北京邮电大学 信息光子学与光通信全国重点实验室,北京 100876
无源光网络(PON)凭借其大带宽、低成本和抗电磁干扰等优势,被认为是下一代工业互联网的重要组网技术之一。然而,以“带宽提升”为主要技术发展思路的常规PON,其传输控制机制难以满足以“时间敏感”为特征的高品质工业业务传输需求,对常规PON的网络传输能力提出了重要挑战,迫使其融入新的特性,即确定性。文章以时分复用(TDM)-PON为主要研究对象,首先阐述了工业互联网的业务特征及传输需求,分析了工业互联场景下常规TDM-PON面临的两大技术挑战:一是传统带宽分配方案引起的时延不确定性;二是队列调度机制僵化引起的时延不确定性。围绕上述挑战,文章介绍了提升TDM-PON确定性网络传输能力的关键技术,如协作传输接口、单帧多突发和确定性带宽分配(DetBA)等。其次,文章介绍了一种基于网络演算的时延边界建模思路作为确定性工业PON系统设计与性能评估的理论模型。最后,文章从业务层、媒质接入控制(MAC)层、物理层及控制管理平面等多个角度探讨了确定性工业PON的潜在技术及发展方向。
工业无源光网络 确定性网络传输技术 确定性带宽分配 网络演算 industrial PON deterministic network transmission technology DetBA network calculus 光通信研究
2024, 50(1): 23016801

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, School of Information and Communication Engineering, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
This Letter proposes a model of indoor visible light communication (VLC) heterogeneous networks entirely based on LEDs with different specifications and applies non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) to it because of the narrow modulation bandwidth of LEDs. Moreover, a user-grouping scheme that is based on matching theory is proposed to improve the network achievable sum rate. Simulation results indicate that when each NOMA cluster contains 6 users, the proposed scheme has a 49.54% sum-rate enhancement compared with the traditional user-grouping scheme. As the number of users in each NOMA cluster increases, the proposed scheme performs better at the cost of computational complexity.
visible light communication non-orthogonal multiple access matching theory user grouping Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(6): 060602
北京邮电大学信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室, 北京 100876
高速宽带光网络是国家信息基础设施的重要组成部分, 其中的灵活控制技术是研究与实现的难点之一, 也是本领域重要的前沿技术之一。回顾了光网络灵活控制技术的主要特征与演进过程, 重点对三种网络形态的灵活控制技术(超大容量光联网、光载无线接入网、数据中心光网络)进行了分析, 包括核心需求、问题难点、基本架构、解决方案与系统应用等, 最后对未来发展愿景进行了展望。
光网络 灵活控制 超大容量 光载无线接入网 数据中心 optical networks flexible control technology high-capacity radio over fiber access networks datacenter

Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications (BUPT), Beijing 100876, China
To extensively deploy quantum key distribution (QKD) systems, copropagating with classical channels on the same fiber using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology becomes a critical issue. We propose a user-based channel-interleaving WDM scheme with unequal frequency spacing (UFS-iWDM) to reduce the impairment on the quantum channels induced by four-wave mixing (FWM), and theoretically analyze its impact on quantum bit error rate (QBER). Numerical simulation results show that a UFS-iWDM can significantly reduce the FWM noise and improve QBER compared with the corresponding WDM scheme with equal frequency spacing (EFS), especially in the case of nonzero dispersion shifted fiber.
270.5565 Quantum communications 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4510 Optical communications Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(6): 060602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
Visible light positioning (VLP) is an emerging candidate for indoor positioning, which can simultaneously meet the requirements for accuracy, cost, coverage area, and security. However, intercell interference caused by light intensity superposition limits the application of VLP. In this Letter, we propose a united block sequence mapping (UBSM)-based VLP that utilizes superposition to integrate the multidimensional information from dense small cells into 2D information. The experimental result shows that UBSM-based VLP can achieve an accuracy of 1.5 cm with a 0.4 m row spacing and 0.35 m column spacing of LED lights.
060.4510 Optical communications 200.2605 Free-space optical communication 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(7): 070601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications (IPOC), Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
2 Beijing University of Technology, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Future Internet Technology, Beijing 100124, China
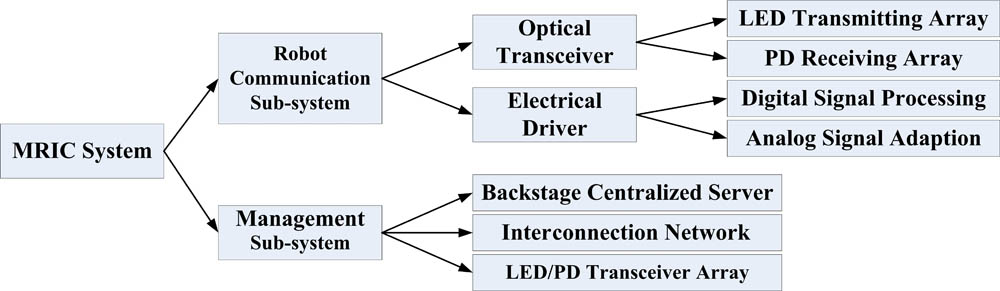
Multi-robot coordination (MRC) is a key challenge for complex artificial intelligence systems, and conventional wireless-communication-based MRC mechanisms that cannot be deployed in radio-frequency-limited environments. In this Letter, we present a promising solution that utilizes indoor omni-directional visible light communication (VLC) technology to realize efficient multi-robot intelligent coordination (MRIC). The specific design is presented along with the implemental details of a practical MRIC experimental platform. The experimental results show that a 50 Mb/s on-off-keying-based omni-directional VLC can be realized with an effective distance of 2.3 m and a bit error rate of <10 6 in the proposed MRIC platform.
230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 060.2605 Free-space optical communication Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(10): 102301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
In visible light communication, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is an effective approach to improve the system speed. However, the nonlinearity of the light-emitting diode (LED) suppresses the transmission performance. The low-frequency part of the transmitted signal from LED suffers more from nonlinearity. Therefore, a pre-equalization scheme which suppresses the low frequency part of the OFDM signal and enhances the high frequency part can decrease the impact of LED nonlinearity. The experimental results show that the bit-error rate performance is largely enhanced by the pre-compensation.
230.4320 Nonlinear optical devices 230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(7): 072302
1 北京邮电大学
2 信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室,北京 100876
在正交频分多址无源光网络上行传输中,不同光网络单元的上行信号如果采用相同波长的不同激光器将会产生光拍频噪声,使得光网络单元的无色性难以实现.本文以正交频分多址无源光网络为研究对象,通过对系统结构的研究和相关公式的推导,分析了信号上行传输中光拍频噪声的产生原因和避免方式.针对下行发送上行载波结合光线路终端相干接收的光拍频噪声避免方案进行了仿真研究.分析了系统的抗色散方案以及色散累积和训练序列长度对系统性能的影响,给出了优化的参数设置,为系统实际应用提供了理论参考.
光通信 无源光网络 仿真分析 正交频分多址无源光网络 光拍频噪声 物理层损伤 optical communication passive optical network orthogonal division multiple access pon optical beating interference physical layer impairments
北京邮电大学信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室, 北京 100876
随着光纤通信系统容量的增加和信道间隔的降低,非线性噪声必然成为限制光传输系统发展的重要因素。提出了一种比较准确的仿真模型用来估计把非线性噪声当作加性高斯处理的高斯噪声(GN)模型的适用范围,同时对该模型进行了大量的仿真验证,包括不同的光纤类型和不同的调制格式。仿真结果证明,GN模型的非线性噪声功率谱密度理论解析式在预色散的系统中是非常准确、可靠的。同时,表明在没有预色散的系统中,非线性噪声与调制格式有关,但是预色散能够消除调制格式对非线性噪声的影响。
非线性光学 相干通信 光纤非线性效应 克尔效应 光学学报
2014, 34(s2): s219003
北京邮电大学 信息与通信工程学院 信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室, 北京 100876
为了得到高性能的多载波光源,研究了射频信号中不同相位差对光多载波的影响.通过理论分析可得,随着相位差从90°降至0°,光多载波性能会逐渐变差,但是相位差偏与90°相差不大时,性能不会下降太多.实验中通过移相器改变相位差,使相位差为90°,45°,0°,得到循环前IQ调制器的输出光谱,并对比循环后光多载波性能.实验结果显示,相位差为90°时,循环前IQ调制器输出为较好的单边带光谱,循环后输出50条平坦稳定光多载波;相位差为45°时,光多载波质量变差;相位差为0°时,得不到光多载波.因此,射频信号相位差为90°时,光多载波的性能最佳,随着相位差变小,性能下降,但是相位差为45°时,产生的光多载波仍可应用于光通信.
光通信 多载波 循环移频 相偏 稳定平坦 Optical communication Multicarrier RFS Phase deviation Stability and flatness





