1 华南师范大学生物光子学研究院,激光生命科学教育部重点实验室暨激光生命科学研究所,广东 广州 510631
2 华南师范大学生物光子学研究院,广东省激光生命科学重点实验室,广东 广州 510631
3 广东省科学院生物与医学工程研究所,广东 广州 510316
识别动脉粥样硬化斑块的易损性是防治急性冠状动脉疾病的重要途径。纤维帽厚度、脂质核心大小、管腔狭窄程度和管腔的力学特性是评估斑块易损性的关键参数。然而,单一模态的血管内成像技术难以通过一次成像获取用于评估斑块易损性的全面信息。本团队通过复用光路和声路,将血管内超声成像(IVUS)和血管内光学相干层析成像(IVOCT)与血管内光声成像(IVPA)、光声弹性成像(IVPAE)有机结合到一起,开发了一种血管内光声-超声-光学相干层析-光声弹性四模态一体化成像探头及成像系统。该一体化成像探头的成像直径仅为0.97 mm,光学相干层析、光声、超声模态的横向分辨率分别为20.5、61.3、122.2 μm,纵向分辨率分别为15.8、57.4、72.5 μm。离体模拟样品和兔腹主动脉的在体成像实验验证了血管内四模态成像能够提供血管壁的宏观和微观结构信息,同时能够特异性识别脂质成分和反映脂质斑块的弹性力学信息。该一体化探头可一次性获取血管内斑块的多物理影像特性,有望为动脉粥样硬化斑块的深入理解和诊治提供新型的介入成像方法和工具。
医用光学 光声成像 超声成像 光学相干层析成像 光声弹性成像 血管内多模态成像

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Laser Life Science & Institute of Laser Life Science, College of Biophotonics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
2 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Laser Life Science, College of Biophotonics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
The previous methods to measure flow speed by photoacoustic microscopy solely focused on either the transverse or the axial flow component, which did not reflect absolute flow speed. Here, we present absolute flow speed maps by combining Doppler bandwidth broadening with volumetric photoacoustic microscopy. Photoacoustic Doppler bandwidth broadening and photoacoustic tomographic images were applied to measure the transverse flow component and the Doppler angle, respectively. Phantom experiments quantitatively demonstrated that ranges of 55° to 90° Doppler angle and 0.5 to 10 mm/s flow speed can be measured. This tomography-assisted method provides the foundation for further measurement in vivo.
medical optics and biotechnology photoacoustic imaging scanning microscopy flow speed Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(10): 101702

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Laser Life Science & Institute of Laser Life Science, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
2 College of Biophotonics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
In this study, the feasibility of visualization of human joints using photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is investigated. To verify this idea, the system of integrated optical fiber bundles and a custom-made flexible transducer is established, both of which give the advantage of morphological adaptation; therefore, the coupling section can be worn on human limbs. The imaging capacity of the flexible-transducer-based PAT system is validated by mapping the structures of the finger and the wrist joint. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time to achieve photoacoustic imaging of such large human wrist joints. The cross-sectional photoacoustic images of a healthy joint clearly exhibit the main internal structures, including the phalanx, tendons, and blood vessels, which are comparable with the corresponding images by 3.0 T magnetic resonance imaging. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed system holds promise for early diagnosis of joint disorders.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(9): 091701
华南师范大学生物光子学研究院激光生命科学研究所暨激光生命科学教育部重点实验室, 广东 广州 510631
医学成像在皮肤病学的病理生理相关性的临床诊断和评估中起着不可或缺的作用。然而, 现有的成像技术很难获得色素性皮肤病的黑色素空间分布和色素浓度。本文中我们提出了一种线性共焦扫描光声显微镜, 用于快速无损地获取色素性皮肤病的病理结构变化和色素异常部位的黑色素分布情况。通过样品试验和动物试验证明了该显微成像系统的可行性及成像能力, 并进一步对咖啡斑患者的正常表皮和病变表皮进行高分辨成像, 图像结果表明, 正常皮肤和咖啡斑皮肤之间黑色素分布及浓度存在着明显的差异。通过使用快速线性共焦扫描模式, 可以在1 s内快速获得检测部位的光声断层图像。线性共焦扫描光声显微镜也可以扩展到诊断其他皮肤性疾病, 是一种具有前景的皮肤病学成像技术。
色素性皮肤病 黑色素 光声显微镜 chromatodermatosis melanin photoacoustic microscopy

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 MOE Key Laboratory of Laser Life Science & Institute of Laser Life Science, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
2 College of Biophotonics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
Photoacoustic (PA) microscopy comes with high potential for human skin imaging, since it allows noninvasively high-resolution imaging of the natural hemoglobin at depths of several millimeters. Here, we developed a PA microscopy to achieve high-resolution, high-contrast, and large field of view imaging of skin. A three-dimensional (3D) depth-coding technology was used to encode the depth information in PA images, which is very intuitive for identifying the depth of blood vessels in a two-dimensional image, and the vascular structure can be analyzed at different depths. Imaging results demonstrate that the 3D depth-coded PA microscopy should be translated from the bench to the bedside.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 170.0110 Imaging systems 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(8): 081701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Remodeling and Function Research, Department of Cardiology, Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan 250012, China
2 MOE Key Laboratory of Laser Life Science and Institute of Laser Life Science, College of Biophotonics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510631, China
3 Department of Cardiology, The Juye Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Heze 274900, China
Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) has been used to characterize the spatial and quantitative features of lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques with high sensitivity and specificity. In this Letter, we first validate that the ultra-low temperature and formaldehyde treatment have no effect on photoacoustic characteristics of the artery samples. Comparative experiments between the PAI and histological results demonstrate that the ultra-low temperature or formaldehyde treatment has few effects on the PAI of the lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques; the lipid relative concentration and the lipid percentage by PAI hold high correlation with histology.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(3): 031702
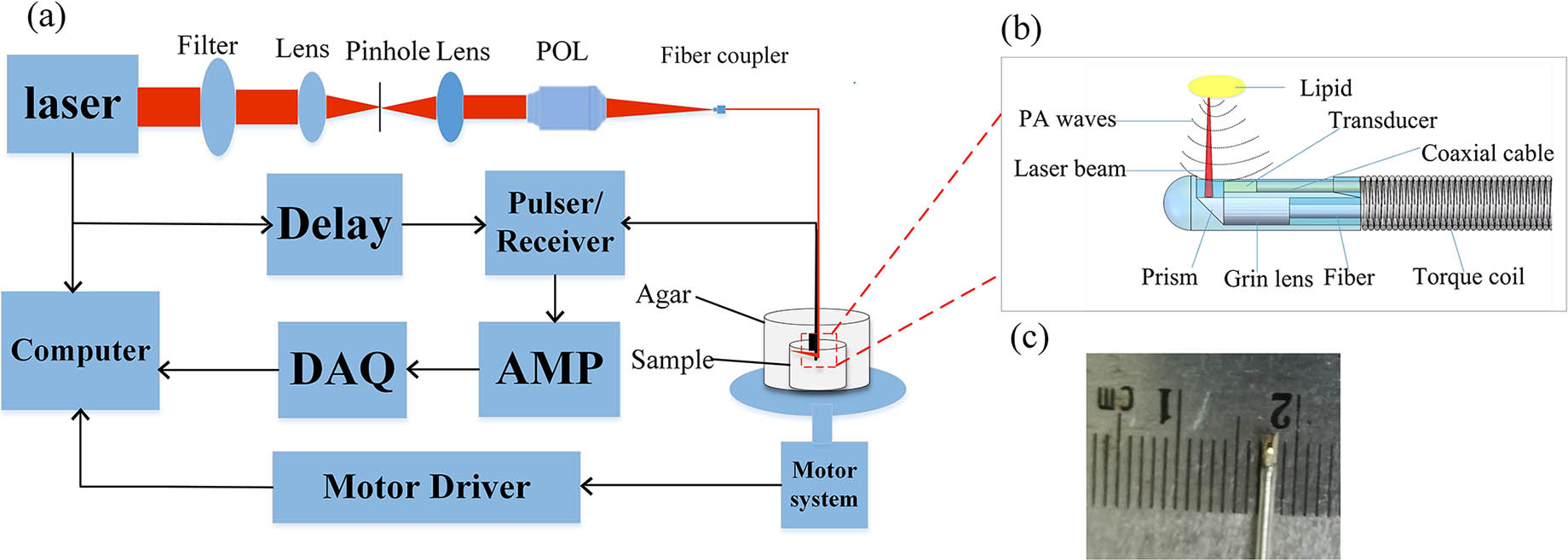
华南师范大学生物光子学研究院激光生命科学研究所暨激光生命科学教育部重点实验室, 广东 广州 510631
光声显微成像技术是近年发展迅速的一种基于光学吸收差异的成像技术,它继承了光学成像对比度高、超声成像深度深的优点,表现出纯光学显微成像技术所无法比拟的优越性。光声显微成像实现了从声学分辨率至光学分辨率的多尺度成像,发展出从单纯的吸收结构到功能的多参量成像、从依靠内源吸收体到外源对比剂的多对比度成像、从依赖超声换能器到全光学激发与探测、从单一吸收成像到与光学相干层析成像、荧光成像、双光子成像、二次谐波成像等结合形成多模态的光声显微成像技术。现已在血管生物学、肿瘤学、神经学、眼科学,以及皮肤学等生物医学领域得到应用。
医用光学 光声成像 光声显微成像 多尺度光声成像 多参量光声成像 多模态光声成像 生物医学
华南师范大学, 生物光子学研究院激光生命科学研究院, 暨激光生命科学教育部重点实验室, 广东 广州 510631
报道了一种利用直线电机连续-步进的扫描方式进行光声显微成像的系统, 该系统在运动时走弓字型路线, 其中直线电机在X轴方向上连续运动, 在Y轴方向上以步进的方式运动, 采集卡只在X轴电机运动的过程中连续采集。该成像系统较之前振镜扫描的方式扫描的范围更大, 可达到厘米尺度范围内的生物组织光声成像; 较之前的步进电机逐点扫描的方式扫描速度明显提高。同时本文采用电机带动光和超声换能器一同扫描的方式, 较光和超声换能器不动电机带动样品扫描的方式更灵活。另外利用包埋碳丝的模拟样品和在体小鼠耳朵血管来验证系统的成像能力。实验结果表明, 这种快速光声显微成像方法及其系统可以实现在体组织的高分辨率成像, 有望成为一种无创、实时的光声显微镜应用于生物医学当中。
连续-步进运动 快速光声成像 光声显微镜 continuous-stepping motion fast photoacoustic imaging photoacoustic microscope
华南师范大学生物光子学研究院激光生命科学研究所、暨激光生命科学教育部重点实验室, 广东 广州510631
光声成像突破了传统的光学成像和超声成像在生物组织成像领域的困境,该技术基于光声(Photoacoustic,PA)效应,脉冲激光激励下的生物组织产生超声信号,超声信号被接收后,通过反投影算法将其携带的时间信息和强度信息转化为能够反映生物组织吸收结构和分布的可视化图像.基于不同生物组织的光吸收差异,当激发光强度均匀且稳定时,光声成像反映的就是该物质对于该波长光的吸收特性.本文中,我们基于导管式的血管内光声断层扫描平台结合多波长激发的光声成像算法开发了基于光谱编码的血管内光声组分成像系统,实现了在离体血管斑块中脂质组分的定量成像,高分辨获得了脂质核心的大小形态和边界信息,表征了斑块内的脂质相对含量.
光谱编码 血管内光声成像 组分成像 spectrum encoding intravascular photoacoustic imaging component imaging





