Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Shanghai 201800, China
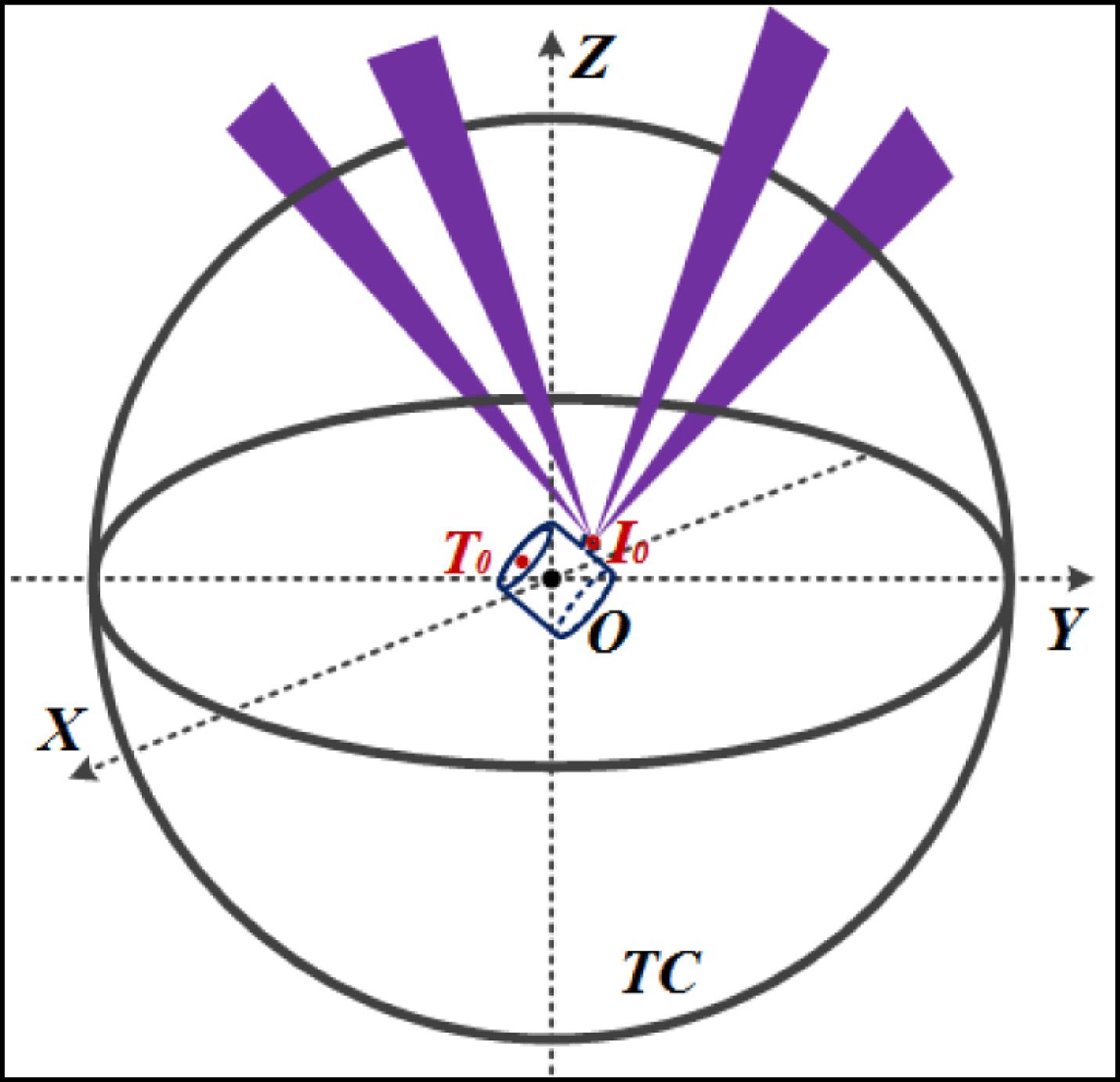
The Shen-Guang II Upgrade (SG-II-U) laser facility consists of eight high-power nanosecond laser beams and one short-pulse picosecond petawatt laser. It is designed for the study of inertial confinement fusion (ICF), especially for conducting fast ignition (FI) research in China and other basic science experiments. To perform FI successfully with hohlraum targets containing a golden cone, the long-pulse beam and cylindrical hohlraum as well as the short-pulse beam and cone target alignment must satisfy tight specifications (30 and $20~\unicode[STIX]{x03BC}\text{m}$ rms for each case). To explore new ICF ignition targets with six laser entrance holes (LEHs), a rotation sensor was adapted to meet the requirements of a three-dimensional target and correct beam alignment. In this paper, the strategy for aligning the nanosecond beam based on target alignment sensor (TAS) is introduced and improved to meet requirements of the picosecond lasers and the new six LEHs hohlraum targets in the SG-II-U facility. The expected performance of the alignment system is presented, and the alignment error is also discussed.
laser drivers petawatt lasers spherical hohlraum target alignment target area High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(1): 01000e10
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai 201800, China
With the increasing number of laser beams, the main difficulty in arranging beam guiding systems (BGSs) involves determining the corresponding relationships between the output and input ports to realize the identified light path length of all beams. Given the basic constraints of geometric arrangement, a BGS model is established, and a base-line algorithm is proposed to address the difficulty mentioned above. Boundary conditions of target area and target chamber are discussed to increase the number of laser beams, and a maximum value exists for a specific target area. Finally, the compatibility of a cylindrical hohlraum target chamber with a spherical hohlraum is analyzed, and a moveable final optics assembly is proposed to execute the switch between the two different targets.
beam guiding system laser drivers spherical hohlraum target areas Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2015, 13(1): e12
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai 201800, China
With the increasing number of laser beams, the main difficulty in arranging beam guiding systems (BGSs) involves determining the corresponding relationships between the output and input ports to realize the identified light path length of all beams. Given the basic constraints of geometric arrangement, a BGS model is established, and a base-line algorithm is proposed to address the difficulty mentioned above. Boundary conditions of target area and target chamber are discussed to increase the number of laser beams, and a maximum value exists for a specific target area. Finally, the compatibility of a cylindrical hohlraum target chamber with a spherical hohlraum is analyzed, and a moveable final optics assembly is proposed to execute the switch between the two different targets.
beam guiding system laser drivers spherical hohlraum target areas High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2015, 3(1): e12
1 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 中国科学技术大学光电子重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230026
光谱色散匀滑(SSD)技术已经广泛应用于国内外各大高功率激光驱动器。但是由于工程设计原因,美国国家点火装置(NIF)以及国内神光-III原型(TIL)装置都只采用了一块光栅,相较于传统SSD技术,焦斑匀滑效果有所不同。经模拟发现,在初始的100 ps以内,缺失色散光栅的SSD技术匀滑性能下降,可以通过优化调制频率来降低这种影响。通过对单光栅下的SSD技术分析研究,为SSD技术在大型激光装置上的优化应用提供理论基础。
激光光学 高功率激光驱动器 光束匀滑 光谱色散匀滑 调制频率 光学学报
2013, 33(s1): s114007
1 中国工程物理研究院激光聚变中心, 四川 绵阳 621900
2 中国科学技术大学光电子重点实验室, 安徽 合肥 230026
在高功率激光驱动的惯性约束聚变(ICF)系统中,为了提高束靶耦合效率,抑制激光与等离子体相互作用时产生的瑞利泰勒流体不稳定性与等离子体不稳定性,需要对光束进行匀滑处理。对各国研究的匀滑技术进行了调研,并对国外大型激光装置的匀滑技术进行了总结分析,分析了我国光束匀滑技术方面的进展情况。
激光光学 高功率激光驱动器 光束匀滑 光谱色散匀滑 偏振匀滑 相位板 激光与光电子学进展
2011, 48(10): 101407





