1 重庆邮电大学通信与信息工程学院,重庆 400065
2 重庆邮电大学智能通信与网络安全研究院,重庆 400065
提出了一种渐进式训练方案来重新配置马赫-曾德尔干涉仪(MZI)前馈光学神经网络(ONN)的相移,从而对抗MZI的相位误差和分束器误差,提高识别准确率。为了验证所提方案,利用Neuroptica Python仿真平台搭建了3层MZI-ONN结构,并在考虑到MZI相位误差和分束器误差的情况下,利用Iris和MNIST数据集验证了所提方案的有效性。仿真结果表明:在Iris数据集下,对于3层4×4 MZI-ONN结构,所提方案的识别准确率能够提升64.15百分点;在MNIST数据集下,对于4×4、6×6、8×8和16×16规模的MZI-ONN,所提方案的识别准确率能够提升2.00~37.00百分点。所提方案极大地提高了MZI-ONN的抗误差性能,有助于未来大规模、高准确率MZI-ONN的实现。
光计算 马赫-曾德尔干涉仪 光学神经网络 相位误差 分束器误差 渐进式训练 抗误差
1 国防科技大学前沿交叉学科学院,湖南 长沙 410073
2 清华大学电子工程系,北京 100084
3 北京信息科学与技术国家研究中心,北京 100084
4 国防科技大学新型纳米光电信息材料与器件湖南省重点实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
5 国防科技大学南湖之光实验室,湖南 长沙 410073
光学神经网络是区别于冯·诺依曼计算架构的一种高性能新型计算范式,具有低延时、低功耗、大带宽以及并行信号处理等优势。片上集成是光学神经网络微型化发展的一种典型方式,近年来片上集成光学神经网络获得了学术界及工业界的广泛关注。对基于不同计算单元结构的片上集成光学神经网络的相关研究工作进行了梳理,并分析了其设计原理、实现方法及系统架构特征。同时结合国内外最新研究进展,进一步分析了片上集成光学神经网络在计算单元大规模拓展、可重构、非线性运算和实用化等方面面临的挑战及其未来发展趋势。
集成光学 光计算 光学神经网络 芯片 人工智能
1 北京大学物理学院人工微结构和介观物理国家重点实验室,北京 100871
2 南开大学物理科学学院,天津 300071
3 北京工业大学理学部信息光子技术研究所,北京 100124
4 山西大学极端光学协同创新中心,山西 太原 030006
神经网络中的非线性激活层可以改变多层网络数据间的线性变换关系,使神经网络得以进行更复杂的学习。为实现处理速度更快,能耗更低的运算,近年来光子领域的神经网络逐渐受到重视,一系列光学非线性激活函数器件应运而生。本文综述了近年来在光学神经网络中引入非线性激活函数的工作,从光学非线性函数的物理机制及其在光学神经网络中的应用出发,对该领域的工作进行了回顾;总结并讨论了光学神经网络中光学非线性激活函数器件发展所面临的挑战及变化趋势,并基于此展望了其发展前景。
非线性光学 光学神经网络 非线性激活函数 光学学报
2023, 43(16): 1623001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Zhejiang University, College of Information Science and Electronic Engineering, State Key Laboratory of Modern Optical Instrumentation, Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Electronics and Smart System of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, China
2 Westlake University, School of Engineering, Key Laboratory of 3D Micro/Nano Fabrication and Characterization of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou, China
3 Institute of Advanced Technology, Westlake Institute for Advanced Study, Hangzhou, China
4 Institute of Microelectronics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
5 Peking University, School of Physics, Frontiers Science Center for Nano-optoelectronics, State Key Laboratory for Mesoscopic Physics, Beijing, China
Optical neural networks (ONNs), enabling low latency and high parallel data processing without electromagnetic interference, have become a viable player for fast and energy-efficient processing and calculation to meet the increasing demand for hash rate. Photonic memories employing nonvolatile phase-change materials could achieve zero static power consumption, low thermal cross talk, large-scale, and high-energy-efficient photonic neural networks. Nevertheless, the switching speed and dynamic energy consumption of phase-change material-based photonic memories make them inapplicable for in situ training. Here, by integrating a patch of phase change thin film with a PIN-diode-embedded microring resonator, a bifunctional photonic memory enabling both 5-bit storage and nanoseconds volatile modulation was demonstrated. For the first time, a concept is presented for electrically programmable phase-change material-driven photonic memory integrated with nanosecond modulation to allow fast in situ training and zero static power consumption data processing in ONNs. ONNs with an optical convolution kernel constructed by our photonic memory theoretically achieved an accuracy of predictions higher than 95% when tested by the MNIST handwritten digit database. This provides a feasible solution to constructing large-scale nonvolatile ONNs with high-speed in situ training capability.
phase-change materials optical neural networks photonic memory silicon photonics reconfigurable photonics Advanced Photonics
2023, 5(4): 046004
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所信息光学与光电技术实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料与光电学院,北京 100049
3 暨南大学光子技术研究院,广东 广州 510632
受益于光子独特的优势,光计算技术在构建高速、高算力和高能效比的专用计算加速器方面被寄予厚望,目前已经涌现出了许多极具吸引力的方案。特别是对于涉及运算量巨大的二维矩阵-矩阵乘加操作的专用场景,光计算有望在算力和能效比等方面实现超越当前最先进电子计算机几个数量级的性能提升。不同于电子计算通过构建逻辑门实现通用数字计算,主要受深度学习驱动而复兴的光计算更倾向于模拟计算。本文从模拟和数字光计算的角度出发对主流的光计算架构进行分析和讨论,指出了目前光计算技术发展面临的瓶颈,并对光计算未来的发展趋势进行了展望。
光计算 模拟光计算 数字光计算 光计算架构 光学矩阵计算 光学神经网络 光电智能计算 光学信号处理
1 华中科技大学武汉光电国家研究中心,湖北 武汉 430074
2 湖北光谷实验室,湖北 武汉 430074
随着人工智能技术的高速发展,全球的计算量急剧增长,需要以快速、高效的方式处理海量数据,这对计算硬件的算力和能效提出了较高的要求。受限于电子器件的固有极限和冯·诺依曼架构,传统的电子计算在速度和能效方面遇到了难以突破的瓶颈。光电智能计算充分融合光学的多维复用、大带宽、低能耗等优势和电学的细粒度灵活控制特性,具有光算电控和软硬协同的特点,是一种更实用、更有竞争力的人工智能计算加速方案。回顾了光电智能计算的研究进展,探讨了目前用于光学信号处理和光学神经网络的主流计算架构在线训练算法以及算力、能效提升方面的挑战,并进行了展望。
光计算 光电智能计算 人工智能 计算加速 光学信号处理 光学神经网络 中国激光
2022, 49(12): 1219001
光子学报
2021, 50(10): 1020001
1 上海理工大学光子芯片研究院, 上海 200093
2 上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院人工智能纳米光子学中心, 上海 200093
人工智能技术,特别是人工神经网络的创新引领了许多领域的应用革命,如网络搜索、计算机识别和语言、图像的识别技术。近年来纳米光子学的发展为传统的人工神经网络技术,特别是光学神经网络的发展带来了全新的物理视角以及截然不同的实现方法。一方面,纳米光子学是一门研究光与材料在纳米尺度相互作用的科学,可以带来全新的技术,如超分辨光学加工技术和超分辨光学成像技术,进而推动微纳尺度上多种功能的光学神经网络的实现。另一方面,纳米光子学中光子传播的多频段、高速度、低功耗的特点,促使了光学神经网络向着小体积、高密度、低功耗的方向发展。人工神经网络自身的发展也促使神经网络算法(如逆向设计、深度学习)在纳米光子学器件的设计中发挥前所未有的作用,以满足纳米光子学器件对自身功能、体积、集成度、计算功能的日益增长的要求。以神经网络的发展为起点,阐述人工神经网络特别是光学神经网络的发展趋势,以及人工神经网络与纳米光子学相互促进的发展历程。
光学器件 人工智能 人工神经网络 光学神经网络 纳米光子学 光学人工智能
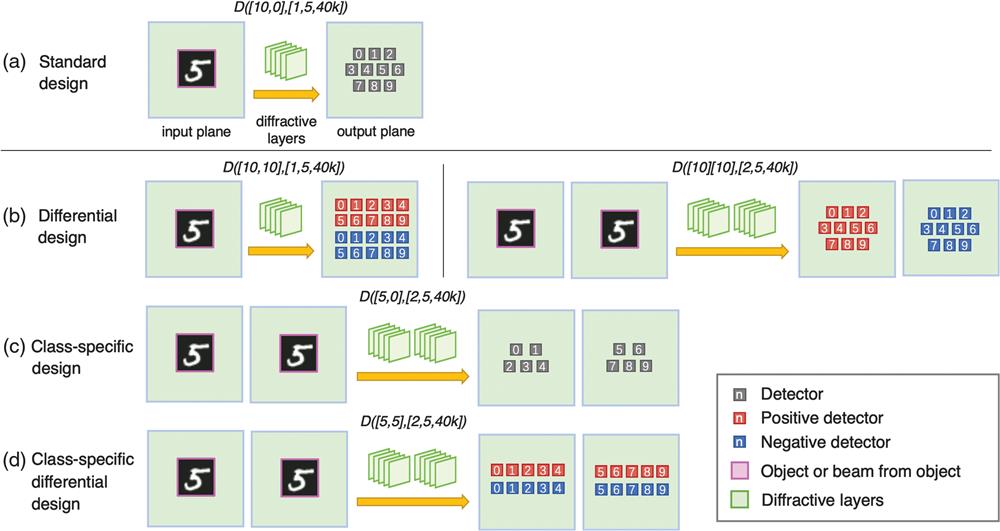
Jingxi Li 1,2,3†Deniz Mengu 1,2,3Yi Luo 1,2,3Yair Rivenson 1,2,3Aydogan Ozcan 1,2,3,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 University of California at Los Angeles, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Los Angeles, California, United States
2 University of California at Los Angeles, Department of Bioengineering, Los Angeles, California, United States
3 University of California at Los Angeles, California NanoSystems Institute, Los Angeles, California, United States
Optical computing provides unique opportunities in terms of parallelization, scalability, power efficiency, and computational speed and has attracted major interest for machine learning. Diffractive deep neural networks have been introduced earlier as an optical machine learning framework that uses task-specific diffractive surfaces designed by deep learning to all-optically perform inference, achieving promising performance for object classification and imaging. We demonstrate systematic improvements in diffractive optical neural networks, based on a differential measurement technique that mitigates the strict nonnegativity constraint of light intensity. In this differential detection scheme, each class is assigned to a separate pair of detectors, behind a diffractive optical network, and the class inference is made by maximizing the normalized signal difference between the photodetector pairs. Using this differential detection scheme, involving 10 photodetector pairs behind 5 diffractive layers with a total of 0.2 million neurons, we numerically achieved blind testing accuracies of 98.54%, 90.54%, and 48.51% for MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, and grayscale CIFAR-10 datasets, respectively. Moreover, by utilizing the inherent parallelization capability of optical systems, we reduced the cross-talk and optical signal coupling between the positive and negative detectors of each class by dividing the optical path into two jointly trained diffractive neural networks that work in parallel. We further made use of this parallelization approach and divided individual classes in a target dataset among multiple jointly trained diffractive neural networks. Using this class-specific differential detection in jointly optimized diffractive neural networks that operate in parallel, our simulations achieved blind testing accuracies of 98.52%, 91.48%, and 50.82% for MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, and grayscale CIFAR-10 datasets, respectively, coming close to the performance of some of the earlier generations of all-electronic deep neural networks, e.g., LeNet, which achieves classification accuracies of 98.77%, 90.27%, and 55.21% corresponding to the same datasets, respectively. In addition to these jointly optimized diffractive neural networks, we also independently optimized multiple diffractive networks and utilized them in a way that is similar to ensemble methods practiced in machine learning; using 3 independently optimized differential diffractive neural networks that optically project their light onto a common output/detector plane, we numerically achieved blind testing accuracies of 98.59%, 91.06%, and 51.44% for MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, and grayscale CIFAR-10 datasets, respectively. Through these systematic advances in designing diffractive neural networks, the reported classification accuracies set the state of the art for all-optical neural network design. The presented framework might be useful to bring optical neural network-based low power solutions for various machine learning applications and help us design new computational cameras that are task-specific.
optical computation optical neural networks deep learning optical machine learning diffractive deep neural networks Advanced Photonics
2019, 1(4): 046001
在研究洗牌网局部互连光学实现问题的基础上,采用洗牌型图样间联想模型建立了具有完整的加权互连、求和、非线性处理及反馈功能的光电混合神经网络实验系统,进行了8×8数字样本的光学联想识别.实验结果证实了洗牌网理论的可行性和洗牌型图样间联想模型光学实现的优越性.
光学神经网络 洗牌 图样间联想 光电混合神经网络





