1 1.中国科学院大学, 北京100049
2 2.中国科学院 上海硅酸盐研究所, 上海200050
3 3.中国科学院 上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
极紫外(Extreme ultra-violet, EUV)光刻机光源主要采用激光产生等离子体技术, 用高功率激光轰击锡液滴靶产生13.5 nm波长的EUV光。其中, 基于逆压电效应的压电式高温锡液滴喷射元件是获取高重频高温锡液滴靶的关键部件。本项工作突破了耐250 ℃高温微细压电陶瓷管的组成设计和精细制备, 以及高温锡液滴喷射元件的结构设计和封装等关键技术, 成功研制了压电式高温液滴喷射元件。并通过自主搭建高温锡液滴靶光学检测平台, 基于此高温液滴喷射元件实现了重复频率20 kHz, 直径~100 μm的高温锡液滴靶的稳定输出。
极紫外光刻 微细压电陶瓷管 高温液滴发生器 高温压电陶瓷 EUV lithography micro piezoelectric ceramic tube piezoelectric high-temperature nozzle high- temperature piezoelectric ceramic
1 上海大学微电子学院,上海 200072
2 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所薄膜光学实验室,上海 201800
3 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所强激光材料重点实验室,上海 201800
自支撑薄膜滤片是极紫外波段重要的透射式光学元件。为获得13.5 nm极紫外高透射率滤片,本文选用硅(Si)作为膜层材料,通过脉冲直流磁控溅射在可溶性衬底沉积厚度为50 nm的Si单层膜,并成功制备了自支撑Si薄膜滤片样品。利用X射线反射、扫描电镜、同步辐射装置等测试手段分别对样品膜厚、形貌以及光学性能进行了表征,结果表明,50 nm厚的Si滤片在13.5 nm处透射率达到86.02%。进一步通过检测样品组分,结合IMD软件计算并分析了滤片氧化程度,解释了其在12.5~20 nm波段理论透射率与测量值之间存在差异的原因。该研究成果将极大地拓宽此类高透射率Si滤片在极紫外光学工程领域的应用前景。
极紫外波段 高透射率 自支撑滤片 硅 薄膜 氧化 光学学报
2023, 43(19): 1936001
北京理工大学光电学院光电成像技术与系统教育部重点实验室,北京 100081
极紫外光刻曝光光学系统是极紫外光刻机的核心部件,其设计直接影响极紫外光刻机的性能。极紫外光刻机曝光系统的设计难度大、研究周期长,国外极紫外光刻机产品已经用于高端芯片的制造,但国外对中国禁运相关产品。国内极紫外光刻机曝光系统的设计和研发始于2002年。国内相关领域的研究主要聚焦在极紫外光刻机曝光光学系统的光学设计、像差检测、公差分析、热变形分析等。结合国内外极紫外光刻机曝光光学系统设计研究的历史和现状,较为系统地综述了极紫外光刻投影物镜和照明系统的设计研究与进展,包括:极紫外光刻机投影物镜系统及其设计方法、极紫外光刻照明系统及其设计方法、极紫外光刻曝光光学系统的公差分析、热变形及其对成像性能的影响研究,这为我国从事极紫外光刻机研制、曝光系统光学设计与加工的学者、工程师等提供了极紫外光刻机曝光系统设计研究的历史、现状和未来趋势的相关信息,助力我国极紫外光刻机的设计和研制。
极紫外光刻 光刻机曝光系统 物镜系统 照明系统 光学设计 光学学报
2023, 43(15): 1522002
1 中国科学院 长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,吉林长春3003
2 中国科学院大学,北京100190
3 上海卫星工程研究所,上海200240
为了预警空间天气,需对日地空间物理过程进行监测,极紫外(Extreme Ultraviolet, EUV)滤光片是极紫外成像仪其中的重要组成部分,用来去除太阳辐射光谱中的非工作波段的辐射。为了优化EUV滤光片在17.1 nm波长处的透过率,本文基于比尔-朗伯定律通过理论计算和软件模拟确定17.1 nm EUV滤光片的材料及厚度。首先,采用真空热蒸发的方式在熔石英基底沉积脱膜层和金属薄膜,成功制备了以镍网为支撑的EUV滤光片。经测试,滤光片在17.1 nm处的透过率约为43.81%,表面光滑平整且无明显针孔。接下来为了说明氧化层对透过率的影响,使用椭圆偏振光谱仪测量滤光膜样品,得到放置不同时间的氧化层膜厚,并测得粗糙度来优化模拟滤光片透过率。利用IMD拟合样品氧化层厚度及粗糙度,调整层厚达到与实际测量值最为接近的曲线。实验结果表明滤光片透过率的模拟值与测量值绝对误差约1%,符合良好。本文为17.1 nm EUV滤光片提供了制备方法以及优化思路,在空间探测领域有重要应用价值。
金属薄膜 滤光片 栅网支撑 极紫外 氧化层 metal thin-film filter mesh support Extreme Ultraviolet(EUV) oxide layer
Wuhan National Research Center for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
Frontiers of Optoelectronics
2021, 14(3): 352–359
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, Shanghai Advanced Research Institute, CAS, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
2 Shanghai Institute of Applied Physical, CAS, Shanghai, People’s Republic of China
This paper introduces the recent progress in methodologies and their related applications based on the soft x-ray interference lithography beamline in the Shanghai synchrotron radiation facility. Dual-beam, multibeam interference lithography and Talbot lithography have been adopted as basic methods in the beamline. To improve the experimental performance, a precise real-time vibration evaluation system has been established; and the lithography stability has been greatly improved. In order to meet the demands for higher resolution and practical application, novel experimental methods have been developed, such as high-order diffraction interference exposure, high-aspect-ratio and large-area stitching exposure, and parallel direct writing achromatic Talbot lithography. As of now, a 25 nm half-pitch pattern has been obtained; and a cm2 exposure area has been achieved in practical samples. The above methods have been applied to extreme ultraviolet photoresist evaluation, photonic crystal and surface plasmonic effect research, and so on.
soft x-ray EUV interference lithography International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing
2020, 2(1): 012005
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 RIKEN Center for Advanced Photonics, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako Saitama 351-0198, Japan
2 Center for EUV Lithography, Laboratory of Advanced Science and Technology for Industry, University of Hyogo, Kamigori, Hyogo 678-1205, Japan
In this review, we describe our research on the development of the 13.5 nm coherent microscope using high-order harmonics for the mask inspection of extreme ultraviolet (EUV) lithography. EUV lithography is a game-changing piece of technology for high-volume manufacturing of commercial semiconductors. Many top manufacturers apply EUV technology for fabricating the most critical layers of 7 nm chips. Fabrication and inspection of defect-free masks, however, still remain critical issues in EUV technology. Thus, in our pursuit for a resolution, we have developed the coherent EUV scatterometry microscope (CSM) system with a synchrotron radiation (SR) source to establish the actinic metrology, along with inspection algorithms. The intensity and phase images of patterned EUV masks were reconstructed from diffraction patterns using ptychography algorithms. To expedite the practical application of the CSM, we have also developed a standalone CSM, based on high-order harmonic generation, as an alternative to the SR-CSM. Since the application of a coherent 13.5 nm harmonic enabled the production of a high contrast diffraction pattern, diffraction patterns of sub-100 ns size defects in a 2D periodic pattern mask could be observed. Reconstruction of intensity and phase images from diffraction patterns were also performed for a periodic line-and-space structure, an aperiodic angle edge structure, as well as a cross pattern in an EUV mask.
high-order harmonics coherent EUV light EUV lithography coherent EUV scatterometry microscope synchrotron radiation EUV mask inspection International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing
2019, 1(3): 032001
1 中国科学院技术生物与农业工程研究所, 安徽 合肥 230026
2 中国科学院大学合肥物质科学研究院, 安徽 合肥 230026
3 中国科学院等离子体物理研究所, 安徽 合肥 230026
4 深圳大学光电工程学院, 广东 深圳 518060
5 光电子器件系统(教育部/广东省)重点实验室, 广东 深圳 518060
6 中国科学技术大学研究生院科学岛分院, 安徽 合肥 230026
介绍了东方超环(experimental advanced supereonducting tokamak, EAST)托卡马克上的两套快速极紫外(EUV)光谱仪系统波长的原位标定方法、 结果及其应用。 这两套谱仪均为掠入射平场谱仪, 时间分辨均为5 ms·frame-1。 两套谱仪分别工作在20~500和10~130 的波段范围, 由步进电机控制探测器在焦平面上移动实现整个观测波段上的波长扫描。 利用这两套谱仪系统观测极紫外波段光谱, 计算EAST中低-高Z杂质离子特征线辐射强度随时间的演化, 监测和研究等离子体中杂质的行为。 高Z杂质尤其是钨、 钼等金属元素, 发出的EUV波段光谱的构成非常复杂, 准确识谱对谱仪精确的波长测量能力以及谱分辨能力要求很高, 因此精确的波长标定是识别钨、 钼等高Z杂质谱线以及研究它们行为的最关键的技术之一。 利用EAST等离子体中类氢到类铍的低、 中Z杂质的特征谱线以及它们的二阶甚至三阶谱线, 结合谱仪系统的色散能力, 对这两套快速极紫外光谱仪的波长进行了精确的原位标定。 用于波长标定的杂质谱线有O Ⅷ 18.97 , O Ⅶ 21.60 , C Ⅵ 33.73 , Li Ⅲ 113.9 , Li Ⅲ 135.0 , Li Ⅱ 199.28 , Ar ⅩⅤ 221.15 , He Ⅱ 256.317 , He Ⅱ 303.78 , Ar ⅩⅥ 353.853 及C Ⅳ 384.174 等。 利用波长标定的结果对观测到的EUV光谱进行谱线识别, 两套谱仪观测到的绝大多数谱线波长与美国技术标准局(National Institute of Standards and Technology, NIST)数据库的标准波长相差分别小于0.08和0.03 。 开发了谱仪波长原位标定程序模块, 将这个模块内嵌到谱仪数据实时上传的交互式软件中, 实现了全谱数据以及特征谱线强度随时间演化数据的实时处理和上传。 同时利用开发的全谱分析交互式软件以及EAST上的数据查看软件, 最终实现了快速EUV谱仪自采数据的准实时分析、 读取和查看。
EAST托卡马克 极紫外波段(EUV)光谱仪 波长标定 钨光谱 EAST Extreme Ultraviolet (EUV) spectrometer Wavelength calibration Tungsten spectra 光谱学与光谱分析
2019, 39(8): 2645
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
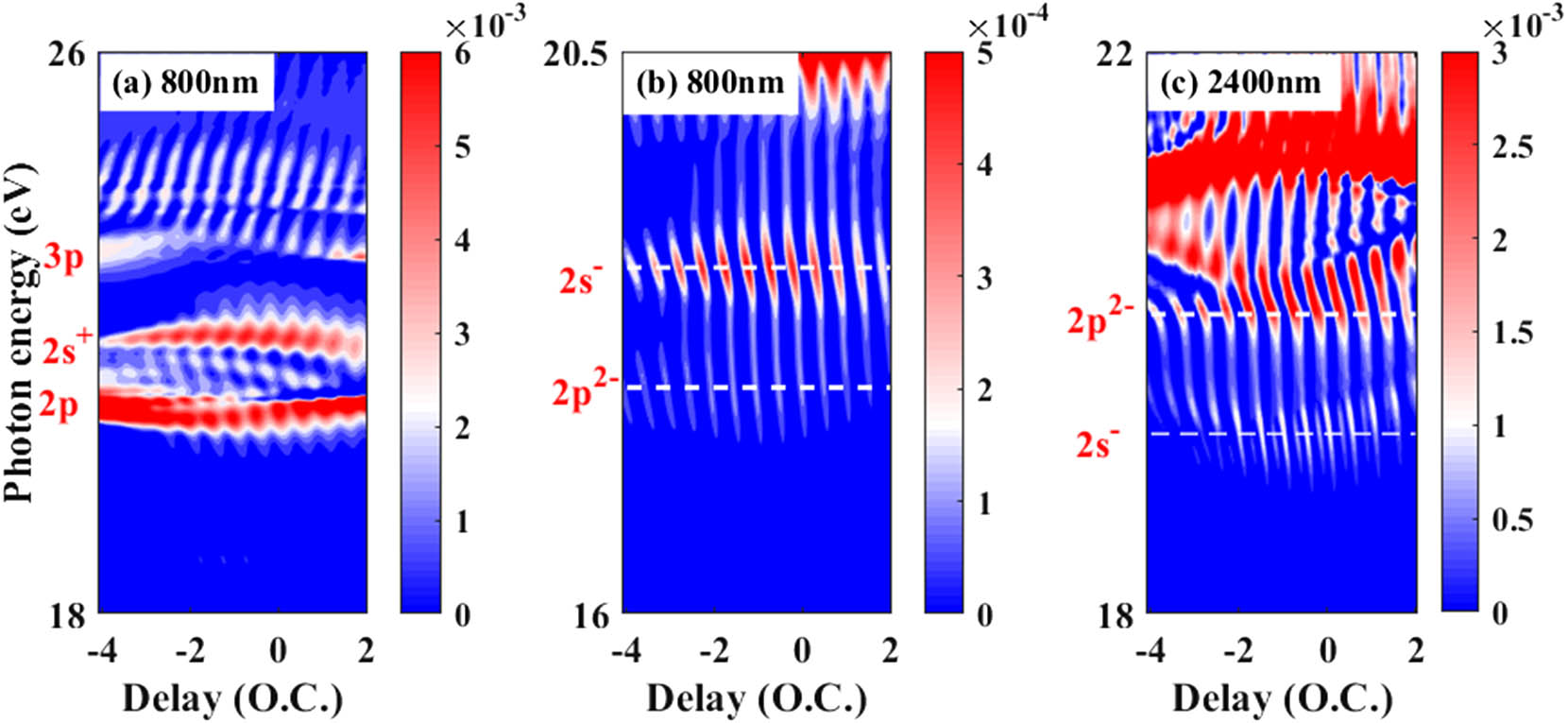
We theoretically investigate the delay-dependent attosecond transient absorption spectra in the helium atom dressed by an infrared laser pulse in the wavelength range of 800–2400 nm. By numerically solving the three-dimensional time-dependent Schr dinger equation, we find that the absorption spectrogram exhibits a multiple-fringe structure for using the mid-infrared dressing pulse. The quantitative calculation of the transition matrix between different Floquet states provides direct evidence on the origin of the multiple-fringe structure. Our result shows that the wavelength of the dressing pulse is an important parameter and the unique feature of attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy can be induced in the mid-infrared regime.
260.3090 Infrared, far 300.1030 Absorption 340.7480 X-rays, soft x-rays, extreme ultraviolet (EUV) Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 082601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 The Institute for Solid State Physics, The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba 277-8581, Japan
2 Current affiliation: School of Information Science and Engineering, Shandong University, Qingdao 266237, China
A monolithic lens-window-prism (LWP) device, made of lithium fluoride (LiF) or magnesium fluoride (MgF2), was proposed. When either of the devices was fixed onto one end of a gas cell filled with Xe, it becomes a “wedge-crystal”-like device and was used to convert a 1 MHz femtosecond 347 nm laser to its third harmonic radiation at 10.7 eV. This led to an improved beam profile and a more compact and less lossy configuration. A stable output power of ~11 μW was demonstrated for 2 h using LiF-LWP. In addition, MgF2-LWP was also verified for its practicability at 10.7 eV.
140.7240 UV, EUV, and X-ray lasers 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 320.7090 Ultrafast lasers Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 051406





