Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Key Laboratory for Biomedical Measurements and Ultrasound Imaging, National-Regional Key Technology Engineering Laboratory for Medical Ultrasound, School of Biomedical Engineering, Shenzhen University Medical School, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronic Information Science and Technology of Jiangxi Province, Nanchang Hangkong University, Nanchang 330063, China
3 College of Physics and Optoelectronics Engineering, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
4 Department of Bioengineering and COMSET, Clemson University, Clemson SC 29634, US
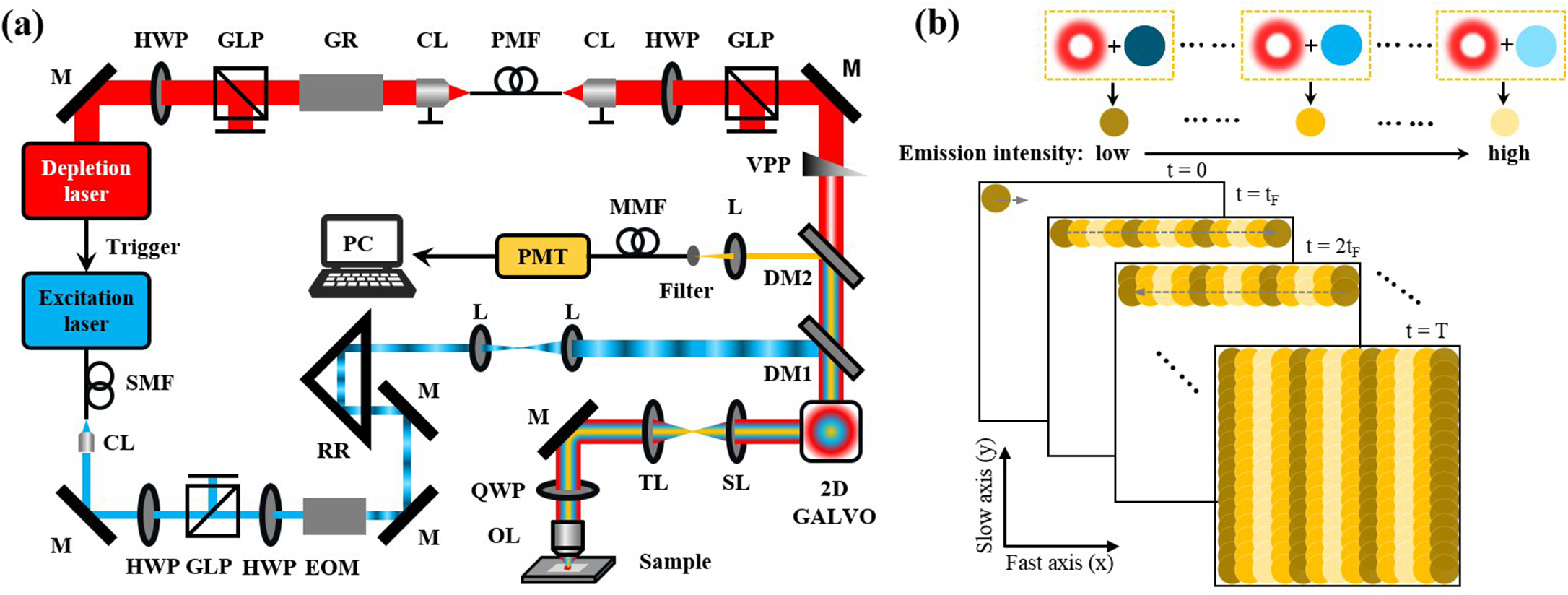
Wide-field linear structured illumination microscopy (LSIM) extends resolution beyond the diffraction limit by moving unresolvable high-frequency information into the passband of the microscopy in the form of moiré fringes. However, due to the diffraction limit, the spatial frequency of the structured illumination pattern cannot be larger than the microscopy cutoff frequency, which results in a twofold resolution improvement over wide-field microscopes. This Letter presents a novel approach in point-scanning LSIM, aimed at achieving higher-resolution improvement by combining stimulated emission depletion (STED) with point-scanning structured illumination microscopy (psSIM) (STED-psSIM). The according structured illumination pattern whose frequency exceeds the microscopy cutoff frequency is produced by scanning the focus of the sinusoidally modulated excitation beam of STED microscopy. The experimental results showed a 1.58-fold resolution improvement over conventional STED microscopy with the same depletion laser power.
stimulated emission depletion structured illumination microscopy superresolution microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031701
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,射频异质异构集成全国重点研究实验室,光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
面向生物粒子操控方法的研究,在生物医学和生命科学等领域具有重要意义。光镊操控具有无接触与高精度的特点,已被广泛应用于多个领域的研究中。然而,传统光镊的光热效应以及衍射极限都制约着光镊在生物医学领域的更广泛应用和发展。近十年来,研究者们将光热效应化劣势为优势,利用光与热的耦合效应实现了多种粒子的精确捕获及操控,即光致温度场光镊(OTFT)。由于此种新型光镊对光能的利用率极高,能量密度低于传统光镊近3个数量级,并可实现颗粒的大范围操控,极大地拓展了光镊可操控粒子的种类,已经成为纳米技术以及生命科学领域的重要研究工具。温度场光镊仍面临诸多问题,例如对于颗粒界面调控的依赖性以及三维捕获受限等,尤其是在生物光子学的研究中,还需要进一步发展和优化。本文对光致温度场光镊操控基本原理及其在生物医学中的应用两个方面进行了系统阐述,并对其今后的发展与挑战进行了展望。
光镊 光热镊 光流控 光热效应 微流控 生物传感器 光学学报
2023, 43(14): 1400001
深圳大学物理与光电工程学院, 光电子器件与系统教育部/广东省重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
二次谐波产生(SHG)成像技术是一种针对非中心对称生物组织的免标记成像技术,已经成为生命科学研究的重要手段。衍射极限使得SHG技术无法分辨衍射极限以下的精细结构。虽然超分辨显微技术取得了突破性进展,但是SHG的相干非线性过程限制了SHG超分辨显微技术的发展。提出了一种点扫描结构光照明SHG超分辨显微(SHG-psSIM)技术,实现了氧化锌颗粒和小鼠尾腱的超分辨SHG显微成像。在传统的SHG显微系统的激发光路中引入电光调制器,通过对激发光正弦调制产生点扫描结构照明图案。基于点扫描结构照明图案与样本结构相互作用产生的莫尔条纹效应,将原本不可探测的样本高频信息搬移到显微镜通频带内,并利用光电倍增管探测。最后,利用软件重构出超分辨率图像。对比传统SHG系统,SHG-psSIM分辨率提高了1.86倍。
显微 二次谐波产生 二次谐波产生显微 结构光照明显微 超分辨显微 光学学报
2022, 42(10): 1018001
1 深圳大学光电工程学院光电子器件与系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室深圳市传感器技术重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
2 深圳市进出口检验检疫局, 广东 深圳 350007
3 福建师范大学医学光电科学与技术教育部重点实验室福建省光子技术重点实验室, 福建 福州 350007
本文提出了基于光谱扫描技术的非机械扫描的表面等离子体共振(SPR)传感技术,采用白光为SPR激发光源,通过单色仪控制入射光的波长实现光谱寻址,在保证灵敏度和动态范围的同时,使系统在整个动态范围内具有较好的线性,简化了传感器结构.理论分析了光谱扫描SPR传感技术的灵敏度和动态范围,搭建了实验系统,并测量了不同浓度的酒精水混合溶液的SPR信号变化.结果表明:系统折射率测量范围为1.30-1.38,灵敏度可达3.1×105RIU.
表面等离子体共振 表面等离子体共振成像 传感器 波长寻址 SPR SPR imaging sensor wavelength addressing
深圳大学光电工程学院, 光电子器件与系统(教育部, 广东省)重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
在荧光显微镜中,微弱的荧光信号一般淹没于较强的激发光中,显微镜的成像质量在很大程度上取决于提取微弱荧光信号的能力。目前,荧光显微镜均根据荧光与激发光波长的差异,采用频率滤波法滤除激发光,实现图像增强。但该方法不仅对滤光片要求高,而且对荧光和激发光的波长有严重的依赖性。基于激发光与荧光在偏振态上的差异,提出了一种用于荧光显微镜的正交偏振滤波图像增强技术。研究表明,正交偏振滤波图像增强技术能够显著地提高成像质量,对光学元件性能参数的要求大幅度降低。丰富了从强激发光中提取弱荧光信号的技术手段,为今后解决波长可调谐的多光谱荧光显微镜、白光照明多光谱荧光显微镜等技术上的瓶颈提供了参考。
生物光学 荧光显微镜 图像增强 正交偏振 滤波 中国激光
2012, 39(10): 1004002
1 海军潜艇学院防化教研室, 山东 青岛 266042
2 深圳大学光电工程学院光电子器件与系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
3 克莱姆森大学生物工程学系, 美国南卡莱罗纳州克莱姆森 29634
发展了一种新型的多焦点多光子激发荧光显微技术,通过软件控制空间光调制器,在所需要的成像区域产生相应的激发光点阵,通过扫描入射角实现激发点阵快速并行扫描激发,通过CCD并行记录所产生的荧光信号,获得任意视场图像。分别实现了10×10和50×50点阵激发下的全视场双光子荧光图像,并且实现了同时多个区域寻址的多焦点激发成像。对比其他多焦点显微技术,该技术具有明显的灵活性,不但保持了多焦点激发的快速成像的优点,而且还增加了任意数量成像区域同时寻址和阵列点密度变化,所有这些变化只需要通过软件加载相应的相位图案给空间光调制器,而不需要任何硬件更改。
显微 多焦点 多光子 空间光调制器 光学学报
2012, 32(10): 1018001
深圳大学光电工程学院光电子器件与系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
提出一种利用高斯函数来表征基于扫描相机的时域荧光测量系统脉冲响应的方法,建立了数学模型,用以描述系统所采集到的时域荧光衰减曲线。用高斯函数对所建立的时域荧光寿命测量系统的脉冲响应函数进行拟合处理,拟合优度达到0.995以上;利用所建立的数学模型对标准荧光染料玫瑰红的测量数据进行拟合处理,拟合优度均值达到0.996以上,荧光寿命标准差仅有1.7 ps。实验表明,利用所建立的数学模型处理基于扫描相机的时域荧光寿命测量数据,具有良好的稳定性和准确性。这种方法提高了系统测量的精度,简化了解卷积运算,只要用多个高斯函数描述脉冲响应函数就可以用于其他时域荧光寿命分析及荧光寿命成像技术中。
测量 扫描相机 荧光寿命 最小二乘法 数据拟合 中国激光
2011, 38(s1): s108001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Institute of Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
We present a miniature fluorescence sectioning microscope which uses a diode-pumped solid-state (DPSS) laser as the light source and a fast translating diffuser to produce dynamically changing speckle patterns onto the back aperture of the objective to illuminate the sample. Optical sectioning, which originates from the statistical characteristics of laser speckles, is obtained by calculating the contrast of a series of fluorescence images. High contrast fluorescence sectioning images of bovine pulmonary artery endothelial (BPAE) cells are obtained. The image quality is similar to that of the images acquired by standard laser scanning confocal microscope (LSCM). Compared with LSCM, the laser speckle fluorescence microscope (LSFM) presented in this letter has many advantages, such as simple configurations, low cost, compact, and easy to operate, which makes it possible to have wide spread applications in biomedicine.
激光散斑 荧光层析 细胞成像 170.1790 Confocal microscopy 180.1790 Confocal microscopy 180.2520 Fluorescence microscopy 180.6900 Three-dimensional microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(10): 944
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Institute of Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
Streak camera has high temporal resolution and high sensitivity, and is a powerful tool in biomedical study to measure fluorescence lifetime and perform fluorescence lifetime imaging. However, nonuniformity of the gain in the streak tube and nonlinearity of the sweeping speed limit the precision of fluorescence lifetime measurement, particularly when fluorescence lifetimes are short. We have constructed a twophoton excitation fluorescence lifetime measurement system that is based on a synchroscan streak camera and have developed accordingly a method to correct the effect of gain nonuniformity and nonlinearity of sweeping speed on the measurement precision. A continuous-wave laser of high stability is used to calibrate the gain of the streak camera, and a Fabry-Perot etalon is used to calibrate the nonlinearity of the sweeping speed. Fitting algorithms are used to correct the gain of the streak camera and nonlinearity of the sweeping speed respectively, which significantly improves the measurement precision of the system, as characterized through the fluorescence lifetime of the short-lived fluorescence dye, Rose Bengal. Experimental results show that the measurement fluctuation of the lifetime has been improved from more than 10% to 2% after correcting the effects of gain nonuniformity and sweeping speed nonlinearity.
荧光寿命成像 扫描相机 扫描速度 非线性 非均匀性 170.0110 Imaging systems 170.0180 Microscopy 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging 170.6920 Time-resolved imaging 320.7080 Ultrafast devices Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(10): 934
1 西安工业大学 光电工程学院,陕西 西安 710032
2 深圳大学 光电子学研究所光电子器件与系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室,广东 深圳 518060
提出一种具有快速层析成像以及光谱分辨功能的多光子激发荧光显微技术。采用微透镜阵列产生激发光点阵,利用线扫描方式扫描阵列点,对样品进行多线并行多光子激发,利用棱镜色散荧光信号,同时,利用面阵CCD并行记录光谱分辨的多线荧光信号。采用4×4的微透镜阵列,仅需要记录128幅图像,即可重构512 pixel×512 pixel的光谱分辨荧光显微图像。对多色荧光珠、染色铃兰根茎以及花粉颗粒等样品进行实验,得到样品的双光子激发荧光光谱分辨图像,光谱测量范围为450-700 nm,光谱分辨率为3 nm。
生物光子学 多光子激发 荧光光谱 荧光显微 多焦点多光子显微





