Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Molecular Vaccinology and Molecular Diagnostics & Center for Molecular Imaging and Translational Medicine, School of Public Health, Xiamen University, Xiamen 361102, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Precision Electronic Manufacturing Technology and Equipment, School of Electromechanical Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
3 Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Optic-Electronic and Communication, Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, Nanchang 330038, China
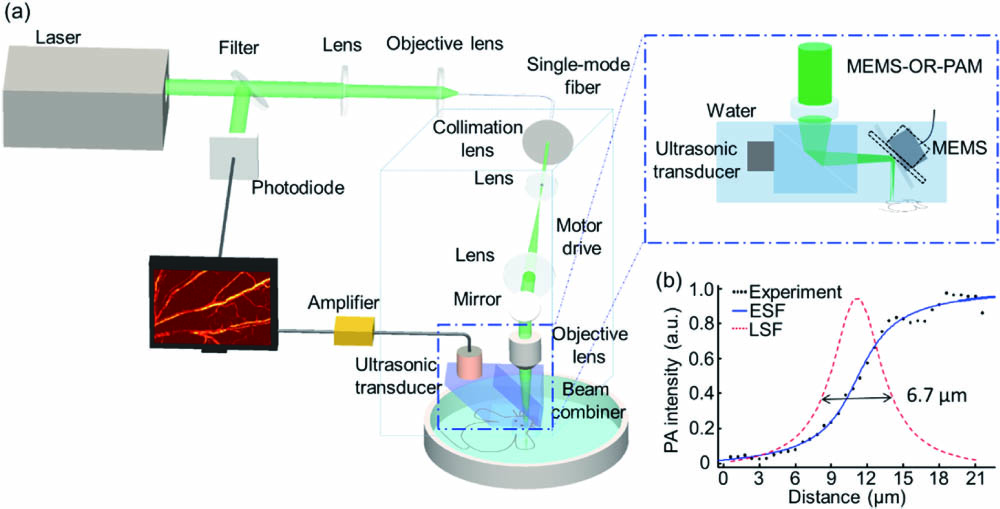
Photoacoustic imaging has been developed to image the immune study at the macro scale. Macrophages play diverse roles in the acute response to infection and tissue repair. However, macrophages activities in acute inflammation at the microscopic level still remain challenging. In this work, we proposed optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy to promptly monitor the labeled macrophages activities in normal and inflammatory groups. The result showed that many labeled macrophages emerged around the vessels firstly, then exuded into tissues, and finally disappeared in the inflammatory group injected with labeled macrophages. In summary, our method allows us to exactly image and track the immune cells of inflammatory diseases.
photoacoustic microscopy macrophages activities vessel parameter Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(12): 121701
清华大学热能工程系热科学与动力工程教育部重点实验室, 北京 100084
利用选择性光热解(SP)的三维光热作用模型, 对血管尺寸、位置和数目等血管参数对皮肤组织选择性光热解作用中光热响应规律的影响进行了理论分析和数值求解。数值结果表明, 当利用选择性光热解效应热损伤皮肤组织内的特定血管时, 假如一定区域内有其他血管存在, 则目标血管的热损伤率会受区域内其他血管的影响而减小。这个区域的大小与激光光斑大小及激光波长有关。一般来说, 当血管处于激光光斑以外或深度超过1 mm(对于585 nm激光)时, 这些血管的影响可忽略不计。
医用光学 选择性光热解 血管参数 光热作用 气化潜热 皮肤外科





