1 北京理工大学光电学院光电成像技术与系统教育部重点实验室,北京 100081
2 北京理工大学珠海学院,广东 珠海 519085
3 天临空地海”复杂环境智能探测重点实验室,广东 珠海 519085
非视域成像是指被测目标在相机探测视场外部,被测目标的光信号需要通过中介面反射后被相机采集,进而实施计算成像的一种技术。针对退化的非视域图像,去除中介面影响而获得清晰目标的过程属于一种光学逆问题。因此,中介面的光学散射特性在逆问题中的模型是一个关键。本文采用光子飞行时间测距(TOF)相机,提出一种非朗伯散射特性中介面的近似数值模型,并通过遗传算法求取,基于所求近似数值解,通过Lucy-Richardson(LR)反卷积实现非视域目标的三维重建。实验中,采用了打磨过的聚丙烯塑料(PP)板和亚克力(PMMA)板作为反射中介面,被测目标为表面形状复杂的石膏雕像、抛光塑料面板和多个目标的自然场景等常见实物,应用所提遗传-反卷积算法对非视域目标进行重构,通过重构前后的主观对比以及均方差的客观数据对比,得出重构后深度图像的均方误差是原始图像均方误差的1/7~1/2,表明了该算法的有效性。
光学数据处理 图像重构 散射后测量 相位测量 光学学报
2023, 43(21): 2111002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Advanced Transducers and Intelligent Control System, Ministry of Education and Shanxi Province, Taiyuan 030024, China
2 College of Physics & Optoelectronics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
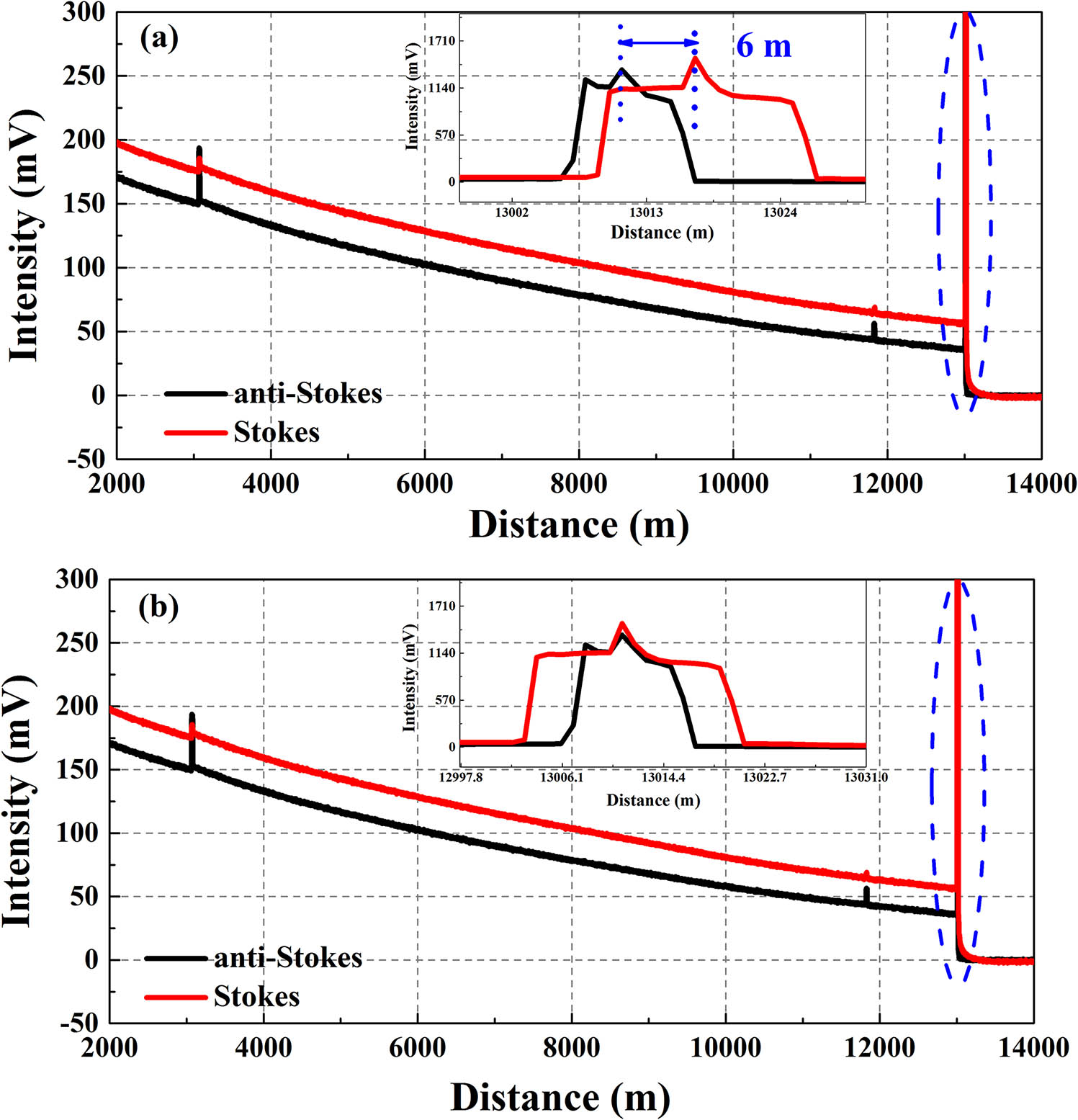
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a novel Raman-based distributed fiber-optics temperature sensor (RDTS) for improving the temperature measurement accuracy and engineering applicability. The proposed method is based on double-ended demodulation with a reference temperature and dynamic dispersion difference compensation method, which can suppress the effect of local external physics perturbation and intermodal dispersion on temperature demodulation results. Moreover, the system can omit the pre-calibration process by using the reference temperature before the temperature measurement. The experimental results of dispersion compensation indicate that the temperature accuracy optimizes from 5.6°C to 1.2°C, and the temperature uncertainty decreases from 16.8°C to 2.4°C. Moreover, the double-ended configuration can automatically compensate the local external physics perturbation of the sensing fiber, which exhibits a distinctive improvement.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 120.5820 Scattering measurements 280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors 290.5860 Scattering, Raman Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 070602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Jiangxi Engineering Laboratory for Optoelectronics Testing Technology, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
2 National Engineering Laboratory for Nondestructive testing and Optoelectric Sensing Technology and Application, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
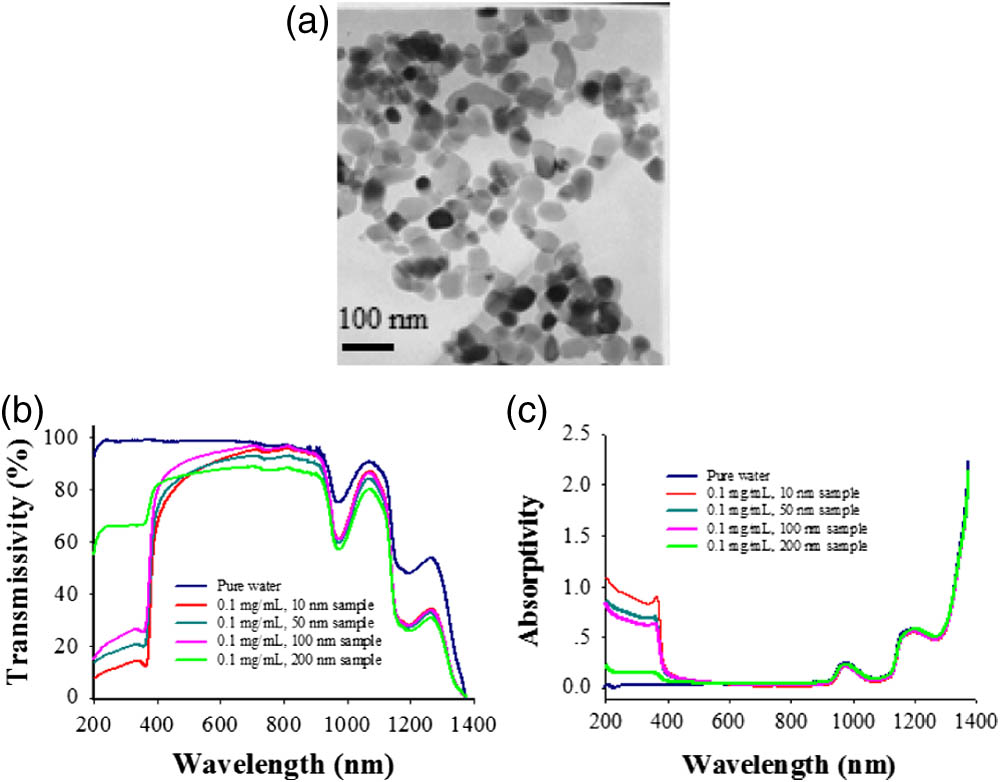
The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres with four different particle diameters of 10, 50, 100, and 200 nm suspended in water are investigated theoretical and experimentally in the spectral range of the entire visible range and part of the near-infrared region. The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres suspended in water are described by employing three main parameters: the angular distribution of the scattering intensity I, the scattering extinction coefficient αscat, and the scattering cross section σscat. The results indicate that (i) at a certain wavelength, the angular distribution of the scattering intensity appears as an obviously forward-propagating feature, and the forward-scattering intensity is dominant gradually when the particle diameter increases from 10 to 200 nm, and (ii) the scattering extinction coefficient and cross section can be determined by using the measured transmittance changes of a pure water sample and a given ZnO sample; they all are shown to be dependent on the particle size and incident wavelength. The experimental results of four different scattering samples agree well with the theoretical predictions within the given wavelength range.
290.5850 Scattering, particles 290.5820 Scattering measurements 290.5825 Scattering theory Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(1): 012901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Lab of Clean Energy Utilization, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China
2 CNRS UMR 6614/CORIA, Saint Etienne du Rouvray BP12 76801, France
Calibration of the relationship between the scattering angle and the CCD pixel is a key part of achieving accurate measurements of rainbow refractometry. A novel self-calibrated global rainbow refractometry system based on illumination by two lasers of different wavelengths is proposed. The angular calibration and refractive index measurement of two wavelengths can be completed simultaneously without extra measurement devices. The numerical and experimental results show the feasibility and high precision of the self-calibration method, which enables the rainbow refractometry to be implemented in a more powerful and convenient way. The self-calibrated rainbow system is successfully applied to measure the refractive indices of ethanol-water solutions with volume concentrations of 10% to 60%.
290.5820 Scattering measurements 120.4820 Optical systems 120.6780 Temperature 290.5820 Scattering measurements 290.3030 Index measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(4): 042902
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Lab of Advanced Transducers and Intelligent Control Systems, Ministry of Education and Shanxi Province, Taiyuan 030024, China
2 Institute of Optoelectronic Engineering, College of Physics & Optoelectronics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
3 Fiber Optics Group, Department of Physics, University of Ottawa, Ottawa K1N 6N5, Canada
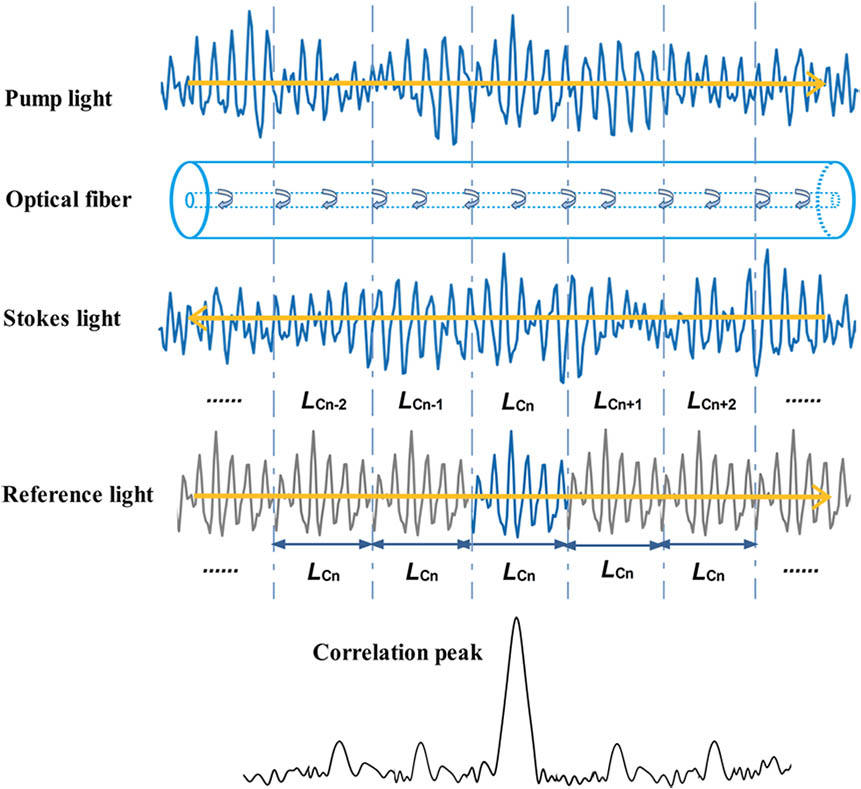
To obtain high spatial resolution over a long sensing distance in Brillouin optical correlation domain reflectometry (BOCDR), a broad laser spectrum and high pump power are used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In this Letter, we use a noise-modulated laser to study the variation of the Brillouin spectrum bandwidth and its impact on the coherent length of BOCDR quantitatively. The result shows that the best spatial resolution (lowest coherent length) is achieved by the lowest pump power with the highest noise-modulation spectrum. Temperature-induced changes in the Brillouin frequency shift along a 253.1 m fiber are demonstrated with a 19 cm spatial resolution.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.4080 Modulation 120.5820 Scattering measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(8): 080603
1 长春理工大学,长春 130022
2 光电测控与光电信息传输技术教育部重点实验室,长春,130022
3 吉林省光电测控仪器工程技术研究中心,长春 130022
4 空军航空大学,长春 130022
为了实现校准能见度仪中标准散射体的快速准确定标,建立了用于校准能见度仪的标准散射体的定标系统.研究了定标系统中全景成像折反光学系统的设计方法.根据抛物面反射镜的光学特性推导出抛物面面型的计算方法.根据定标系统对光学系统的要求,完成全景成像色度计光学系统的设计.对全景成像折反光学系统进行建模仿真并设计实验验证光学系统的设计与仿真结果的正确性.实验结果表明: 全景成像折反光学系统的空间检测俯仰角范围为0°~90°,方位角范围为0°~360°,且最小角分辨率为1°,与仿真结果基本一致,满足用于校准能见度仪的标准散射体定标系统中光学系统的设计要求.
仪器光学设计 前向散射式能见度仪 全景成像光学系统 校准 散射测量 Optical design of instruments Forward scattering visibility meter Panoramic imaging optical system Calibration Scattering measurements

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
2 Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center on Atmospheric Environment and Equipment Technology, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
3 School of Electronic & Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
4 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Meteorological Observation and Signal Processing, Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing 210044, China
In order to improve the inversion precision of aerosol mass concentrations based on the particle group light scattering method, the concept that particles through a laser beam are equivalent to an aggregate is proposed. A fractal model for aerosol mass concentration using the signal amplitude distribution of aggregates is presented, and then the subsection calibration method is given. The experimental results show that the mass concentrations inversed by this model agree well with those measured by the norm-referenced instrument. The average relative errors of the two experiments are 5.6% and 6.0%, respectively, which are less than those obtained by the conventional inversion model.
290.5850 Scattering, particles 120.5820 Scattering measurements 010.1100 Aerosol detection Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(11): 112901
1 山东理工大学 电气与电子工程学院, 山东 淄博 255049
2 山东理工大学 光电技术研究所, 山东 淄博 255049
采用两种常用的粒度反演方法——正则化和Chahine算法, 对90 nm与250 nm单峰分布、50 nm与200 nm双峰分布、100 nm与300 nm双峰分布的模拟动态光散射数据, 以及105 nm、300 nm标准颗粒的实测动态光散射数据进行了反演分析.结果表明: 噪声水平的高低是影响粒度分布反演准确性的关键因素之一, 反演结果的准确性随噪声水平的增加而降低, 噪声水平超过某一阈值后, 将无法得到有意义的反演结果; 不同反演方法具有不同的抗噪能力, 在低噪声水平下反演结果无显著差别, 随着噪声水平的增加, 反演结果表现出很大差异; 正则化方法通过正则参数的选择可以有效抑制噪声影响, 表现出强于Chahine算法的抗噪能力; 与Chahine算法相比, 正则化方法不需要假定初始分布, 因此, 在噪声较大的实验或生产过程中进行颗粒分布测量时, 宜采用正则化方法.
散射测量 粒度分布 颗粒测量 反问题 正则化算法 Chahine算法 Scattering measurements Particle size distribution Particle sizing Inverse problems Regularization algorithm Chahine algorithm 光子学报
2016, 45(11): 1112004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Lab of Advanced Transducers and Intelligent Control System, Ministry of Education and Shanxi Province, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
2 Institute of Optoelectronic Engineering, College of Physics and Optoelectronics, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
We propose and demonstrate a scheme to measure the distribution of temperature along an optical fiber based on pseudo-random sequence modulation. In our experimental work, current modulation with a pseudo-random bit sequence (PRBS) is applied to a laser diode that serves as the Brillouin pump light and reference light. Because of the independence of the spatial resolution on the PRBS length, the measurement range can be extended while maintaining high spatial resolution using a long PRBS length. Temperature-induced changes in a Brillouin frequency shift of 250 m fiber sections are clearly observed with 54 cm spatial resolution by this method.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.4080 Modulation 120.5820 Scattering measurements 290.5830 Scattering, Brillouin Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(8): 080604
Author Affiliations
Abstract
We present a method by which to determine the bulk viscosity of water from pulse duration measurements of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS). Beginning from a common model of Brillouin scattering, the bulk viscosity is shown to play an important role in Brillouin linewidth determination. Pulse durations of SBS back-reflected optical pulses are measured over the temperature range of 5–40 oC. SBS linewidths are determined via Fourier transformation of the time-domain results, and the bulk viscosity of water is measured and derived from the obtained values. Our results show that the proposed method for measurement of pulse durations is an effective approach for determining bulk viscosity. The method can be easily extended to determine bulk viscosities of other Newtonian liquids.
290.5820 Scattering measurements 290.5900 Scattering, stimulated Brillouin 190.5890 Scattering, stimulated Chinese Optics Letters
2013, 11(11): 112902





