Author Affiliations
Abstract
Nanophotonic Sensors & Optofluidics Lab, Faculty of Physics, Kharazmi University, Tehran 15719-14911, Iran
Intelligent food packaging with the multisensory analysis is promising as the next generation technology of food packaging. The oxygen content in food packaging is one of the crucial parameters affecting the food quality and shelf life. Caviar is among the most nutritious and costly food sources. Here, a photonic oxygen-sensing system, based on the time-resolved phosphorescence spectroscopy of a platinum complex, is developed for non-contact, non-intrusive, and real-time vacuum packaging quality control, and implemented for caviar packaging. The sensor is embedded in protective polyethylene layers and excited with a short-pulsed light emitting diode (LED) source. Integration of a blue pulsed light source, a fast and amplified silicon photodiode controlled by the Spartan-6 field programmable gate array (FPGA), and a long lifetime platinum complex results in a photonics-based oxygen sensor with a fast response and high sensitivity to the vacuum packaging damage, which is suitable for caviar. It is revealed that applying the polyethylene layers protects the caviar from the platinum complex, leaching while not interfering with the sensor functionality. Characterizing the photonic system based on its sensitivity, repeatability, stability, and long-term operation demonstrates its capability for this application.
Caviar photoluminescence lifetime oxygen sensor platinum porphyrin complex vacuum packaging Photonic Sensors
2024, 14(1): 240120
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
荧光寿命显微成像(FLIM)已经广泛应用于生命科学研究领域,具有高灵敏和高特异性的特点,在对组织微环境进行定量表征方面具有独特优势,但由于成像速度相对较慢,限制了FLIM的活体应用。近年来,随着光电子器件和人工智能等技术的发展,开启了FLIM活体成像新篇章。介绍通过优化硬件和算法两方面提升时域和频域FLIM技术的成像速度,以及其在生物医学基础研究和临床疾病诊断中的应用研究进展。最后,对活体FLIM成像的未来发展进行展望。
荧光寿命显微成像 人工智能 活体成像 癌症诊断 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(6): 0618005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentations, Centre for Optical and Electromagnetic Research, College of Optical, Science and Engineering, International Research Center for Advanced Photonics, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, P. R. China
2 Dr. Li Dak Sum & Yip Yio Chin Center for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, P. R. China
3 College of Biomedical Engineering and Instrument Science, Interdisciplinary Institute of Neuroscience and Technology (ZIINT), Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, P. R. China
Fluorescence imaging in the second near-infrared window (NIR-II, 900–1880nm) with less scattering background in biological tissues has been combined with the confocal microscopic system for achieving deep in vivo imaging with high spatial resolution. However, the traditional NIR-II fluorescence confocal microscope with separate excitation focus and detection pinhole makes it possess low confocal efficiency, as well as difficultly to adjust. Two types of upgraded NIR-II fluorescence confocal microscopes, sharing the same pinhole by excitation and emission focus, leading to higher confocal efficiency, are built in this work. One type is fiber-pinhole-based confocal microscope applicable to CW laser excitation. It is constructed for fluorescence intensity imaging with large depth, high stabilization and low cost, which could replace multiphoton fluorescence microscopy in some applications (e.g., cerebrovascular and hepatocellular imaging). The other type is air-pinhole-based confocal microscope applicable to femtosecond (fs) laser excitation. It can be employed not only for NIR-II fluorescence intensity imaging, but also for multi-channel fluorescence lifetime imaging to recognize different structures with similar fluorescence spectrum. Moreover, it can be facilely combined with multiphoton fluorescence microscopy. A single fs pulsed laser is utilized to achieve up-conversion (visible multiphoton fluorescence) and down-conversion (NIR-II one-photon fluorescence) excitation simultaneously, extending imaging spectral channels, and thus facilitates multi-structure and multi-functional observation.
Self-confocal fiber-pinhole air-pinhole multi-channel fluorescence lifetime imaging multi-color imaging Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2024, 17(1): 2350025
1 赋同量子科技(浙江)有限公司,浙江 嘉兴 314100
2 集成电路材料全国重点实验室,中国科学院上海微系统与信息技术研究所,上海 200050
自2001年被发明以来,超导纳米线单光子探测器(SNSPD)迅速成长为近红外波段的明星光子探测器,其在近红外波段如1550 nm处系统探测效率超过95%,暗计数率低于1 cps(counts per second),时间抖动优于10 ps,探测速率高于1 GHz,并广泛应用在量子信息领域。近年来,研究人员开始将SNSPD引入到生物领域,以替代在近红外波段具有低信噪比、多后脉冲的半导体单光子探测器。本文将介绍SNSPD的探测原理和性能指标,并系统地阐述SNSPD在生物领域中的应用现状和发展前景。
超导纳米线单光子探测器 共聚焦显微镜 单线态氧检测 漫反射光谱 荧光寿命成像 激光与光电子学进展
2024, 61(1): 0104002
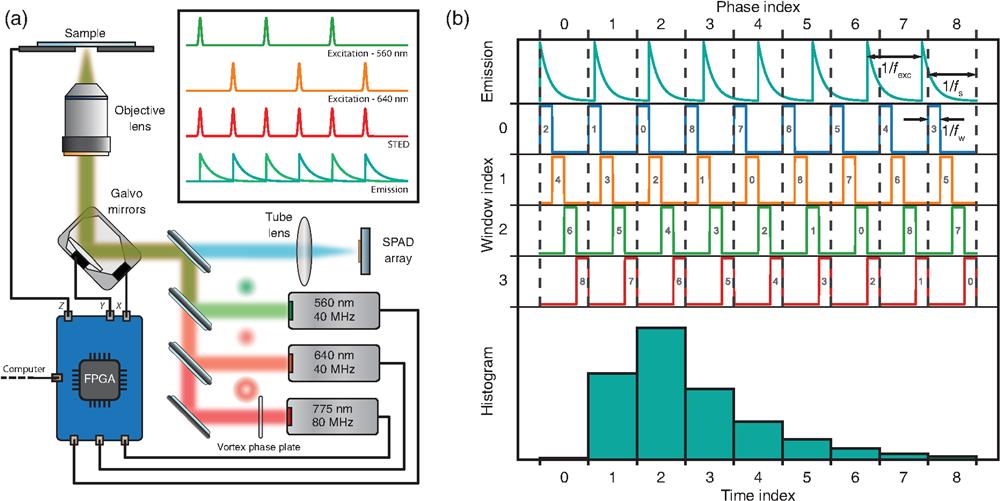
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Molecular Microscopy and Spectroscopy, Genoa, Italy
2 Genoa Instruments, Genoa, Italy
3 University of Genoa, Dipartimento di Informatica, Bioingegneria, Robotica e Ingegneria dei Sistemi, Genoa, Italy
4 Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Nanoscopy and NIC@IIT, Genoa, Italy
Fluorescence confocal laser-scanning microscopy (LSM) is one of the most popular tools for life science research. This popularity is expected to grow thanks to single-photon array detectors tailored for LSM. These detectors offer unique single-photon spatiotemporal information, opening new perspectives for gentle and quantitative superresolution imaging. However, a flawless recording of this information poses significant challenges for the microscope data acquisition (DAQ) system. We present a DAQ module based on the digital frequency domain principle, able to record essential spatial and temporal features of photons. We use this module to extend the capabilities of established imaging techniques based on single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) array detectors, such as fluorescence lifetime image scanning microscopy. Furthermore, we use the module to introduce a robust multispecies approach encoding the fluorophore excitation spectra in the time domain. Finally, we combine time-resolved stimulated emission depletion microscopy with image scanning microscopy, boosting spatial resolution. Our results demonstrate how a conventional fluorescence laser scanning microscope can transform into a simple, information-rich, superresolved imaging system with the simple addition of a SPAD array detector with a tailored data acquisition system. We expected a blooming of advanced single-photon imaging techniques, which effectively harness all the sample information encoded in each photon.
fluorescence lifetime image scanning microscopy digital frequency domain single photon Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(1): 016003
1 西安电子科技大学 光电工程学院,陕西 西安 710071
2 国防科技大学 电子对抗学院 红外与低温等离子体安徽省重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230000
在对Nd:YAG调Q激光器进行分析和设计时,研究人员通常选择忽略激光下能级寿命对脉冲波形的影响。当激光脉宽远大于激光下能级寿命时,这种近似一般不会带来太大偏差;而当脉宽达到纳秒量级时,Nd:YAG 晶体约30 ns的下能级寿命对脉冲波形的影响会变得非常严重。建立了Nd:YAG下能级寿命对输出脉冲波形影响的理论分析模型,并对窄脉宽的Nd:YAG调Q激光器的输出波形进行仿真研究。研究结果表明,在窄脉宽激光输出情形下,激光下能级寿命会导致调Q脉冲在主峰后出现尾峰,尾峰能量可达主峰能量的一倍以上。同时建立了Nd:YAG声光调Q激光器实验系统,在与仿真计算近似的条件下测量调Q脉冲波形,观察到与仿真结果一致的尾峰现象,实验验证了理论模型的正确性。
固体激光器 下能级寿命 Nd:YAG solid state laser lower level lifetime Nd:YAG
中国计量大学 光学与电子科技学院,杭州 310018
以柠檬酸和尿素为前驱体通过水热法制备得到绿色荧光碳点,通过透射电子显微镜、紫外可见吸收光谱、荧光光谱以及时间分辨荧光光谱对碳点进行表征和分析。碳点的粒径为6.5 nm,在252 nm、273 nm和410 nm处存在吸收峰,最佳激发和发射波长分别为400 nm和517 nm,根据已有研究推测碳点的荧光主要来源于4-羟基-1H-吡咯并[3,4-c]吡啶-1,3,6(2H,5H)-三酮。发现不同溶剂中的碳点具有不同的发光特性,包括荧光强度、发射峰位和荧光寿命,因此将碳点作为荧光探针检测质子溶剂乙醇和非质子溶剂二甲基甲酰胺中的水含量。实验结果表明随着水含量的增加,混合溶液中碳点的荧光强度下降,发射峰位红移,发射峰轻微加宽,荧光寿命缩短。碳点的荧光强度、发射峰位以及荧光寿命三者与水含量之间均存在线性响应关系,检测范围宽至0~100%。本方法同样适用于甲醇和乙二醇,具有普适性,该碳点有望成为快速灵敏检测有机溶剂中水含量的潜在探针。
碳点 荧光光谱 荧光寿命 含水量 有机溶剂 Carbon dots Fluorescence spectroscopy Fluorescence lifetime Water content Organic solvent 光子学报
2023, 52(12): 1216001
1 清华大学环境学院环境污染溯源与精细监管技术研究中心, 北京 100084 清华苏州环境创新研究院先进监管技术仪器研发团队, 江苏 苏州 215163
2 北京 100084 清华苏州环境创新研究院先进监管技术仪器研发团队, 江苏 苏州 215163
近年来, 三维荧光技术已经成为常用的化学分析技术, 但有些结构相近的荧光有机物的三维荧光光谱十分相似, 可能导致分析结果错误。 因此, 如何精准区分具有相似三维荧光光谱的有机物是十分重要且亟待解决的问题。 荧光量子产率和荧光寿命是荧光有机物两个重要的光学参数, 对于分子结构的差异更灵敏。 对吲哚、 3-甲基吲哚和L-色氨酸的三维荧光光谱、 荧光量子产率和荧光寿命进行了研究。 结果表明, 它们的三维荧光光谱都出现两个荧光峰, 且荧光峰位置十分接近。 吲哚和L-色氨酸的荧光峰大致位于[激发波长, 发射波长]=[275, 340~350]和[220, 340~350] nm附近, 3-甲基吲哚的荧光峰位于[激发波长, 发射波长]=[280, 365]和[225, 365] nm附近。 在相同浓度下, 三种有机物在激发波长为275~280 nm处的最高荧光强度依次为: 吲哚>3-甲基吲哚>L-色氨酸。 利用绝对量子产率测量技术测得吲哚、 3-甲基吲哚和L-色氨酸的荧光量子产率分别约为0.264、 0.347和0.145; 利用时间相关单光子计数技术测得吲哚、 3-甲基吲哚和L-色氨酸的荧光寿命分别约为4.149、 7.896和2.715 ns。 研究表明, 荧光寿命和荧光量子产率能区分三维荧光光谱相似的荧光有机物, 研究结果在荧光有机物的准确识别上具有重要的价值。
三维荧光光谱 荧光有机物 荧光量子产率 荧光寿命 Excitation-emission matrix Fluorescent organic matter Fluorescence quantum yield Fluorescence lifetime 光谱学与光谱分析
2023, 43(12): 3758
1 上海理工大学 理学院,上海 200093
2 中国科学院上海技术物理研究所 中国科学院红外成像材料与器件重点实验室,上海 200083
在测试中波碲镉汞光伏器件的瞬态响应时,当激光光斑照射器件表面位置距离光敏面较远时,器件表现为特殊的双峰脉冲响应现象,分析表明出现这种异常双脉冲现象的原因是光敏区内的少子漂移和光敏区外侧向收集的少子扩散有时间上的差异。通过对器件施加反向偏压,脉冲响应随反向偏压的增大由双峰变成单峰的实验结果,验证了少子侧向收集是导致器件形成双峰的主要原因。对第二个峰拟合得到p区的少数载流子寿命。将瞬态响应获得的少子寿命与该p型中波碲镉汞材料的理论计算和光电导衰退法得到的少子寿命相对比,发现三种方式得到的少子寿命随温度的变化趋势基本一致,这说明了可以通过瞬态光响应得到中波碲镉汞器件的少子寿命。
瞬态响应 少子寿命 少子侧向收集 光电导衰退 HgCdTe HgCdTe transient response minority carrier lifetime minority carrier lateral collection photoconductive decay
1 量子光学与光量子器件国家重点实验室 山西大学光电研究所 山西 太原 030006
2 山西大学 极端光学协同创新中心 山西 太原 030006
在87Rb冷原子系综中通过自发拉曼散射过程产生原子自旋波与光子的关联, 利用偏振干涉仪将与磁敏感自旋波关联的Stokes光子的两个空间模式编码为一个偏振量子比特, 产生磁敏感自旋波与光子的纠缠源。采用近共线装置和精确补偿地磁场, 纠缠源的寿命达到900s, Bell参量S=2.58±0.03。
光与原子纠缠源 磁敏感自旋波 纠缠寿命 偏振干涉仪 atom-photon entanglement magnetically field sensitive spin-wave entanglement lifetime polarization interferometer 量子光学学报
2023, 29(1): 010601





