
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Amity School of Engineering & Technology, Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India
2 Computational Optics Research Group, Advanced Institute of Materials Science, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
3 Faculty of Applied Sciences, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
4 Division of Computational Physics, Institute for Computational Science, Ton Duc Thang University, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam
5 Amity School of Applied Sciences, Amity University Rajasthan, Jaipur, India
A micro stereo sensor system is proposed for human sensors, where eyes, ears, tongue, nose, body, and brain are applied by six panda rings embedded in a Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI). The input power is applied to the upper branch of MZI and propagates within the system. The six antennas (sensors) are formed by the whispering gallery modes of the panda rings. The space–time modulation signal is applied to the MZI lower branch. The modulated stereo signals can be configured as the plasmon (electron) spin orientations, which can be identified and applied for quantum codes and quantum consciousness.
micro-optical devices electro-optical devices integrated optics devices Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(10): 101301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Space Utilization, Technology and Engineering Center for Space Utilization, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100094, China
2 AVIC Hisense Photoelectric Technology Co., Ltd., Qingdao 266100, China
3 Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, IPOC, Beijing 100876, China
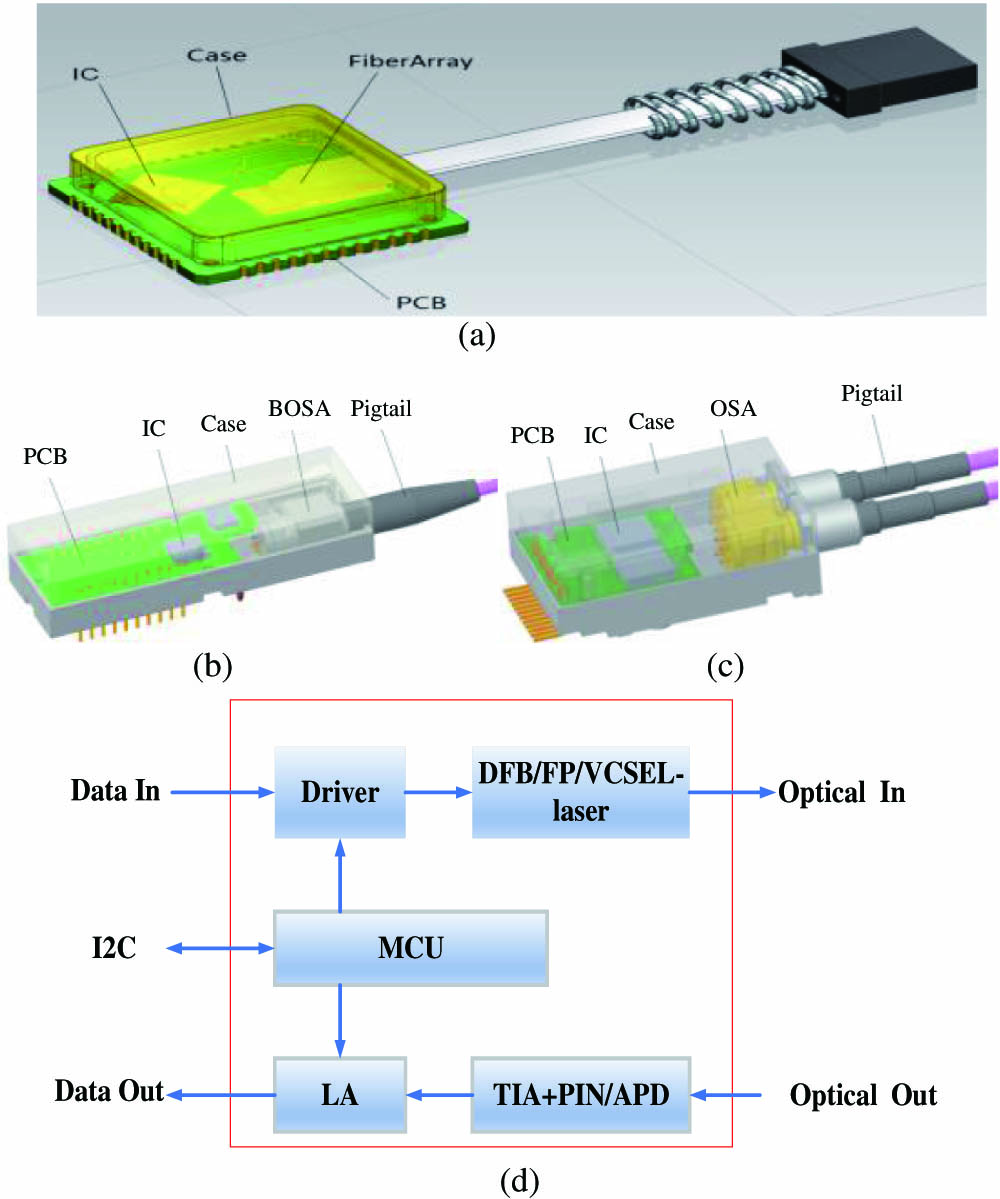
In our Letter, we selected several commercial optical transceivers, which consist of single-channel transceiver modules, parallel transmitting and receiving modules, and Ethernet passive optical network (EPON) optical line terminal (OLT) and optical network unit (ONU) modules, to do the total ionizing dose (TID) testing via the gamma-ray radiation method. The changing of current and receiver sensitivity of optical transceivers is discussed and analyzed. Based on the TID testing exposed to a TID of 50 krad (Si) at a dose rate of about 0.1 rad (Si)/s, the performance of single-channel transceivers and parallel receiving modules has not changed after 50 krad (Si) exposure, the parallel transmitting and EPON ONU modules have not worked after 40 krad (Si) and 47 krad (Si) exposure, the EPON OLT module has bit error in the process of irradiation, and it can work well after annealing; the reason for the error of OLT is analyzed. Finally, based on the theoretical analysis and testing results, this Letter provides several design suggestions to improve the reliability for optical transceivers, which can be referenced by satellite system designation for various space missions.
230.2090 Electro-optical devices 350.5610 Radiation 060.4510 Optical communications 000.2658 Fundamental tests Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(5): 052302
商继芳 1,2,3,*孙军 1,2,3李清连 1,2,3吴婧 1,2,3[ ... ]许京军 2,3
1 南开大学 物理科学学院, 天津 300071
2 南开大学 教育部弱光非线性光子学重点实验室, 天津 300457
3 山西大学 极端光学协同创新中心, 太原 030006
4 中国电子科技集团公司第二十七研究所, 郑州 450000
研制了一种基于铌酸锂(LN)电光调Q的高重复频率窄脉宽短腔激光器.通过测量激光穿过置于正交偏振镜间的电光晶体后, 透射强度随晶体上施加的脉冲高压的变化情况, 探究了不同尺寸LN晶体中的压电振铃效应, 并与磷酸钛氧铷(RTP)晶体中的压电振铃效应进行了比较.实验发现, 块状LN晶体中的压电振铃效应严重, 而小尺寸LN晶体中的压电振铃效应和RTP晶体中的相似, 基本可以忽略.结合压电效应理论得出, 压电振铃效应的强弱与外加电压大小及晶体固有的压电共振频率有关, 电压越低, 压电共振频率越大, 压电振铃效应越弱.在此基础上, 制备了可高重频应用的尺寸为1.2 mm×9 mm×9.4 mm的LN调Q开关, 并实现了LN晶体的高重频调Q运转.激光增益介质采用具有较大受激发射截面和较短荧光寿命的Nd∶YVO4晶体, 其一端镀有1.064 μm的全反膜, 另一端沿布儒斯特角切割, 从而省去了全反镜和偏振镜, 缩短了腔长。泵浦源采用中心波长为808 nm的光纤耦合激光二极管.设计的激光器谐振腔长度仅为20 mm。在退压式电光调Q运转下, 获得了最大重复频率为15 kHz、脉宽为5.4 ns、峰值功率为2.94 kW的稳定的激光输出.
固体激光器 脉冲激光 电光器件 铌酸锂 脉冲重复频率 电光Q开关 压电效应 窄脉冲宽度 Solid state lasers Pulsed lasers Electro-optical devices Lithium niobate Pulse repetition rate Electro-optic Q-switching Piezoelectric effects Short pulse width 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
School of Engineering and Information Technology, Charles Darwin University, Darwin, NT 0909, Australia
New techniques for controlling the amplitudes of two orthogonal linearly polarized light are presented. One is based on adjusting the DC voltage into a Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) to alter the amplitude of the light traveling on the slow axis of a fiber into the modulator with little changes in the fast-axis light amplitude. Another is based on adjusting the input DC voltages of a dual-polarization MZM operating in the reverse direction, which enables independent control of the two input orthogonal linearly polarized light amplitudes. Experimental results demonstrate that more than 30 dB difference in slow- and fast-axis light power can be obtained by controlling an MZM input DC voltage, and over 24 dB independent power adjustment for light traveling on the slow and fast axes into a dual-polarization MZM.
230.0250 Optoelectronics 230.5440 Polarization-selective devices 230.2090 Electro-optical devices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 042301

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Nano Photonic Information Technology, College of Electronic Science and Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
2 SZU-NUS Collaborative Innovation Center for Optoelectronic Science & Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
To seek high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is critical but challenging for single-shot intense terahertz (THz) coherent detection. This paper presents an improved common-path spectral interferometer for single-shot THz detection with a single chirped pulse as the probe for THz electro-optic (EO) sampling. Here, the spectral interference occurs between the two orthogonal polarization components with a required relative time delay generated with only a birefringent plate after the EO sensor. Our experiments show that this interferometer can effectively suppress the noise usually suffered in a non-common-path interferometer. The measured single-shot SNR is up to 88.85, and the measured THz waveforms are independent of the orientation of the used ZnTe EO sensor, so it is easy to operate and the results are more reliable. These features mean that the interferometer is quite qualified for applications where strong THz pulses, usually with single-shot or low repetition rate, are indispensable.
Far infrared or terahertz Ultrafast measurements Electro-optical devices Spectroscopy, terahertz Interferometry Photonics Research
2018, 6(3): 03000177
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 IOBA, Universidad de Valladolid, Valladolid, Spain
2 GDAF-UC3M, Grupo de Displays y Aplicaciones Fotonicas, Department de Tecnologia Electronica, Universidad Carlos III de Madrid, Spain
3 IK4-CIDETEC, Parque Tecnologico de San Sebastian, Guipuzcoa, Spain
4 Indo Optical Group, Departamento I+D SantCugat del Valles, Barcelona, Spain
5 GIDFYS, European University Miguel de Cervantes(UEMC), Department of Health, Sciences, Spain
Purpose: To evaluate the potential clinical usability of a new prototype of ophthalmic blue light filters developed by using electrochromic technology in pseudophakic patients complaining of glare. Methods: A prototype of electrochromic device was developed, with a specific frame that enclosed an electronic driver that allowed personalizing its function for each patient. A pro-spective, observational case series study was performed to test it. Five patients who had un-dergone cataract surgery with clear intraocular lenses and complaining of glare were included in the study. Main outcome measures were the results obtained in the satisfaction questionnaire that was delivered to patients. Then, visual acuity, contrast sensitivity, and reading ability data were evaluated with and without the prototype under different lighting conditions and different modes of the prototype after a complete month of use. Lens transmittance was also measured. Results: Visual acuity, contrast sensitivity and reading function did not change significantly with prototype use. The main activity for which the prototype was used was walking. Only one patient found that the dimming level was insufficient. No patients reported variable discomfort when passing tunnels, not sufficiently clear indoors, or put on and remove discomfort. The lenses slightly decreased their transmittance at the end of the study. Conclusion: Glasses based on electrochromic technology may be acceptable for outdoor/indoor use and for distance–near vision. Future studies with larger samples must be conducted to confirm the clinical usability of these glasses.
Optical filters electro-optical devices technical visual aids electronic control Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2017, 10(1): 1650028

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC 3010, Australia
2 Data 61/Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Parkville, VIC 3052, Australia
3 School of Engineering, Monash University Malaysia, 47500 Bandar Sunway, Selangor, Malaysia
Changes in refractive index and the corresponding changes in the characteristics of an optical waveguide in enabling propagation of light are the basis for many modern silicon photonic devices. Optical properties of these active nanoscale waveguides are sensitive to the little changes in geometry, external injection/biasing, and doping profiles, and can be crucial in design and manufacturing processes. This paper brings the active silicon waveguide for complete characterization of various distinctive guiding parameters, including perturbation in real and imaginary refractive index, mode loss, group velocity dispersion, and bending loss, which can be instrumental in developing optimal design specifications for various application-centric active silicon waveguides.
Electro-optical devices Optical properties Photonics Research
2017, 5(4): 04000305
Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Electronic Science and Technology of Shenzhen University, THz Technical Research Center of Shenzhen University, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronics Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
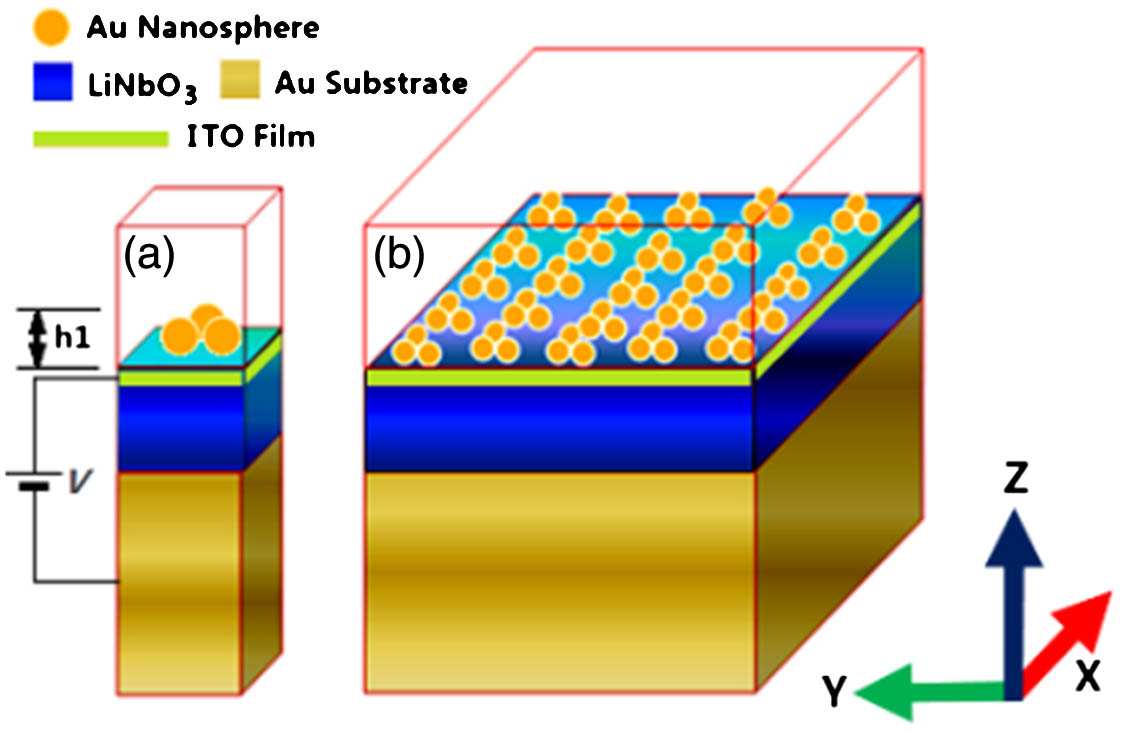
A narrowband tunable antireflection optical filter is proposed and numerically studied. The structure is a metasurface based on plasmonic nanoparticles on an electro-optic film in a three-layer configuration of metal-dielectric-metal (MDM) in the visible near-infrared range. By tuning the voltage and thus tuning the refractive index of the dielectric LiNbO3, one can shift the wavelength of minimum reflection as desired. The parameters of gold nanoparticles and other elements used for the filter design and refractive index of the dielectric are obtained by the finite-element method (FEM). An analytical theory is presented to explain the FEM simulation results, and they agree well with each other. It is found that the frequency of the plasmonic resonance wave on the metasurface should be equal to that of the Fabry–Perot resonator formed by the MDM to have a good filtering property. Theoretical spectra obtained by FEM simulation show that the structure has extensive potential for the design of tunable narrow-band filters for modulators, displayers, and color extraction for imaging.
(120.2440) Filters (230.2090) Electro-optical devices (240.6680) Surface plasmons (160.3918) Metamaterials. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000500
西北大学 光子学与光子技术研究所, 光电技术与功能材料省部共建国家重点实验室培育基地, 陕西省全固态激光及应用工程技术研究中心, 西安 710069
报道了一种1 kHz窄脉冲宽度、高峰值功率的电光腔倒空1 064 nm全固态激光器.该激光器采用808 nm 脉冲LD侧面泵浦Nd:YAG 晶体棒的双凹型折叠谐振腔结构和同步延迟MgO∶LN晶体横向加压式电光腔倒空技术,通过优化设计谐振腔结构,在脉冲重复频率200 Hz时,获得了最大单脉冲能量46.7 mJ、脉冲宽度4.06 ns、峰值功率11.50 MW的1 064 nm脉冲激光稳定输出,脉冲宽度和能量的峰峰值不稳定度分别为±1.52%和±2.02%;在1 kHz时,最大单脉冲能量达到18.3 mJ,脉冲宽度5.02 ns,峰值功率3.69 MW,脉冲宽度和能量的峰峰值不稳定度分别为±2.75%和±3.52%,激光束因子为3.849和3.868,远场发散角为3.46 mrad和3.55 mrad,束腰直径为1 508.84 μm和1 477.30 μm.
固体激光器 脉冲激光 脉冲重复频率 电光调制 激光谐振腔 腔倒空 MgO∶LN电光晶体 窄脉冲宽度 高峰值功率 高稳定性 Solid state lasers Pulsed laser Pulse repetition rate Electro-optical devices Laser cavities Cavity-dumping MgO∶LN electro-optic crystal Short pulse width High peak power High stability

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Photonics and Institute of Electro-Optical Engineering, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu 30010, China
2 Department of Applied Chemistry, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu 30010, China
3 Department of Electric and Computer Engineering, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Kowloon 999077, Hong Kong ASR, China
4 Institute of Photonic System, National Chiao Tung University, Tainan 711, China
In this study, a full-color emission red–green–blue (RGB) quantum-dot (QD)-based micro-light-emitting-diode (micro-LED) array with the reduced optical cross-talk effect by a photoresist mold has been demonstrated. The UV micro-LED array is used as an efficient excitation source for the QDs. The aerosol jet technique provides a narrow linewidth on the micrometer scale for a precise jet of QDs on the micro-LEDs. To reduce the optical cross-talk effect, a simple lithography method and photoresist are used to fabricate the mold, which consists of a window for QD jetting and a blocking wall for cross-talk reduction. The cross-talk effect of the well-confined QDs in the window is confirmed by a fluorescence microscope, which shows clear separation between QD pixels. A distributed Bragg reflector is covered on the micro-LED array and the QDs’ jetted mold to further increase the reuse of UV light. The enhanced light emission of the QDs is 5%, 32%, and 23% for blue, green, and red QDs, respectively.
(120.2040) Displays (160.4236) Nanomaterials (230.2090) Electro-optical devices (230.3670) Light-emitting diodes. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000411





