光学 精密工程, 2024, 32 (1): 111, 网络出版: 2024-01-23
适应大范围星场密度变化的恒星辨识与抑制
Identification and suppression of stars under large range of star field density variation
目标检测 恒星辨识与抑制 中高轨目标搜索 惯性坐标系 target detection identification and suppression of stars search of GEO and MEO inertial coordinate system
摘要
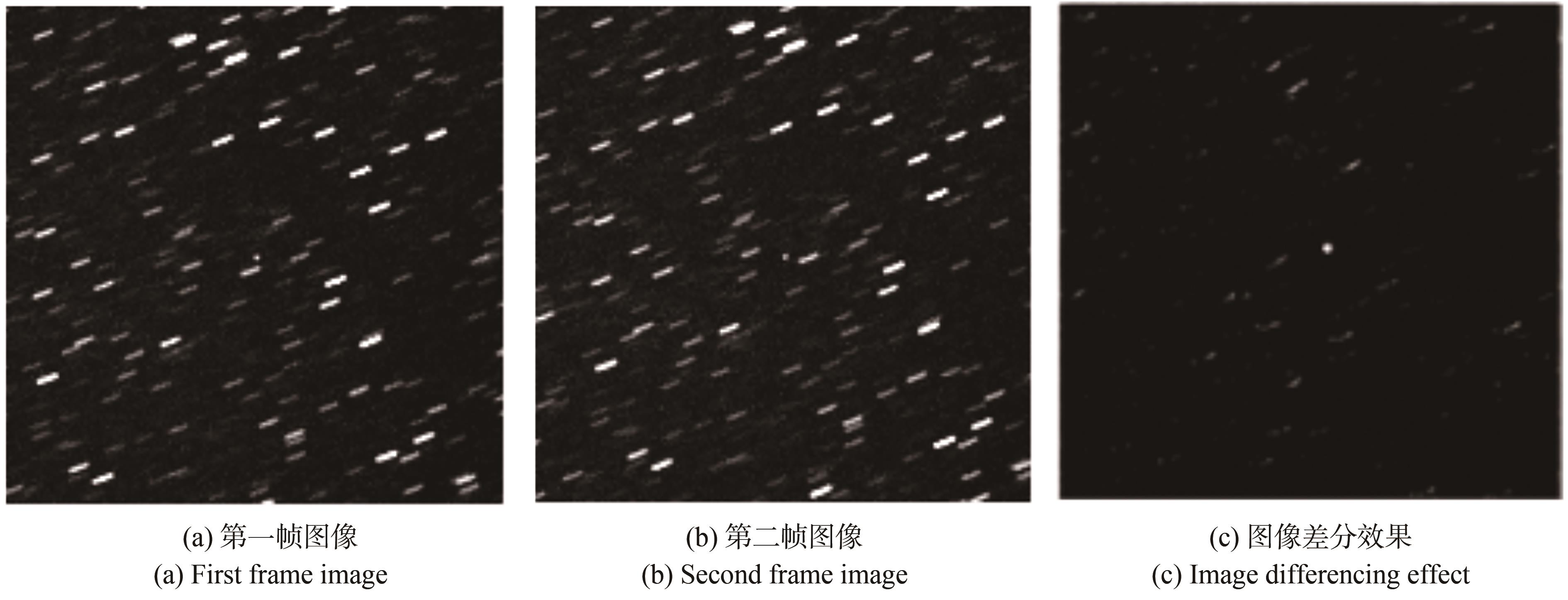
大视场光学望远镜是中高轨目标搜索的重要设备,在搜索图像中除中高轨目标外还存在恒星目标,对恒星目标进行辨识与抑制是中高轨目标检测的必要环节之一。考虑银道面附近天区、曝光时间差异以及多云遮挡等因素的影响,图像中的星场密度变化区间非常大,传统的恒星辨识方法在计算准确性与实时性方面均存在局限性,导致恒星虚警、计算超时等情况的发生。为解决该问题,提出了一种基于惯性坐标时域相对不变性的恒星辨识与抑制方法。推导了地平坐标系与惯性坐标系的数学转换关系,并由此构建了恒星辨识模型;在不同的静态系统误差条件下,量化分析了恒星目标的惯性坐标时域相对不变性;最后,开展了恒星辨识与抑制算法的仿真与实验验证。仿真与实验结果表明:在时间间隔为10 s、静态系统误差为10″的条件下,恒星的惯性坐标最大相对差异为0.51″(赤经),0.16″(赤纬),其时域相对不变性满足恒星辨识需求,辨识过程完全不依赖星场密度。经100圈次中高轨目标实测图像验证,本文方法未出现恒星虚警及中高轨目标检测缺失的现象。
Abstract
The large field optical telescope is an important equipment for the search of medium-high orbit targets. However, stellar targets also appear in the search images. Thus, the identification and suppression of stellar targets is a necessary step in the detection of medium-high orbit targets. Considering the influence of the sky area near the galactic plane, difference in exposure time, and cloudy occlusion, the variation in the star field density within the image is very large. The traditional star identification method has limitations in the calculation accuracy and real-time performance, which leads to the occurrence of false alarm of stars and calculation timeout. To solve these problems, this study proposes a method of star identification and suppression based on the relative invariance of inertia coordinates in time domain. First, the mathematical transformation relationship between the horizon coordinate system and the inertial coordinate system is derived, and the star identification model is constructed accordingly. Then, the time domain relative invariance of the inertial coordinates of the stellar target is quantitatively analyzed under different static system errors. Finally, the star identification and suppression algorithm was verified via simulation and experiment. As a result, the maximum relative difference in the inertial coordinates of stars is 0.51" (right longitude) and 0.16" (declination) when the time interval is 10" and the static system error is 10". Thus, the time domain relative invariance meets the requirements regarding star identification, and the corresponding process is completely independent of star field density. The proposed method was also verified considering 100 measurement images of medium-altitude orbit objects, and no false alarm of stars and missing detection phenomenon of medium-altitude orbit objects were observed.
杨禹凯, 谷健, 王建立, 刘俊池. 适应大范围星场密度变化的恒星辨识与抑制[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2024, 32(1): 111. Yukai YANG, Jan GU, Janli WANG, Junchi LIU. Identification and suppression of stars under large range of star field density variation[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2024, 32(1): 111.