1 西南交通大学物理科学与技术学院,成都 四川 610031
2 西南交通大学信息科学与技术学院,成都 四川 610031
常规数值求解方法在表征光纤中超短脉冲的非线性传输过程时存在计算量大、效率低等局限。随着人工智能的快速发展,深度学习技术展现出了强大的计算能力、广泛的适用范围、良好的硬件移植性,在光纤中超短脉冲非线性传输过程表征和控制研究中具有巨大潜力。本文概述了深度学习技术及其在预测光纤中超短脉冲传输、超短脉冲重构及参数估计方面的研究进展,同时展望了深度学习与光纤中超短脉冲非线性传输这一新兴交叉技术的发展方向和挑战。
光纤光学 超短激光脉冲传输 非线性薛定谔方程 光纤非线性效应 深度学习 中国激光
2023, 50(11): 1101011
1 北京工业大学材料与制造学部,北京市激光应用技术工程技术研究中心,北京 100124
2 北京工业大学跨尺度激光成型制造技术教育部重点实验室,北京 100124
3 北京工业大学激光工程研究院,北京 100124
4 Edgewave公司,Würselen 52146,德国
本文报道了利用自制低损耗、无节点反谐振空芯光纤传输高功率1064 nm皮秒脉冲激光的研究。光纤包层由7根平均壁厚为700 nm的细玻璃管组成,纤芯直径为42 μm,外径为175 μm。选择脉冲宽度为15 ps且重复频率可调谐的高功率激光器作为实验光源。使用不同长度的光纤进行了传输测试,测试结果表明:当输入单脉冲能量为403 μJ、平均功率为40.3 W、峰值功率为26.8 MW的激光时,最高可实现370 μJ的高能量激光输出,传输效率高达91.8%。分析了超短脉冲经过不同长度光纤后时域和频域的变化情况,结果表明:当光纤长度为1 m时,脉冲保持无畸变传输,光谱发生轻微变形;当光纤长度增长至3.3 m时,由于非线性效应的影响,脉冲宽度展宽至26 ps,光谱展宽至70 nm。本研究表明无节点反谐振空芯光纤有望在超短脉冲激光的传输应用领域发挥重要作用。
激光光学 超短脉冲传输 无节点反谐振空芯光纤 峰值功率 单脉冲能量 非线性效应

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communication Networks, School of Information and Communication Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 611731, China
We demonstrate a novel method to control the free spectral range (FSR) of silica micro-rod resonators precisely. This method is accomplished by iteratively applying laser annealing on the already-fabricated micro-rod resonators. Fine and repeatable increasing of resonator FSR is demonstrated, and the best resolution is smaller than 5 MHz, while the resonator quality-factor is only slightly affected by the iterative annealing procedure. Using the fabricated micro-rod resonators, single dissipative Kerr soliton microcombs are generated, and soliton repetition frequencies are tuned precisely by the iterative annealing process. The demonstrated method can be used for dual-comb spectroscopy and coherent optical communications.
microcavities nonlinear optics pulse propagation temporal solitons Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(7): 071903

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
Microcomb generation with simultaneous χ(2) and χ(3) nonlinearities brings new possibilities for ultrabroadband and potentially self-referenced integrated comb sources. However, the evolution of the intracavity field involving multiple nonlinear processes shows complex dynamics that are still poorly understood. Here, we report on strong soliton regulation induced by fundamental–second-harmonic (FD-SH) mode coupling. The formation of solitons from chaos is extensively investigated based on coupled Lugiato–Lefever equations. The soliton generation shows more deterministic behaviors in the presence of FD-SH mode interaction, which is in sharp contrast with the usual cases where the soliton number and relative locations are stochastic. Deterministic single soliton transition, soliton binding, and prohibition are observed, depending on the phase-matching condition and coupling coefficient between the fundamental and second-harmonic waves. Our finding provides important new insights into the soliton dynamics in microcavities with simultaneous χ(2) and χ(3) nonlinearities and can be immediate guidance for broadband soliton comb generation with such platforms.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Harmonic generation and mixing Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing Microcavities Photonics Research
2018, 6(10): 10000948
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Electronic and Information Engineering, Ankang University, Ankang, 725000, China
Starting from the basic equations describing the evolution of the carriers and photons inside a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA), the equation governing pulse propagation in the SOA is derived. By employing homotopy analysis method (HAM), a series solution for the output pulse by the SOA is obtained, which can effectively characterize the temporal features of the nonlinear process during the pulse propagation inside the SOA. Moreover, the analytical solution is compared with numerical simulations with a good agreement. The theoretical results will benefit the future analysis of other problems related to the pulse propagation in the SOA.
Semiconductor optical amplifier pulse propagation homotopy analysis method series solution Photonic Sensors
2018, 8(2): 188

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Centre de Nanosciences et de Nanotechnologies, CNRS, Université Paris-Sud, Université Paris-Saclay, C2N Marcoussis, 91460 Marcoussis, France
2 Thales Research and Technology France, 1 avenue Augustin Fresnel, 91120 Palaiseau, France
3 Université Paris Diderot, Sorbone Paris Cité, 75013 Paris, France
We introduce a nanoscale photonic platform based on gallium phosphide. Owing to the favorable material properties, peak power intensity levels of 50 GW/cm2 are safely reached in a suspended membrane. Consequently, the field enhancement is exploited to a far greater extent to achieve efficient and strong light–matter interaction. As an example, parametric interactions are shown to reach a deeply nonlinear regime, revealing cascaded four-wave mixing leading to comb generation and high-order soliton dynamics.
Kerr effect Nonlinear wave mixing Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Integrated optics materials Photonic crystals Microwaves Photonics Research
2018, 6(5): 05000B43
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Max Planck Institute for the Science of Light, Staudtstrasse 2, 91058 Erlangen, Germany
Spectral anti-crossings between the fundamental guided mode and core-wall resonances alter the dispersion in hollow-core anti-resonant-reflection photonic crystal fibers. Here we study the effect of this dispersion change on the nonlinear propagation and dynamics of ultrashort pulses. We find that it causes emission of narrow spectral peaks through a combination of four-wave mixing and dispersive wave emission. We further investigate the influence of the anti-crossings on nonlinear pulse propagation and show that their impact can be minimized by adjusting the core-wall thickness in such a way that the anti-crossings lie spectrally distant from the pump wavelength.
Pulse propagation and temporal solitons Photonic crystal fibers Photonics Research
2018, 6(2): 02000084
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optical Information and Technology, Ministry of Education, Tianjin Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Sensor and Sensing Network Technology, and Institute of Modern Optics, Nankai University, Tianjin 300350, China
We report a regime of the loose soliton bunch in an erbium-doped passively mode-locked fiber laser. In this state, every soliton bunch consists of multiple pulses. The amount of multiple pulses inside the soliton bunch increase as the pump power rises. Moreover, the temporal average pulse-to-pulse separation decreases in general with the increase of the pump power. Further, the spatial-temporal sequences based on the dispersive Fourier transformation technique show that pulse-to-pulse interactions and time jitter can result in pulse forking inside the soliton bunch. Finally, we theoretically demonstrate the soliton bunch with different pulse-to-pulse separations.
060.5530 Pulse propagation and temporal solitons 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3500 Lasers, erbium Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 080605
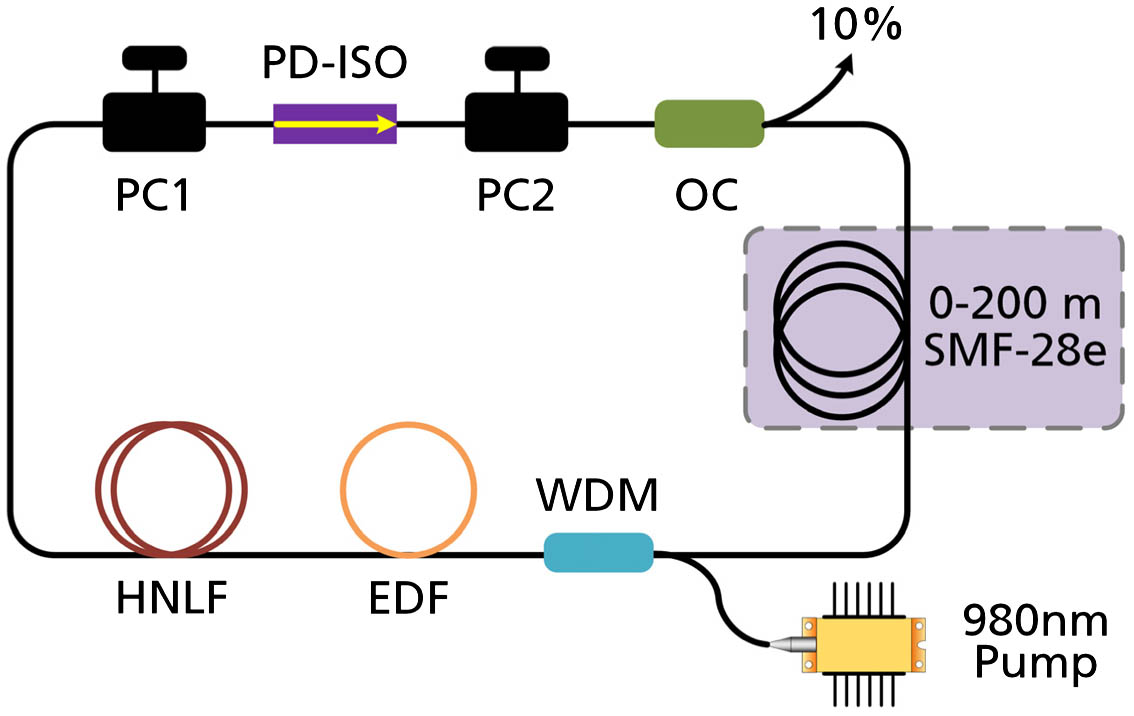
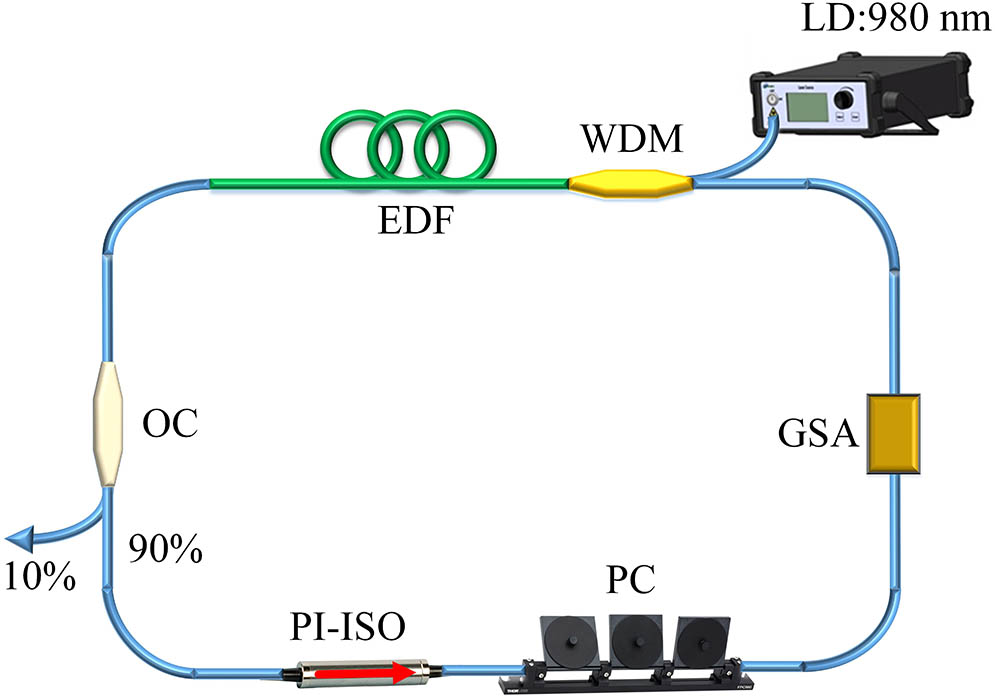
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Electronic Thin Films and Integrated Devices, School of Optoelectronic Information, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
The pulse dynamics of harmonic mode-locking in a dissipative soliton resonance (DSR) region in an erbium-doped fiber ring laser is investigated at different values of anomalous dispersion. The fiber laser is mode-locked by a nonlinear polarization rotation technique. By inserting 0–200 m anomalous dispersion single-mode fiber in the laser cavity, the cavity length is changed from 17.3 to 217.3 m, and the corresponding dispersion of the cavity ranges from ?0.27 to ?4.67 ps2. The observed results show that the tuning range of repetition rate under a harmonic DSR condition is highly influenced by the cavity dispersion. Furthermore, it is found that, by automatically adjusting their harmonic orders, the lasers can work at certain values of repetition rate, which are independent of the cavity length and dispersion. The pulses at the same repetition rate in different laser configurations have similar properties, demonstrating that each achievable repetition rate represents an operation regime of harmonic DSR lasers.
(060.4370) Nonlinear optics fibers (060.5530) Pulse propagation and temporal soliton (140.3510) Lasers fiber (140.4050) Mode-locked lasers. Photonics Research
2017, 5(6): 06000612
1 北京工业大学激光工程研究院国家产学研激光技术中心, 北京 100124
2 Edgewave公司, Würselen 52146, 德国
拉制了两种低损耗、单模、近红外宽带传输的空芯反谐振光纤,并用于高功率超短皮秒脉冲传输。利用无节点结构的空芯反谐振光纤实现了平均功率为74 W、单脉冲能量为185 μJ、峰值功率为10.8 MW的超短脉冲传输,且输出激光在频域和时域上均没有发生明显变化。
激光光学 空芯反谐振光纤 超短脉冲传输 单脉冲能量 峰值功率





