激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61 (4): 0411001, 网络出版: 2024-02-22
基于改进PointNet++的Lidar点云分割模型
Lidar Point Cloud Segmentation Model Based on Improved PointNet++
点云分割 PointNet++ Lidar 特征偏差值 注意力机制 特征融合 残差结构 point cloud segmentation PointNet++ Lidar feature deviation value attention mechanism feature fusion residual structure
摘要
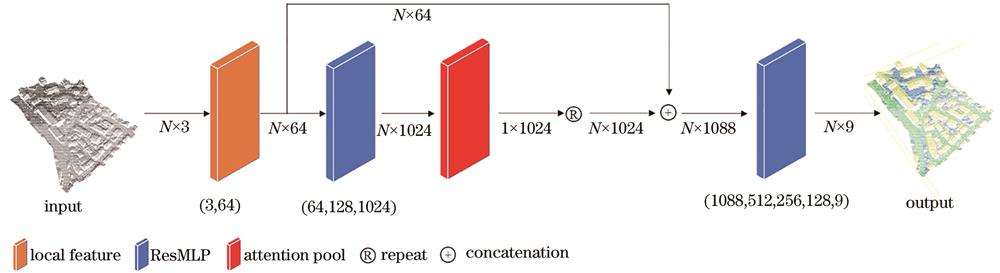
针对PointNet++在特征提取阶段未能深层挖掘Lidar点云的语义特征及其在特征聚合阶段采用最大池化聚合导致特征丢失,进而导致点云分割精度下降的问题,通过改进PointNet++的特征提取及特征聚合模块,提出一种基于特征偏差值和注意力机制的点云分割模型。首先,利用球形采样获取不同的局部邻域,并采用K最近邻(KNN)算法筛选邻域点,计算不同邻域的特征偏差值,获取点云的深层语义信息,增强模型对不同局部邻域的识别能力;其次,利用基于注意力机制的特征聚合模块代替PointNet++中的最大池化模块,在聚合特征阶段学习不同特征的权重,从而提高模型对不同结构信息的筛选能力,增强模型的分割性能;最后,为了进一步优化模型架构,在全连接层中加入残差模块,共享权重,避免参数冗余,提升模型性能。基于ISPRS提供的Vaihingen数据集与斯坦福的S3DIS数据集进行实验验证,实验结果表明,所提模型总体精度达到86.69%,较PointNet++提高了5.49个百分点,同时平均F1得分达到了73.97%,较PointNet++提高了8.30个百分点。在S3DIS数据集上的实验结果表明,与PointNet++、RandLA-Net和ConvPoint等主流模型相比,所提模型结果较PointNet++也有提升,即相较于PointNet++的分割结果,改进后的模型能够充分提取点云的语义特征,有效提高模型分割精度。
Abstract
It is known that PointNet++ cannot deeply explore the semantic features of Lidar point clouds during feature extraction and loses features due to the use of maximum pooling during feature aggregation. These problems result in a decrease in point cloud segmentation accuracy. To address these problems, this study proposes a point cloud segmentation model based on feature deviation values and attention mechanisms by improving the feature extraction and feature aggregation modules of PointNet++. First, different local neighborhoods are obtained using spherical sampling, and then neighborhood points are selected using the K-nearest neighbor (KNN) method to calculate the feature deviation values of different neighborhoods. This enhances the model's recognition ability for different local neighborhoods and obtains deep semantic information of the point cloud. Second, an attention-based feature aggregation module is used to replace the maximum pooling module in PointNet++ to learn the weights of different features during feature aggregation. This improves the model's ability to filter information from different structures and enhances the segmentation performance of the model. To further optimize the model architecture, a residual module is added to the fully connected layer to avoid parameter redundancy and improve the model performance through weight sharing. Experimental results are validated on the Vaihingen and S3DIS datasets provided by ISPRS and Stanford University, respectively, and are compared with the results of the experiments and mainstream models provided by ISPRS. The overall accuracy (OA) and average F1 score reach 86.69% and 73.97%, respectively, which are 5.49 percentage points and 8.30 percentage points higher than those of PointNet++, respectively. The experimental results on the S3DIS dataset are compared with those of PointNet++, RandLA-Net, and ConvPoint, and show a clear improvement over those of PointNet++. The experiments show that the improved model can fully extract the semantic features of point clouds and effectively improve the segmentation accuracy of the model as compared with the segmentation results of PointNet++.
张驰, 王志杰, 吴昊, 陈动. 基于改进PointNet++的Lidar点云分割模型[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(4): 0411001. Chi Zhang, Zhijie Wang, Hao Wu, Dong Chen. Lidar Point Cloud Segmentation Model Based on Improved PointNet++[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(4): 0411001.