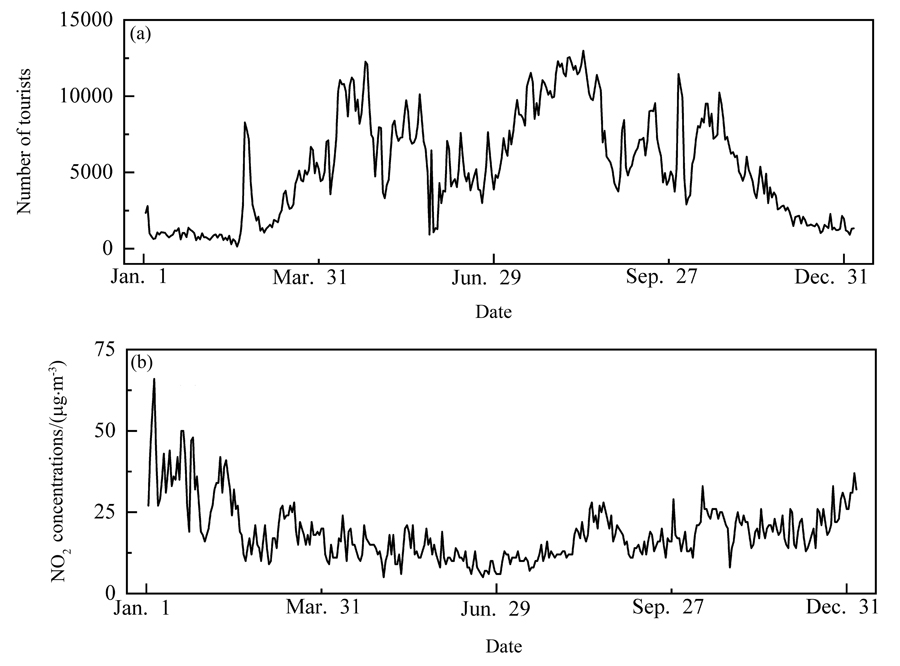
短周期高强度旅游活动对城市空气质量的影响
杜娟, 欧阳文言, 刘春琼, 吴波, 张娇, 史凯. 短周期高强度旅游活动对城市空气质量的影响[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2023, 18(1): 36.
Juan DU, Wenyan OUYANG, Chunqiong LIU, Bo WU, Jiao ZHANG, Kai SHI. Influence of short-duration high-strength tourism activities on urban air quality[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2023, 18(1): 36.
[1] 乔雪, 肖维阳, 唐亚, 等. 旅游和区域大气污染对四川九寨沟气溶胶的贡献[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(1): 14-21.
Qiao X, Xiao W Y, Tang Y, et al. Contributions of local tourism and regional air pollution to atmospheric aerosols in Jiuzhaigou, Sichuan, China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(1): 14-21.
[2] 周长春, 王晓青, 孙小银, 等. 旅游洞穴环境变化监测分析及其影响因素研究: 以山东沂源九天洞为例[J]. 旅游学刊, 2009, 24(2): 81-86.
Zhou C C, Wang X Q, Sun X Y, et al. A test analysis of environmental changes of tourism Karst caves and study on influencing factors — A case of Jiutian cave in Yiyuan County, Shandong Province[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2009, 24(2): 81-86.
[3] 郑凯莉, 黄毅, 姚小云, 等. 张家界市PM2.5、NO2与旅游活动及天气因素的相关性分析[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2020, 15(5): 347-356.
[4] 石培华. 构建国家旅游创新体系, 加快推进中国旅游4.0战略[J]. 旅游学刊, 2015, 30(11): 13-14.
Shi P H. Constructing the national tourism innovation system and accelerating the strategy of China tourism 4.0[J]. Tourism Tribune, 2015, 30(11): 13-14.
[5] 史凯, 刘春琼, 吴生虎. 基于DCCA方法的成都市市区与周边城镇大气污染长程相关性分析[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2014, 23(11): 1633-1640.
Shi K, Liu C Q, Wu S H. Long range correlation of air pollution between Chengdu City and its surrounding towns[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2014, 23(11): 1633-1640.
[6] Shi K, Liu C Q, Ai N S, et al. Using three methods to investigate time-scaling properties in air pollution indexes time series[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2008, 9(2): 693-707.
[7] Lee C K, Juang L C, Wang C C, et al. Scaling characteristics in ozone concentration time series (OCTS)[J]. Chemosphere, 2006, 62(6): 934-946.
[8] Shi K, Liu C Q, Huang Y. Multifractal processes and self-organized criticality of PM2.5 during a typical haze period in Chengdu, China[J]. Aerosol and Air Quality Research, 2015, 2015(3): 926-934.
[9] Shi K. Detrended cross-correlation analysis of temperature, rainfall, PM10 and ambient dioxins in Hong Kong[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2014, 97: 130-135.
[10] 吴生虎, 史凯, 刘春琼, 等. 成都市一次重雾霾期间PM10自组织演化的分形特征及DFA分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2014, 14(5): 285-291.
Wu S H, Shi K, Liu C Q, et al. Fractal feature and DFA analysis of PM10 evolution in a typical fog-haze episode in Chengdu[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2014, 14(5): 285-291.
[11] Wu Z H, Huang N. Ensemble empirical mode decomposition: A noise-assisted data analysis method[J]. Advances in Adaptive Data Analysis, 2009, 1(01): 1-41.
[12] 唐洁, 刘晓琴, 傅明星. 集合经验模态分解在陕西降水多尺度分析中的应用[J]. 陕西理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 34(1): 87-92.
Tang J, Liu X Q, Fu M X. Multiscale analysis of precipitation in Shaanxi Province based on ensemble empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 34(1): 87-92.
[13] Kim T, Shin J Y, Kim S, et al. Identification of relationships between climate indices and long-term precipitation in South Korea using ensemble empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 557: 726-739.
[14] Wang J, Wang X, Lei X, et al. Teleconnection analysis of monthly streamflow using ensemble empirical mode decomposition[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 582: 124411.
[15] Xu M, Shang P, Lin A. Cross-correlation analysis of stock markets using EMD and EEMD[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2016, 442: 82-90.
[16] Zhang N N, Lin A J, Shang P J. Multidimensional k-nearest neighbor model based on EEMD for financial time series forecasting[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2017, 477: 161-173.
[17] Gong X, Lin B. Modeling stock market volatility using new HAR-type models[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 516: 194-211.
[18] Podobnik B, Stanley H E. Detrended cross-correlation analysis: A new method for analyzing two nonstationary time series[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2008, 100(8): 084102.
[19] Vassoler R T, Zebende G F. DCCA cross-correlation coefficient apply in time series of air temperature and air relative humidity[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2012, 391(7): 2438-2443.
[20] Yuan N M, Fu Z T. Different spatial cross-correlation patterns of temperature records over China: A DCCA study on different time scales[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2014, 400: 71-79.
[21] Shi K, Di B F, Zhang K S, et al. Detrended cross-correlation analysis of urban traffic congestion and NO2 concentrations in Chengdu[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2018, 61: 165-173.
[22] Huang N E, Shen Z, Long S R, et al. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 1998, 454(1971): 903-995.
[23] Ouyang Q, Lu W X, Xin X, et al. Monthly rainfall forecasting using EEMD-SVR based on phase-space reconstruction[J]. Water Resources Management, 2016, 30(7): 2311-2325.
[24] Ferreira P, Loures L, Nunes J, et al. Are renewable energy stocks a possibility to diversify portfolios considering an environmentally friendly approach: The view of DCCA correlation coefficient[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2018, 512: 675-681.
[25] Xue L, Chen F, Guo S, et al. Time varying correlation structure of Chinese stock market of crude oil related companies greatly influenced by external factors[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2019, 530: 121086.
[26] Zhang C, Ni Z W, Ni L P. Multifractal detrended cross-correlation analysis between PM2.5 and meteorological factors[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2015, 438: 114-123.
[27] Zebende G F, Brito A A, Silva Filho A M, et al. ρDCCA applied between air temperature and relative humidity: An hour/hour view[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2018, 494: 17-26.
[28] 庄大春, 邓祥征, 战金艳. 武陵源风景区环境质量评估[J]. 地理研究, 2004, 23(2): 192-200.
Zhuang D C, Deng X Z, Zhan J Y. Assessment of the environmental quality for Wulingyuan Scenic Spot in Hunan Province[J]. Geographical Research, 2004, 23(2): 192-200.
杜娟, 欧阳文言, 刘春琼, 吴波, 张娇, 史凯. 短周期高强度旅游活动对城市空气质量的影响[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2023, 18(1): 36. Juan DU, Wenyan OUYANG, Chunqiong LIU, Bo WU, Jiao ZHANG, Kai SHI. Influence of short-duration high-strength tourism activities on urban air quality[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2023, 18(1): 36.