中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,上海 201800
掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤在高峰值功率超快激光放大器中有着重要的应用价值,其研究得到了广泛关注。首先简要介绍了国内外掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤的研究进展,阐述了掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤的基本设计思路,对比说明了保偏型掺镱光子晶体光纤的设计制备方法。重点介绍了近十年来中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所在掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤方面的研究进展。包括掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤的纤芯折射率大小和均匀性控制、光子晶体光纤微结构控制等关键技术。采用自主研制的四种芯径为40~100 μm的掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤开展了皮秒脉冲激光放大实验。利用40 μm芯径的保偏掺镱光子晶体光纤实现了平均功率为100 W、光束质量因子(M2)小于1.4的稳定输出,偏振消光比为12 dB。利用100 μm芯径的保偏掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤实现了M2小于1.5的高光束质量脉冲放大。上述研究为掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤的国产化应用奠定了基础。
光纤光学 掺镱石英玻璃 大模场光子晶体光纤 皮秒脉冲激光放大 光纤激光
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光单元技术实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 国科大杭州高等研究院,浙江 杭州 310024
4 俄罗斯科学院光纤研究中心,莫斯科 119333,俄罗斯
中国激光
2023, 50(15): 1516001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光单元技术实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 国科大杭州高等研究院,浙江 杭州 310024
4 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所中国科学院空间激光信息传输与探测技术重点实验室,上海 201800
中国激光
2022, 49(22): 2216001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光单元技术实验室,上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学,北京 100049
3 中国科学院大学杭州高等研究院,浙江 杭州 310024
Nd3+ 900 nm激光可用于泵浦掺Yb3+激光材料和大气探测,其倍频产生的深蓝激光在面向水下通信、原子冷却、生物医学、激光存储、激光显示及激光加工等领域具有重大意义,但实现Nd3+ 900 nm激光必须要解决Nd3+ 1060 nm 跃迁竞争的问题。本文介绍了各类掺Nd3+激光材料900 nm激光的研究发展历程,并简单总结了抑制1060 nm激光的方法。结合本课题组研究工作,指出进一步提高Nd3+ 900 nm激光输出功率,关键是保证较低浓度猝灭几率并提高材料自身900 nm荧光分支比。通过向Nd3+石英玻璃中掺入非氧阴离子基团调节Nd3+微观配位环境,大大提高了Nd3+ 900 nm荧光分支比,将该玻璃拉制成芯包比为20/125 μm光纤,初步主振荡功率放大实验结果显示,该光纤对1060 nm放大的自发辐射具有很好的抑制效果,为实现Nd3+ 900 nm高功率激光输出提供了新的技术方案。
材料 Nd3+掺杂石英玻璃 900 nm激光 荧光分支比 光纤激光 微观配位环境 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(15): 1516004

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100039, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
Large-size co-doped silica glass with 5000 ppm and 50,000 ppm doping concentrations was prepared by the modified sol-gel method combined with high-temperature melting and molding technology. Electron probe micro-analyzer tests indicated that high doping homogeneity was achieved with this sample preparation method. The spectral properties of the ions were evaluated. -doped silica fiber (NDF) with a core-to-clad ratio of 20/125 μm was drawn from the preform with the co-doped silica glass as the core. In the laser oscillation experiment, a maximum output power of 14.6 W at 1.06 μm with a slope efficiency of 39.6% was obtained from the NDF pumped by a commercial 808 nm laser diode. To the best of our knowledge, this is the highest laser power reported for an NDF operated at 1060 nm and prepared by a non-chemical vapor deposition method. In the master oscillator power amplifier experiment, a maximum power of 16.6 W corresponding to a slope efficiency of 30.5% at 1061 nm was also demonstrated. The laser performance of the NDF exhibited the great advantages and potential of the modified sol-gel method in fabricating -doped silica glass for a new type of NDFs like large mode area fibers and fibers with large diameter ratio of core/cladding.
Nd3+-doped silica sol-gel doping homogeneity Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(9): 091601
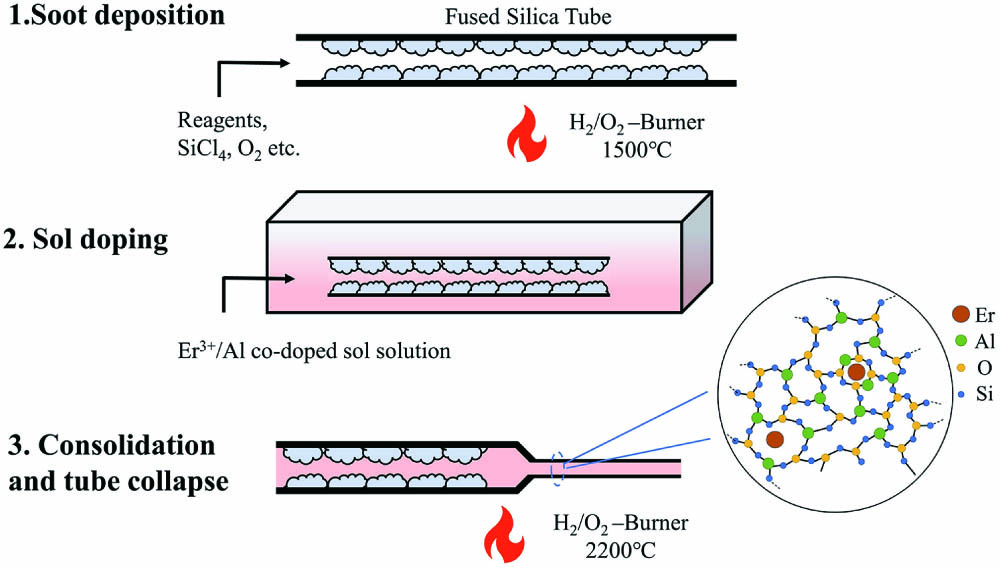
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Materials Science and Engineering, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
2 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser Materials, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
In this work, a heavily Er-doped fiber with an 8 µm core diameter and a numerical aperture of 0.13 was prepared by the modified chemical vapor deposition (MCVD) technique combined with the sol-gel method. The background loss and absorption coefficient at 1530 nm were measured to be 20 dB/km and 128 dB/m, respectively. Thanks to the sol-gel method, the fiber showed a good doping homogeneity, which was confirmed through unsaturable absorption measurement. The net gains of three 25, 45, and 75-cm-long fibers were measured in the range of 1520 to 1600 nm, and the highest gain reached above 23 dB at both 1530 and 1560 nm in 25 and 75-cm-long fibers, respectively. The short-cavity laser performance was measured using centimeter-scale fibers. The maximum output power of 12 mW was demonstrated in a 6.5-cm-long active fiber with a slope efficiency of 20.4%. Overall, the prepared heavily Er-doped silica fiber is a promising item to be applied in a high-repetition-rate or single-frequency fiber laser.
erbium-doped fiber short-cavity fiber laser sol-gel method Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(11): 110603
1 南京邮电大学电子与光学工程、 微电子学院, 江苏 南京 210023
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所高功率激光单元技术实验室, 上海 201800
采用溶胶-凝胶法结合纳米粉体高温烧结工艺制备了Yb-Al、Yb-Al-P和Yb-P三个体系共掺石英玻璃,系统探究了Al 3+和P 5+的含量变化对掺Yb 3+石英玻璃在1018 nm处吸收和荧光性能的影响规律。通过对比不同掺杂体系在1018 nm处的光谱性能发现,随着P 5+掺杂浓度的提高,1030 nm附近的荧光次峰蓝移至1018 nm附近,Yb-P掺杂石英玻璃系列样品在1018 nm处的归一化荧光强度明显优于其他系列。利用Raman光谱结合超低温电子顺磁共振(EPR, 4 K)从原子尺度上对Yb 3+的配位环境进行了精确解析。Al 3+和P 5+的引入使得Yb 3+的配位环境迥异,这与Al 3+、P 5+对Yb 3+在1018 nm处光谱性质的影响规律相符。
材料 掺Yb
3+石英玻璃 1018 nm同带泵浦 光谱性能 稀土离子局域环境 中国激光
2021, 48(11): 1103001
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,上海 201800
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,上海 201800;中国科学院大学 杭州高等研究院,浙江 杭州 310024
基于自制的掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤,探索出一种高效快速的光子晶体光纤端面处理工艺。使用二氧化碳激光熔接机对光子晶体光纤进行旋转加热处理,并配合大口径光纤切割刀对塌缩区域进行切割。通过对比光纤在不同激光加热功率和加热时间下的塌缩效果,确定了最佳的加热功率和时间。对端面处理后的光纤进行激光震荡实验,测试光纤的激光性能,与未进行端面处理时的激光实验结果相比较,端面塌缩处理没有对光纤的激光性能产生较大的影响。通过所述的实验方法,成功得到高质量光子晶体光纤塌缩端面,空气孔塌缩界面齐整,且没有对光纤本身的激光性能产生较大的影响。实验工艺周期短、成功率高,证明利用激光加热塌缩来处理光子晶体光纤端面是一种非常有效的方法,极大地拓展了光子晶体光纤的使用范围,具有很强的实用价值。
光子晶体光纤 大模场光纤 二氧化碳激光 光纤塌缩 photonic crystal fiber large mode area fiber carbon dioxide laser fiber collapse 红外与激光工程
2020, 49(12): 20201065
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
近年来,掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤由于在高峰值功率皮秒超快激光放大器方面的重要应用而受到广泛关注。简要分析了掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤的研制难点,介绍了国内外掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤的研究进展,以及应用于掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤制备的掺镱石英玻璃芯棒制备方法及其光学、光谱性能,重点介绍了中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所基于溶胶-凝胶工艺制备大直径、低数值孔径掺镱石英玻璃芯棒玻璃,以及大模场掺镱光子晶体光纤的制备及其用于皮秒脉冲激光放大的研究进展。最后对掺镱大模场光子晶体光纤的研发及应用进行了总结及展望。
光纤光学 掺镱石英玻璃 大模场面积光子晶体光纤 皮秒脉冲激光放大 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(17): 170602
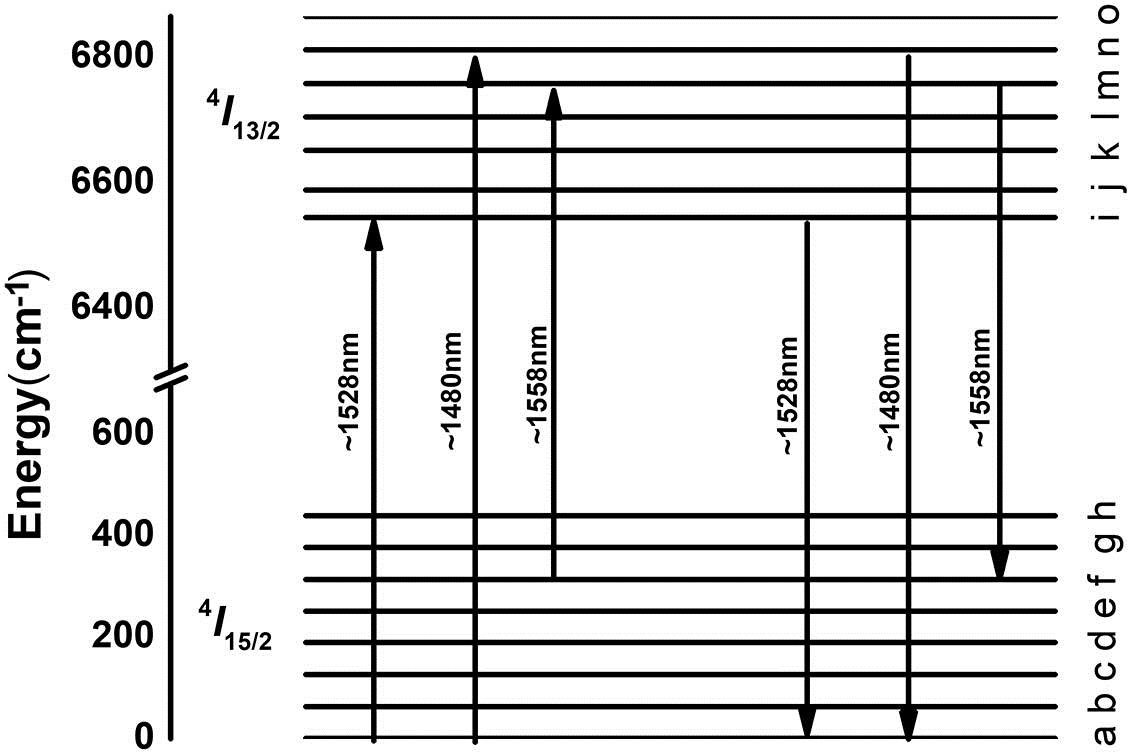
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
Using a heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber prepared by the sol-gel method combined with high temperature sintering, the temperature dependence of the spectrum around the 1.55 nm band and single-mode fiber laser properties were investigated, respectively. The absorption cross section increases 29.2% at ~1558 nm with the temperature increasing from 20°C to 140°C, while the emission cross section slightly increases 4.3%. In addition, the laser slope of the heavily erbium-doped aluminosilicate fiber at 1558 nm decreases 4.4% from 10.8% to 6.4% with the temperature increasing from 18°C to 440°C. Meanwhile, an experiment lasting 3 h proves that the fiber laser has excellent stability below 440°C.
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 060.2400 Fiber properties 120.6810 Thermal effects 140.3425 Laser stabilization Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 101401





