基于BiT的早期胃癌内镜图像识别  下载: 765次特邀研究论文
下载: 765次特邀研究论文
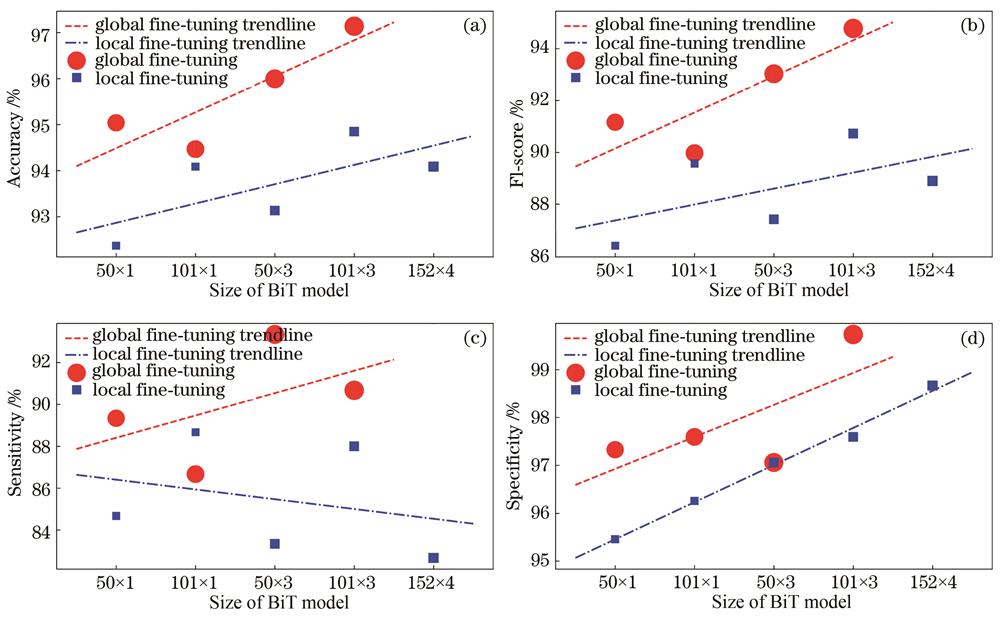
胃癌是我国主要的致死癌症之一,大部分患者发现时已处于进展期,如果能通过大规模筛查在早期发现胃癌,则可大大提高患者生存率。制约我国胃癌大规模筛查的障碍有二,其一是内镜的侵入性高,患者接受度低,其二是我国内镜医师相较于庞大的人口数量严重短缺。第一个障碍可通过胶囊内镜机器人得到缓解,第二个障碍则有望通过人工智能技术解决。将领域前沿的Big Transfer(BiT)技术迁移到一个小样本的早期胃癌内镜图像数据集上,构建了基于白光内镜图像的早期胃癌分类识别模型。在实现迁移过程中,对BiT的超参数调整规则进行了本地化适配,根据GPU内存的限制,选择了单批次数量;利用线性缩放规则,根据单批次数量动态调整了优化算法的初始学习率;固化小型目标数据集上的训练图像总量为256000张,在此基础上设置了迁移学习的其他超参数。对多个模型进行实验,所有模型的结构均为ResNet-v2,只是深度和宽度不同。最佳模型的深度为101,宽度为初始结构的3倍,在测试集上的准确率为97.14%,F1分值为94.77%,敏感度为90.67%,特异度为99.73%。此外,结果表明,单批次数量对模型训练效果的影响不具有显著的统计学差异。所提模型通过对BiT进行本地化适配,成功地在小规模内镜图像数据集上实现了较大模型的迁移,这将会促进大模型技术在内镜图像分析领域的应用,从而有助于早期胃癌大规模筛查的实现。
Gastric cancer is one of the significant lethal cancers in China. Most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage, and if gastric cancer can be detected at an early stage through large-scale screening, patient survival can be considerably improved. In China, there are two obstacles toward the large-scale screening of early gastric cancer. One is that endoscopy is overly invasive, resulting in low patient acceptance, and the other is that the number of endoscopists is too small compared with China's large population. A capsule endoscopic robot can alleviate the first obstacle, and the second obstacle is expected to be solved using artificial intelligence. We transferred the state-of-the-art Big Transfer (BiT) to a small dataset of early gastric cancer endoscopic images and built an early gastric cancer classification model based on white-light endoscopic images. We customized the BiT hyperparameter rules in transfer learning based on local situations. The batch size was selected according to the GPU memory limit, and based on the batch size, the linear scale rules were used to adjust the optimizer's initial learning rate dynamically. The total number of training images for the small dataset was set at 256000, on which other hyperparameters of the transfer learning were set. This study experimented with multiple models having the same structure of ResNet-v2 but different depths and widths. The best model has a depth of 101 and a width three times the original one. It has an accuracy of 97.14%, an F1 score of 94.77%, a sensitivity of 90.67%, and a specificity of 99.73% on the test set. Furthermore, the results show that the effect of batch size on the model training is statistically insignificant. This paper transferred a large model to a small dataset of endoscopic images with the BiT customization. This will promote the use of large-scale models in the field of endoscopic image analysis, which can help realize a large-scale screening of early gastric cancer.
李宏霄, 李姝, 石霞飞, 董晓曦, 金歌, 朱兰平, 李迎新, 阴慧娟. 基于BiT的早期胃癌内镜图像识别[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(6): 0617028. Hongxiao Li, Shu Li, Xiafei Shi, Xiaoxi Dong, Ge Jin, Lanping Zhu, Yingxin Li, Huijuan Yin. BiT-Based Early Gastric Cancer Classification Using Endoscopic Images[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(6): 0617028.