光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41 (10): 3227, 网络出版: 2021-10-29
马达加斯加玛瑙的光谱学特征研究
Spectral Characteristics of Madagascar Agates
马达加斯加玛瑙 纹带结构 光谱学特征 成因机制 六方纤铁矿(δ-FeOOH) Madagascar agates Spectral characteristics Banded structure Formation mechanism Feroxyhyte (δ-FeOOH)
摘要
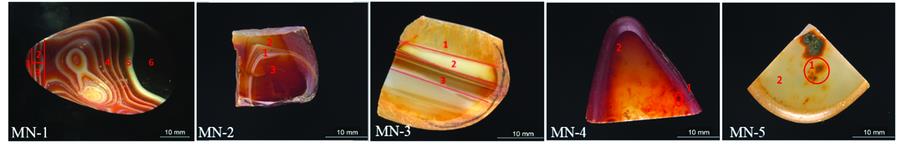
玛瑙在世界各地分布广泛, 有关玛瑙矿物学和光谱学特征的研究颇丰, 但对产自马达加斯加安楚希希市和马哈赞加省的玛瑙的光谱学和产地特征研究甚少。 采用正交偏光显微镜、 红外光谱和拉曼光谱仪对5块来自安楚希希市和马哈赞加省具有纹带结构的玛瑙样品进行光谱学特征分析。 结果表明: 这两个产地玛瑙的主要矿物成分一致, 均为α-石英和斜硅石。 来自马哈赞加省的样品靠近中心的白色、 红色部分斜硅石的特征拉曼峰(501cm-1)缺失, 根据前人研究发现是与玛瑙内部的结构水之间发生脱水反应形成中性水分子, 而这些中性水分子与斜硅石反应生成了石英颗粒有关。 然而两产地玛瑙的致色矿物不同, 马哈赞加省玛瑙棕色和红色部分具有222, 294, 410以及1 316 cm-1的特征拉曼位移峰, 与赤铁矿的拉曼特征峰相符, 确定这部分的致色矿物是赤铁矿, 而安楚希希市玛瑙黄色部分只具有400和1 160 cm-1的特征峰, 与六方纤铁矿的拉曼特征峰相符, 因此此部分的致色矿物是六方纤铁矿(δ-FeOOH)。 部分来自安楚希希市的玛瑙具有少量的杂质矿物, 通过拉曼测试发现杂质矿物的成分也是六方纤铁矿(δ-FeOOH)和α-石英。 结合六方纤铁矿的特性推测来自安楚希希市的四块样品是处于低温(<80 ℃)、 Fe2+含量很少(β<0.03)且空气不流通的偏酸性的环境当中形成的。 红外光谱测试发现两个产地的玛瑙均有液态水(3 400 cm-1左右)和结构水(3 750~3 500 cm-1)的红外特征峰, 安楚希希市的结构水红外特征峰位于3 740 cm-1处, 可推测该结构水位于结构缺陷处。 结合马达加斯加玛瑙的光谱学特征和纹带结构的讨论, 对推测马达加斯加玛瑙的形成机制有着重要的意义; 并且六方纤铁矿(δ-FeOOH)可以作为区别于其他产地的标型矿物, 具有产地特征意义; 同时为研究马达加斯加玛瑙形成的地质环境提供了数据支持。
Abstract
The origin of agate is distributed worldwide, and the mineralogical and spectroscopic characteristics of agates in most areas at home and abroad have been well studied. However, little research has been focused on the spectral characteristics and origin characteristics of agates from Madagascar. The banded structure and spectral characteristics of five agate samples from Antsohihy and Mahajanga were analyzed using polarization microscope, infrared spectrometer, and Raman spectrometer. The main mineral compositions of the samples from Mahajanga and Antsohihy are the same, which include α-quartz and moganite. The absence of characteristic Raman peaks (501 cm-1) of white and red moganite near the center of the sample from Mahajanga, combining with the previous studies, is related to the dehydration reaction between structural water in the agate to form neutral water molecules, which react with moganite to form the quartz particles. However, the secondary minerals from those two areas are different. The Raman peaks of the agate from Mahajanga are 222, 294, 410, 1 316 cm-1, which are proved to be hematite. But the Raman peaks of the samples from Antsohihy are 400~1 160 cm-1.Therefore the secondary mineral is feroxyhyte. The impurity minerals in some samples from Antsohihy were proved to be α-quartz (moganite) and feroxyhyte by Raman spectrometer.It was speculated that four agates from Antsohihy were formed in a low-temperature (<80 ℃) environment with less Fe2+ content (β<0.03) and poor ventilation of air. Infrared spectrum test of agates from these two areas found that there were infrared characteristic peaks of liquid water (about 3 400 cm-1) and structural water (3 750~3 500 cm-1), the structural water (3 740 cm-1) in agates from Antsohihy was proved to be located at structural defects. It is of great significance to speculate the formation mechanism of Madagascar agates by combining with the texture and spectral characteristics of Madagascar agates. Moreover, feroxyhyte can be used as a common mineral which is different from other producing areas and has the significance of producing areas. It also provides support for studying the geological environment of the formation of Madagascar agates.
张志琦, 赵彤, 刘玲, 李妍. 马达加斯加玛瑙的光谱学特征研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(10): 3227. Zhi-qi ZHANG, Tong ZHAO, Ling LIU, Yan LI. Spectral Characteristics of Madagascar Agates[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(10): 3227.