强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35 (10): 104002, 网络出版: 2023-11-30
基于机器学习的地球静止轨道质子能谱反演
Geostationary orbital proton energy spectrum inversion based on machine learning
宇宙线能谱 机器学习 中子探测 遗传算法 航天工程应用 cosmic ray spectroscopy machine learning neutron detection genetic algorithm aerospace engineering applications
摘要
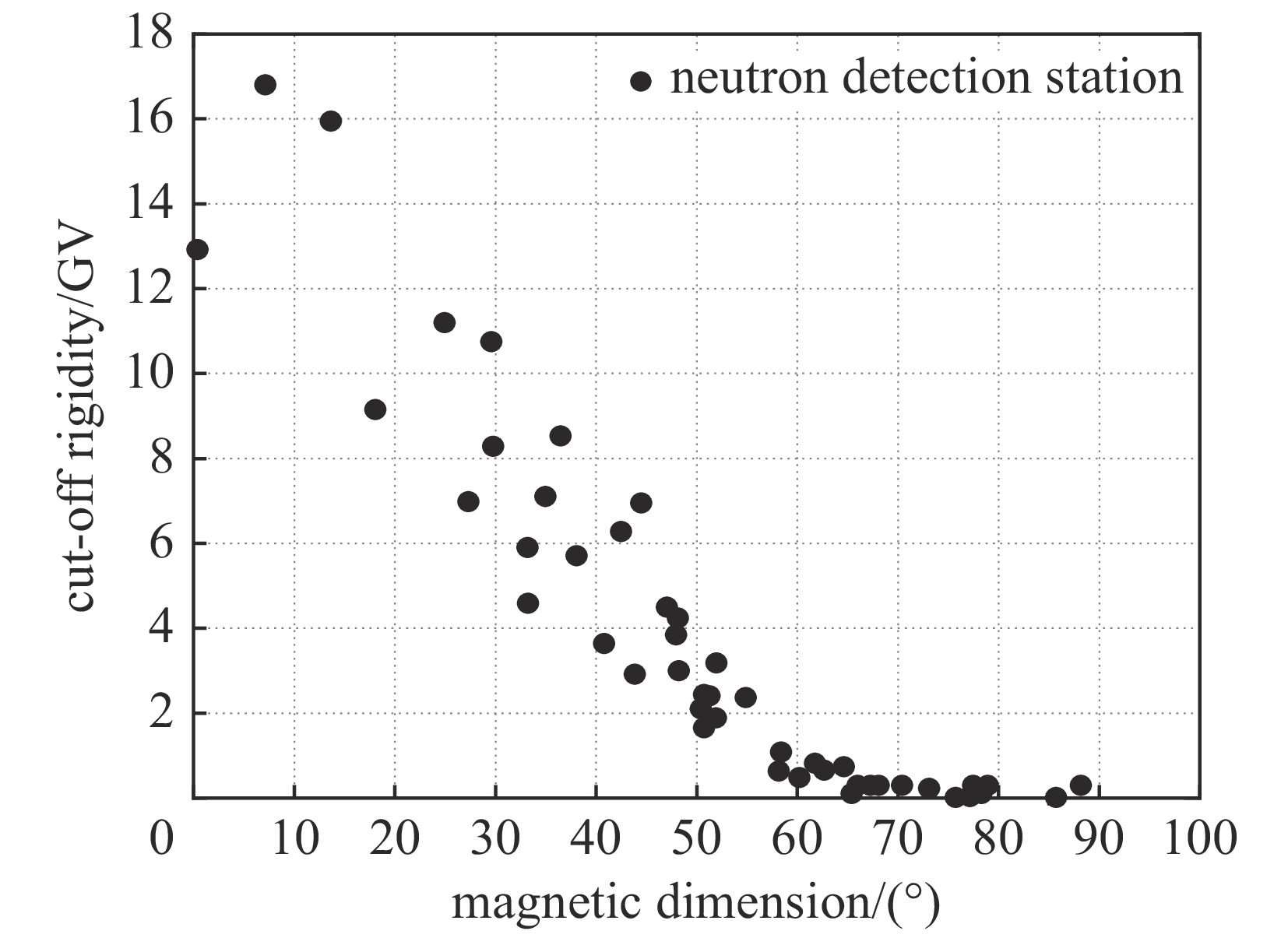
根据地面中子探测与宇宙线环境之间的关联性,在太阳活动平静期以地球静止环境业务卫星及全球各个中子探测站的探测数据构建数据集。基于极端梯度提升决策树(XGBoost)和人工神经网络建立了由地面中子探测数据反演宇宙线质子环境的模型。模型采用遗传算法求解模型的最优超参数并对神经网络的各个神经元参数进行训练,实现了宇宙线质子环境在太阳活动平静期的反演,模型训练的均方差MSE为0.499,对测试集的平均反演误差分别为26.9%,对比航天常用的辐射环境模型误差通常在200%以内,提高显著。同时使用包括支持向量回归、误差反向传播算法、长短期记忆在内的多种其他机器学习算法进行了对比,结果表明本文所建立的模型具有训练时间短、计算速度快、占用资源小的优点。
Abstract
Based on the correlation between ground neutron detection and the cosmic ray environment, a dataset was constructed using the detection data of geostationary operational environmental satellites and various neutron detection stations worldwide for the solar activity quiet period. Models for inverting the cosmic ray proton environment from ground neutron detection data were established based on the extreme gradient boost decision tree (XGBoost) and artificial neural network. They use genetic algorithm to solve the optimal hyperparameter and train the parameters of each neuron of the neural network to realize the inversion of the cosmic ray proton environment. The mean square error of the model training is 0.499, and the average inversion error of the test set is 26.9% respectively. Compared with the radiation environment model commonly used in aerospace, the error is usually within 200%, which is significantly improved. Multiple other machine learning algorithms, including support vector regression, error back propagation training, long short-term memory network, were compared and the results show that the model established in this paper has the advantages of short training time, fast computation speed, and low resource consumption.
陈建飞, 周宏涛, 方美华, 吴康, 宋定一. 基于机器学习的地球静止轨道质子能谱反演[J]. 强激光与粒子束, 2023, 35(10): 104002. Jianfei Chen, Hongtao Zhou, Meihua Fang, Kang Wu, Dingyi Song. Geostationary orbital proton energy spectrum inversion based on machine learning[J]. High Power Laser and Particle Beams, 2023, 35(10): 104002.