
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Interface Science and Engineering in Advanced Materials, Ministry of Education, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, China
2 State Key Laboratory for Artificial Microstructure & Mesoscopic Physics, School of Physics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Quantum Matter, Beijing 100871, China
Solid-state sources of single-photon emitters are highly desired for scalable quantum photonic applications, such as quantum communication, optical quantum information processing, and metrology. In the past year, great strides have been made in the characterization of single defects in wide-bandgap materials, such as silicon carbide and diamond, as well as single molecules, quantum dots, and carbon nanotubes. More recently, single-photon emitters in layered van der Waals materials attracted tremendous attention, because the two-dimensional (2D) lattice allows for high photon extraction efficiency and easy integration into photonic circuits. In this review, we discuss recent advances in mastering single-photon emitters in 2D materials, electrical generation pathways, detuning, and resonator coupling towards use as quantum light sources. Finally, we discuss the remaining challenges and the outlooks for layered material-based quantum photonic sources.
270.5565 Quantum communications 270.5585 Quantum information and processing 160.2100 Electro-optical materials 160.2220 Defect-center materials 160.4760 Optical properties Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(2): 020011
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Information and Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
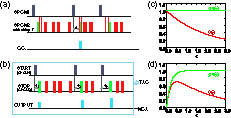
The measurement of the second-order degree of coherence [g(2)(τ)] is one of the important methods used to study the dynamical evolution of photon-matter interaction systems. Here, we use a nitrogen-vacancy center in a diamond to compare the measurement of g(2)(τ) with two methods. One is the prototype measurement process with a tunable delay. The other is a start-stop process based on the time-to-amplitude conversion (TAC) and multichannel analyzer (MCA) system, which is usually applied to achieve efficient measurements. The divergence in the measurement results is observed when the delay time is comparable with the mean interval time between two neighboring detected photons. Moreover, a correction function is presented to correct the results from the TAC-MCA system to the genuine g(2)(τ). Such a correction method will provide a way to study the dynamics in photonic systems for quantum information techniques.
160.2220 Defect-center materials 270.5290 Photon statistics Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(7): 072701

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 China MOE Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro-structured Materials, Institute of Precision Optical Engineering, School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
2 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049, China
We report the upconversion luminescence of lithium fluoride single crystals excited by an infrared femtosecond laser at room temperature. The luminescence spectra demonstrate that upconversion luminescence originates from the color center of F3+. The dependence of fluorescence intensity on pump power reveals that a two-photon excitation process dominates the conversion of infrared radiation into visible emission. Simultaneous absorption of two infrared photons is suggested to produce the F3+ center population, which leads to the characteristic visible emission. The results are on the reveal and evaluation of the simultaneous two-photon absorption on the green upconversion process.
320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 300.6410 Spectroscopy, multiphoton 190.7220 Upconversion 160.2220 Defect-center materials Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(8): 083201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Material Science and Technology for High Power Lasers, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
The growth of a Mn-doped LiAlO2 single crystal by the Czochralski (CZ) method and the characterization of its spectroscopy and thermoluminescence (TL) are presented. The X-ray rocking curve and chemical etching analysis show that the as-grown crystal has good crystallinity. The full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the LiAlO2 (200) \omega rocking curve is 23.2 arcsec and the etching pits density of the (100) plane is (1.6–4.0)×104 cm-2. The transmission spectrum indicates that the crystal is highly transparent in the 200–1500-nm wavelength range. The emission spectrum of the crystal consists of a peak around 579 nm when excited with 428-nm light. The TL spectra show that the LiAlO2:Mn crystal has glow peaks at 150 and 172 ℃. The change of TL characteristics of the crystal before and after thermal annealing in the air is discussed, and the effect of annealing and irradiation on the evolution of defect types is analyzed.
LiAlO2:Mn晶体 提拉法 结晶质量 光谱 热释光 160.2220 Defect-center materials 160.6990 Transition-metal-doped materials 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 300.6550 Spectroscopy, visible Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(4): 414
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Science, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
2 Shanghai Key Laboratory of Contemporary Optics System, Shanghai 200093, China
The electronic structures and optical properties of both the perfect CsI crystal and the crystal containing a pair of V1-Cs-V1+I are calculated using CASTEP code with the lattice structure optimized. The calculated results indicate that the optical symmetry of the CsI crystal coincides with the lattice structure geometry of the CsI crystal. The absorption spectrum of the CsI crystal containing a pair of V1-Cs-V1+I also does not occur in the visible and near-ultraviolet range. It reveals that the existence of the pair of V1-Cs-V1+I in CsI crystal has no visible effects on the optical properties of the CsI crystal.
CsI晶体 电子结构 光学性质 V1-Cs-V1+I缺陷对 160.4670 Optical materials 160.2220 Defect-center materials 160.4760 Optical properties Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(1): 74





