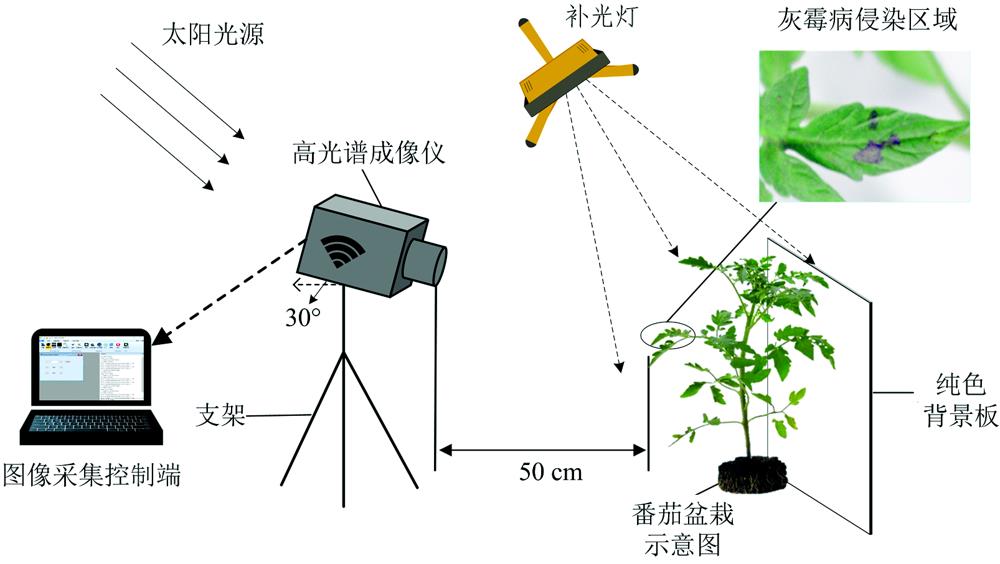
光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42 (10): 3226, 网络出版: 2022-11-23
基于多维随机森林的番茄灰霉病高光谱图像早期检测
Early Detection of Tomato Gray Mold Disease With Multi-Dimensional Random Forest Based on Hyperspectral Image
早期病害识别 高光谱成像技术 番茄灰霉病 随机森林 多维时间序列 Early disease detection Hyperspectral imaging Tomato gray mold Random forest Multi-dimensional times series
摘要
植物病害的自动早期检测对于作物精确保护至关重要。 提出了一种基于多维光谱序列(multi-dimensional spectral series, MDSS)和加权随机森林(weighted random forest, WRF)的番茄灰霉病早期诊断与鉴别方法。 目的是利用叶片多个观测维度的光谱曲线整体变化趋势建立作物病害检测模型, 以期在肉眼明显可见叶面病斑前对作物病害实现诊断。 将健康叶片接种灰霉病菌第3天作为叶片成功染病第1天。 试验首先采集番茄健康叶片和染病叶片7天内每天的高光谱图像, 提取感兴趣区域并计算平均光谱作为初始光谱数据, 经筛选共得到(156×7)组有效样本。 将样本数据按时间顺序拆分成分别包含1~7个维度的光谱数据形成多维原始光谱序列, 为增加维度间差异性, 相邻原始光谱序列相减构成多维关联光谱序列。 分别采用符号聚合近似估计(symbolic aggregate approximation, SAX)和符号傅里叶近似估计(symbolic Fourier approximation, SFA)两种符号化方法将光谱序列离散成局部辨别性特征。 基于多维光谱序列的局部辨别性特征建立加权随机森林(MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF)分类模型, 实现病害早期检测。 相应地, 基于单维光谱序列(single-dimensional spectral series, SDSS)的番茄灰霉病识别模型被作为基准模型与MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF模型比较。 试验结果显示, MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF检测模型在包含2至7个光谱序列维度的56个测试样本数据中均获得90%以上识别准确率, 在包含5个光谱序列维度测试集中得到最高99%的识别准确率, 较SDSS-SAX-SFA-MRF检测模型在染病第5天的识别率高8.2个百分点。 另外受随机干扰的影响, SDSS-SAX-SFA-MRF模型准确率在染病5~7 d出现大幅度回落至最低84%, MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF模型识别率在肉眼可见病斑阶段依然保持超过98%的较高检测水准, 未过度回落。 因此, 提出的基于多维光谱曲线整体变化趋势和加权随机森林(MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF)的分类模型能够有效实现番茄灰霉病早期检测, 并具有较强的鲁棒性, 为染病初期的番茄灰霉病鉴别提供新思路。
Abstract
Automatic early detection of plant diseases is essential for precision crop protection. This paper proposes an early diagnosis and detection method for tomato gray mold based on multi-dimensional spectral series (MDSS) and weighted random forest (WRF) algorithm. The aim was to establish a crop disease detection model by utilizing the overall trend of the spectral curve among multiple observation dimensions of the target leaves to realize the diagnosis before the leaf spot is visible. Generally, the third day after healthy leaves were inoculated with the Botrytis cinerea was treated as the first day that was successfully infected. Therefore, hyperspectral images were recorded from both healthy and infected leaves for 7 days after infection respectively. Then extracted, the region of interest and calculated the average spectrum to form the original spectral samples, whilst (156×7) groups were obtained in total after selection. The group samples were split into multi-dimensional spectral series with 1~7 dimensions per the course of the disease to make up multi-dimensional original spectral series. In order to increase the difference between dimensions, the adjacent original spectral series were subtracted to generate multi-dimensional related spectral series. Afterwards, two symbolic methods, symbolic aggregate approximation (SAX) and symbolic Fourier approximation (SFA), were employed to discretize each spectral series into local discriminant features. Finally, a weighted random forest classification model (MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF) based on the local discriminant features of multi-dimensional spectral series is established to realize early disease detection. Accordingly, the model based on single-dimensional spectral series (SDSS) is also built as the benchmark to compare with the MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF model. The experiment results indicate that the MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF detection model achieves detection accuracies of more than 90% in 56 testing samples containing 2 to 7 spectral series dimensions, and the highest accuracy up to 99% reached in the 5-dimensional sample data, which is 8.2 percentage higher than that of SDSS-SAX-SFA-MRF detection model on the 5th day of infection. Different from the SDSS-SAX-SFA-MRF model detection performance dropped significantly to the lowest 84% in the 5th~7th days of infection due to random interference. While the discrimination accuracy of the MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF model still retained a high level of more than 98% in the visible stage of infection without excessive decline. Therefore, the classification model based on the overall change trend of the multi-dimensional spectral curve and weighted random forest (MDSS-SAX-SFA-WRF) proposed in this paper can effectively realize the early detection of tomato gray mold with the strong robustness, which provides a new idea for the early differentiation of crop disease.
高荣华, 冯璐, 张月, 原继东, 吴华瑞, 顾静秋. 基于多维随机森林的番茄灰霉病高光谱图像早期检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42(10): 3226. Rong-hua GAO, Lu FENG, Yue ZHANG, Ji-dong YUAN, Hua-rui WU, Jing-qiu GU. Early Detection of Tomato Gray Mold Disease With Multi-Dimensional Random Forest Based on Hyperspectral Image[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022, 42(10): 3226.