光电工程, 2023, 50 (2): 220313, 网络出版: 2023-04-13
碲化镉片上集成波导的自相位调制特性研究
Self-phase modulation in integrated cadmium telluride polycrystalline waveguide
摘要
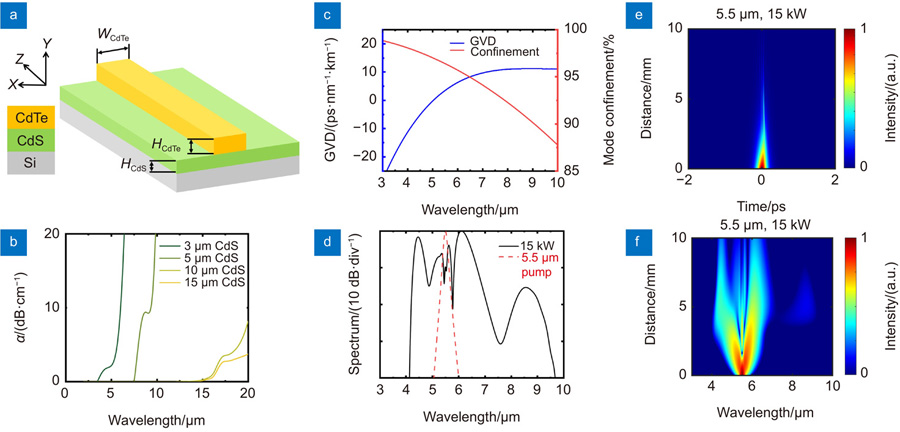
中红外(2.5 μm~25 μm)波段包含许多重要的原子和分子共振峰,因此中红外超连续谱广泛应用于生物医学、光谱学和环境科学等领域。碲化镉(cadmium telluride, CdTe)在中红外波段具有超宽的透射光谱范围0.86 μm~25 μm,同时CdTe具有较大的三阶非线性系数,是实现中红外超连续谱的理想材料。本文设计并加工了一种基于CdTe为芯层、低折射率介质硫化镉为缓冲层、硅为衬底的波导。采用广义非线性薛定谔方程仿真了该波导以中心波长为5.5 μm中红外激光作为泵浦,能够实现4.1 μm~9.7 μm的超连续谱输出。实验中通过湿法刻蚀制作CdTe多晶波导,并采用中心波长为1030 nm,脉冲宽度为250 fs的激光器作为泵浦源,观察到在波导中发生明显的自相位调制而产生的光谱展宽。该工作为CdTe集成波导应用于中红外超连续谱及中红外波段的片上光学器件提供了新的可能。
Abstract
Overview: The mid-infrared (MIR) wavelength coincides with various molecular resonances and spectroscopy, which is universally used to identify chemical and biological substances. In particular, the 13 μm~20 μm wavelength window has fingerprints of unique material groups such as organometallic, halogenated, and aromatic bonds. Thus, the MIR supercontinuum generation (SCG) is widely used in the fields of biomedicine, spectroscopy, and environmental science. Thanks to the mature semiconductor growth technology combined with the advanced CMOS integration technology, SCG in on-chip devices has been studied in recent years. Cadmium telluride (CdTe) has an ultra-broad transparent spectral range, from 0.86 μm to 25 μm, and one of the largest third-order nonlinear coefficients (n2~5×10?17 m2/W at 1.55 μm, 2×10?17 m2/W at 5.5 μm, which are several times larger than that of silicon) among the MIR materials, which makes CdTe become an excellent candidate for long-wavelength MIR on-chip SCG. As an important material of solar cells, there is a mature film growth and etching technology for CdTe. In this work, we designed a large-core CdTe integrated waveguide on a low-refractive-index cadmium sulfide (CdS) film with a silicon substrate. The waveguide structure is designed with CdS as the intermediate cladding layer to achieve a low waveguide loss and high mode confinement. A large-core CdTe waveguide is tailored to generate a low and flat dispersion in the MIR spectral range, while balancing the large effective nonlinearity and the convenience of coupling. The effective refractive index in the CdTe waveguide is obtained by finite element method. Then, the simulated results solved by the nonlinear Schr?dinger equation manifest that a CdTe waveguide with a propagation distance as short as 1 cm can broaden the MIR spectrum covering 4.1 μm to 9.7 μm pumped by a 5.5 μm femtosecond laser. Experimentally, polycrystalline CdS and CdTe films were deposited by magnetron sputtering, and the CdTe waveguides were fabricated by photolithography followed by wet etching. In particular, the sidewall of the waveguide is almost perpendicular to the substrate due to the large difference in the longitudinal and transverse etching rates caused by the unique grain arrangement of the film. A near-infrared femtosecond laser centered at 1030 nm with a pulse width of 250 fs at a 500 kHz repetition rate is employed as the pump source, and an apparent spectral broadening based on self-phase modulation was observed. The numerical simulations match well with the experimental results. These results pave the way for long-wavelength mid-infrared light sources and provide abundant new opportunities for MIR microphotonics.The mid-infrared (MIR) wavelength coincides with various molecular resonances and spectroscopy. It is a universal way to identify chemical and biological substances. Thus, the MIR supercontinuum generation (SCG) is widely used in biomedicine, spectroscopy, and environmental science. Cadmium telluride (CdTe) has an ultra-broad transparent spectral range, from 0.86 μm to 25 μm, and one of the largest third-order nonlinear coefficients. It makes CdTe become an excellent candidate for long-wavelength MIR on-chip SCG. As an important material of solar cells, there is a well-established thin film growth technology for CdTe. We designed a CdTe integrated waveguide on a low-refractive-index CdS film with a silicon substrate. The simulation results solved by the nonlinear Schr?dinger equation manifest that the MIR SCG covering 4.1 μm to 9.7 μm can be generated from a 1 cm CdTe waveguide pumped by a 5.5 μm femtosecond laser. We experimentally fabricated the waveguide via the lithography and wet-etching techniques. The spectral broadening based on self-phase modulation from the large-core CdTe integrated waveguide is demonstrated by a femtosecond laser at the central wavelength of 1030 nm with a pulse width of 250 fs. The numerical simulations match well with the experimental results. These results pave the way for long-wavelength mid-infrared light sources and provide abundant new opportunities for MIR micro photonics.
龙哲, 杨航, 吴函, 李阳, 梁厚昆. 碲化镉片上集成波导的自相位调制特性研究[J]. 光电工程, 2023, 50(2): 220313. Zhe Long, Hang Yang, Han Wu, Yang Li, Houkun Liang. Self-phase modulation in integrated cadmium telluride polycrystalline waveguide[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2023, 50(2): 220313.