory 110.6150 Speckle imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(7): 070301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory on Integrated Optoelectronics, College of Electronic Science and Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun 130012, China
2 Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics and Center for Cold Atom Physics of CAS, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 e-mail: gongwl@siom.ac.cn
The features of the characteristic matrix used in linear intensity correlation reconstruction methods are directly related to the quality of ghost imaging. In order to suppress the noise caused by the off-diagonal elements in the characteristic matrix, we propose a reconstruction method for ghost imaging called scalar-matrix-structured ghost imaging (SMGI). The characteristic matrix is made to approximate a scalar matrix by modifying the measurement matrix. Experimental results show that SMGI improves the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the object reconstruction significantly compared with differential ghost imaging, even in the case of a nonzero two-arm longitudinal difference, which is a promising result for practical applications.of China (2013AA122901); National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61571427); Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2013162).
Image formation theory Image formation theory Coherence imaging Coherence imaging Speckle Speckle Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000281

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Signal Processing and Transmission, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications (NUPT), Nanjing 210003, China
In this paper, we propose a ghost imaging scheme with fast Walsh–Hadamard transform, named GIFWHT. In the scheme, Walsh–Hadamard pattern pairs are used to illuminate an object to generate pairs of detection results, and the corresponding differential detection result is used as the result as that from the conventional bucket detector. By performing the fast Walsh–Hadamard transform on 2k (k is a positive integer) differential detection results, the image of the object can be recovered. The experimental and numerical simulation results show that the reconstruction time of GIFWHT is greatly reduced, and the quality of the recovered image is noticeably improved. In addition, GIFWHT is robust against interference from environmental illumination and could savememory.Network Technology, Ministry of Education (NYKL2015011).
Computational imaging Computational imaging Image reconstruction techniques Image reconstruction techniques Image formation theory Image formation theory Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000240
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics and Center for Cold Atom Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics,Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
The influence of the axial relative motion between the target and the source on ghost imaging (GI) is investigated. Both the analytical and experimental results show that the transverse resolution of GI is reduced as the deviation of the target’s center position from the optical axis or the axial motion range increases. To overcome the motion blur, we propose a deblurring method based on speckle-resizing and speed retrieval, and we experimentally validate its effectiveness for an axially moving target with an unknown constant speed. The results demonstrated here will be very useful to forward-looking GI remote sensing.imaging;Image analysis
Image formation theory Image formation theory Quantum optics Quantum optics Computational Computational Photonics Research
2015, 3(4): 04000153
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics and Center for Cold Atom Physics of CAS, Shanghai Institute of Optics andFine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
We present a pseudo-inverse ghost imaging (PGI) technique which can dramatically enhance the spatial transverse resolution of pseudo-thermal ghost imaging (GI). In comparison with conventional GI, PGI can break the limitation on the imaging resolution imposed by the speckle’s transverse size on the object plane and also enables the reconstruction of an N-pixel image from much less than N measurements. This feature also allows high-resolution imaging of gray-scale objects. Experimental and numerical data assessing the performance of the technique are presented.
Quantum optics Quantum optics Image formation theory Image formation theory Image reconstruction techniques Image reconstruction techniques Speckle Speckle Photonics Research
2015, 3(5): 05000234
1 中国科学院电子学研究所, 北京 100190
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
合成孔径激光雷达(SAL)能实现远距离目标的高分辨成像,但是,其测绘带宽一般很小,不利于其在对地观测中的应用。针对这一问题,给出了宽测绘带SAL 实际成像范围的建议,具体研究了采用方位向短、距离向长的非对称光斑照明实现宽测绘带SAL 的成像处理问题。采用波动光学衍射理论,给出了这种宽测绘带SAL 的详细成像理论描述和数学仿真成像演示。结果表明,由于光学的短波长特性,非对称光斑照明的宽测绘带SAL 也近似遵循基本SAL图像形成方法:傅里叶变换实现距离压缩,匹配滤波实现方位图像聚焦。
遥感 激光雷达 合成孔径 成像理论 宽测绘带





