
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Center for Attosecond Science and Technology, State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
3 Shanxi University, Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Taiyuan, China
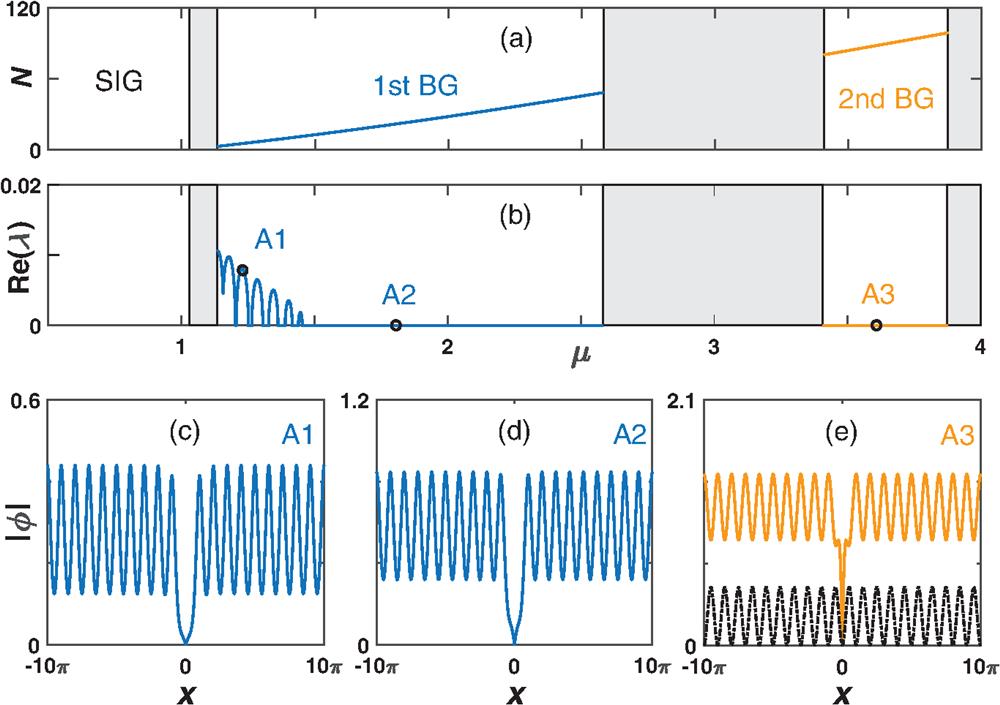
Moiré superlattices, a twisted functional structure crossing the periodic and nonperiodic potentials, have recently attracted great interest in multidisciplinary fields, including optics and ultracold atoms, because of their unique band structures, physical properties, and potential implications. Driven by recent experiments on quantum phenomena of bosonic gases, the atomic Bose–Einstein condensates in moiré optical lattices, by which other quantum gases such as ultracold fermionic atoms are trapped, could be readily achieved in ultracold atom laboratories, whereas the associated nonlinear localization mechanism remains unexploited. Here, we report the nonlinear localization theory of ultracold atomic Fermi gases in two-dimensional moiré optical lattices. The linear Bloch-wave spectrum of such a twisted structure exhibits rich nontrivial flat bands, which are separated by different finite bandgaps wherein the existence, properties, and dynamics of localized superfluid Fermi gas structures of two types, gap solitons and gap vortices (topological modes) with vortex charge S = 1, are studied numerically. Our results demonstrate the wide stability regions and robustness of these localized structures, opening up a new avenue for studying soliton physics and moiré physics in ultracold atoms beyond bosonic gases.
moiré optical lattices gap solitons ultracold Fermi gases density-functional equation Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(3): 036006
1 中北大学信息商务学院 基础部,山西 晋中 030600
2 山西大学 光电研究所 量子光学与光量子器件国家重点实验室,山西 太原 030006
利用Gerchberg-Saxton算法生成任意的二维光晶格阵列的全息图,并且将全息图加载到液晶型空间光调制器上,然后将850 nm的激光照射到空间光调制器的液晶屏上,利用透镜的傅里叶变换特性,成功地显示或构建任意形状的二维光晶格阵列。将该系统应用到87Rb的冷原子实验中,成功俘获冷原子,这为接下来的单原子多量子位的量子模拟实验奠定了基础。
GS算法 液晶型空间光调制器 光晶格 相息图 GS algorithm liquid crystal on silicon SLM optical lattices phase hologram
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) exhibits a variety of fascinating and unexpected macroscopic phenomena, and has attracted sustained attention in recent years—particularly in the field of solitons and associated nonlinear phenomena. Meanwhile, optical lattices have emerged as a versatile toolbox for understanding the properties and controlling the dynamics of BEC, among which the realization of bright gap solitons is an iconic result. However, the dark gap solitons are still experimentally unproven, and their properties in more than one dimension remain unknown. In light of this, we describe, numerically and theoretically, the formation and stability properties of gap-type dark localized modes in the context of ultracold atoms trapped in optical lattices. Two kinds of stable dark localized modes—gap solitons and soliton clusters—are predicted in both the one- and two-dimensional geometries. The vortical counterparts of both modes are also constructed in two dimensions. A unique feature is the existence of a nonlinear Bloch-wave background on which all above gap modes are situated. By employing linear-stability analysis and direct simulations, stability regions of the predicted modes are obtained. Our results offer the possibility of observing dark gap localized structures with cutting-edge techniques in ultracold atoms experiments and beyond, including in optics with photonic crystals and lattices.
Bose–Einstein condensates optical lattices photonic crystals and lattices self-defocusing Kerr nonlinearity dark gap solitons and soliton clusters Advanced Photonics
2019, 1(4): 046004
1 天津工业大学光电检测技术与系统天津市重点实验室, 天津 300387
2 天津工业大学电子与信息工程学院, 天津 300387
对中心对称光折变晶体中扭曲孤子的形成及其稳定性进行了研究。结果表明: 在自聚焦非线性光格子中, 扭曲孤子存在于半无穷间隙和第一间隙中; 在半无穷间隙中, 扭曲孤子的状态不稳定; 在第一间隙中的扭曲孤子均处于稳定状态, 且存在区域随着晶格深度p的增加而增加; 对于给定的p, 扭曲孤子能流随传播常数b的增加而增加; 在相同的参数下, 阶数高的扭曲孤子占据的格子更多, 且能流更高; 在自散焦非线性光格子中, 扭曲孤子仅存在于半无穷间隙中, 并且所有的扭曲孤子均为不稳定状态; 当b较小时, 扭曲孤子含有较多的振幅振荡, 随着b增加, 扭曲孤子的能流和振幅振荡都变小。
非线性光学 光折变晶体 扭曲孤子 光格子 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(3): 031901
运城学院物理与电子工程系, 山西 运城 044000
用交替隐式差分法研究了高斯光束在二维正方格子和贝塞尔晶格中的传输特性。结果表明:高斯光束在二维正方格子中传输时可形成 能量主要集中在中心区域的晶格孤子,也可通过参数调节形成其他空间分立形态的孤子; 对贝塞尔晶格,当其横向尺度较小即入射高斯光束的能量主要集中在贝塞尔晶格的 中心信道时,可在一定外加电场和光伏电场参数下形成类三环孤子。逐渐增加晶格的横向尺度,可形成单一的类环形孤子和类高斯孤子。光折变晶格孤子的多样性在 全光孤子开关等方面具有潜在应用价值。
非线性光学 高斯光束 光折变效应 光子晶格 nonlinear optics Gaussian beam photorefractive effect optical lattices
1 江苏大学机械工程学院光信息科学与技术系, 江苏 镇江 212013
2 宁波大学光学研究所, 浙江 宁波 315211
对提出的两种复周期Kerr非线性调制光晶格中的孤子开关特性进行了研究, 并与单周期余弦型调制晶格的情形进行了比较。通过数值模拟, 分析了3种不同模型对孤子脉冲能量的保持情况, 以及注入相同孤子脉冲时, 脉冲被晶格俘获前可穿越的晶格通道的数量。研究发现, 当注入脉冲的能量范围相同时, 3种模型中孤子的开关通道数有较大差别; 而在穿越通道数相同的情况下, 开关效应的响应时间却不相同。
非线性光学 光学晶格 空间孤子 开关效应
对囚禁在由谐振势和一维光晶格势构成的组合势中的玻色凝聚气体,基于Gross-Pitaevskii理论,并运用G-P能量泛函和变分方法,研究了组合势中子凝聚体的高斯宽度与光晶格势强度之间的关系。在分析了无相互作用的理想玻色气体的高斯宽度的基础上,提出了考虑相互作用后的高斯近似模型,并求解出高斯宽度随光晶格势强度变化的解析表达式。然后,将所得到的解析结果与直接的数值计算进行比较,表明高斯近似模型与数值计算结果更加接近,并且随着光晶格势强度的增加两者趋于一致。
量子光学 高斯宽度 G-P能量泛函 一维光晶格势 玻色凝聚气体 quantum optics Gaussian width G-P energy functional 1D-optical lattices potential Bose-condensed gas
华东师范大学物理系,光谱学与波谱学教育部重点实验室,上海 200062
首先介绍了近年来发展起来的晶格原子光学,包括冷原子光学晶格、磁晶格和磁光晶格,并报道了国内一些小组研究磁晶格和磁光晶格的一些新结果。其次,简单综述了光学晶格中原子动力学、玻色-爱因斯坦凝聚(BEC)和量子态的相干传输与控制等晶格原子光学研究的最新进展。最后,介绍了冷原子光学晶格、磁晶格和磁光晶格在光子晶体制备等方面的潜在应用。
量子光学 原子光学 光学晶格 冷原子 磁晶格 磁光晶格 玻色-爱因斯坦凝聚 quantum optics atom optics optical lattices cold atoms magnetic lattices magneto-optical lattices Bose-Einstein condensation(BEC)





