
Author Affiliations
Abstract
University of Kassel, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Measurement Technology Group, Kassel, Germany
We present a unified electromagnetic modeling of coherence scanning interferometry, confocal microscopy, and focus variation microscopy as the most common techniques for surface topography inspection with micro- and nanometer resolution. The model aims at analyzing the instrument response and predicting systematic deviations. Since the main focus lies on the modeling of the microscopes, the light–surface interaction is considered, based on the Kirchhoff approximation extended to vectorial imaging theory. However, it can be replaced by rigorous methods without changing the microscope model. We demonstrate that all of the measuring instruments mentioned above can be modeled using the same theory with some adaption to the respective instrument. For validation, simulated results are confirmed by comparison with measurement results.
interference microscopy coherence scanning interferometry confocal microscopy focus variation microscopy electromagnetic modeling surface topography measurement Advanced Photonics Nexus
2024, 3(1): 016013
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Bundesanstalt für Materialforschung und -prüfung (BAM), Division 6.1 Surface Analysis and Interfacial Chemistry, Unter den Eichen 44–46, D-12203 Berlin, Germany
Critical defects, also known as device killers, in wide bandgap semiconductors significantly affect the performance of power electronic devices. We used the methods imaging ellipsometry (IE) and white light interference microscopy (WLIM) in a hybrid optical metrology study for fast and non-destructive detection, classification, and characterisation of defects in 4H–SiC homoepitaxial layers on 4H–SiC substrates. Ellipsometry measurement results are confirmed by WLIM. They can be successfully applied for wafer characterisation already during production of SiC epilayers and for subsequent industrial quality control.
Imaging ellipsometry White light interference microscopy 4H–SiC Defects Journal of the European Optical Society-Rapid Publications
2023, 19(1): 2023018
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所精密光学制造与检测中心,上海 201800
2 上海交通大学机械与动力工程学院,上海 200240
3 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,中国-俄罗斯“一带一路”激光科学联合实验室,上海 201800
4 上海理工大学光电信息与计算机工程学院,上海 200093
扫描白光干涉术是目前最精确的表面形貌测量技术之一,被广泛应用于工业与科研领域。从发明至今的三十余年间,在精密光学、半导体、汽车及航天等先进制造领域的需求牵引下,该技术不断取得新的进展与突破。本文从技术应用、方法和算法创新、系统设计、理论模型、校准与误差补偿等方面,总结了过去二十年扫描白光干涉技术的重要进展,对该领域进一步发展提出了展望。
测量 白光干涉术 表面形貌 计量学 光学成像 干涉显微术 先进制造 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(3): 0312005
医学光电科学与技术教育部重点实验室, 福建省光子技术重点实验室, 福建师范大学, 福建 福州 350007
首先从理论上推导准相干或宽带光照明下空间光干涉光场的分布,由此可得准相干或宽带光照明下的四步相移法。其次,通过搭建绿光空间光干涉显微镜(SLIM)系统,以直径为6 μm的聚苯乙烯微球分散于显微镜物镜用油模拟细胞的微环境。最后,利用4幅SLIM图像成功重建出油浸微球的相位分布,平均半径相对误差为6.5%,光程差体积相对误差为8.4%。由于相干光的四步相移法和宽带光的四步相移法重建结果相差较小,因此,在追求成像速度的场合且细胞厚度较小时,可不对四步相移法进行修正,以加快相位重建的速度。
显微 空间光干涉显微镜 细胞 聚苯乙烯微球 光程差 四步相移法 激光与光电子学进展
2020, 57(13): 131801
1 南京理工大学 电子工程与光电技术学院, 江苏 南京 210094
2 南京理工大学 自动化学院, 江苏 南京 210094
受衍射极限的影响, 传统光学显微镜的分辨率最高约为波长的一半, 突破衍射极限, 获得更高的成像分辨率是近年来显微成像领域的研究热点。相比于其他超分辨显微成像方式, 基于微球透镜的超分辨显微成像方式具有简单直接、免标记等优点。主要介绍国内外研究团队将微球与传统的光学显微镜结合实现超分辨显微成像的研究进展, 从微球透镜参数选择、成像方案、成像分辨率、成像视场及成像机理等多角度进行总结与比对; 并结合课题组工作, 介绍了将微球透镜与干涉显微技术相结合的三维超分辨检测技术, 阐述了Linnik型与Mirau型两种检测光路原理, 分析了三维超分辨检测的效果; 展望了微球透镜超分辨显微技术在显微成像与显微干涉检测两个方面待解决的问题与发展方向。
微球透镜 衍射极限 光子纳米喷射 倏逝波 干涉显微 超分辨成像 microsphere lens diffraction limit photon nanojet evanescent wave interference microscopy super-resolution imaging
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Neurosurgery Wuhan General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command of PLA 627 Wuluo Road, Wuhan 430070, P. R.China
2 Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics Huazhong University of Science and Technology Wuhan 430074, P. R. China
3 School of Physical Education, Jianghan University Wuhan 430056, P. R. China
4 First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University Nanjing 210029, P. R. China
Identification of motor and sensory nerves is important in applications such as nerve injury repair. Conventional practice relies on time consuming staining methods for this purpose. Here, we use laser scanning infrared differential interference contrast (IR-DIC) microscopy for label-free observation of the two types of nerve. Ventral and dorsal nerve roots of adult beagle dogs were collected and sections of different thicknesses were imaged with an IR-DIC microscope. Different texture patterns of the IR-DIC images of the motor and sensory nerve can be distinguished when the section thickness increases to 40 μm. This suggests that nerve fibers in motor and sensory nerves have different distribution patterns. The result hints a potential new way for more rapid identification of nerve type in peripheral nerve repair surgery.
Differential interference microscopy nerve repair nerve root image pattern Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2016, 9(5): 1643001
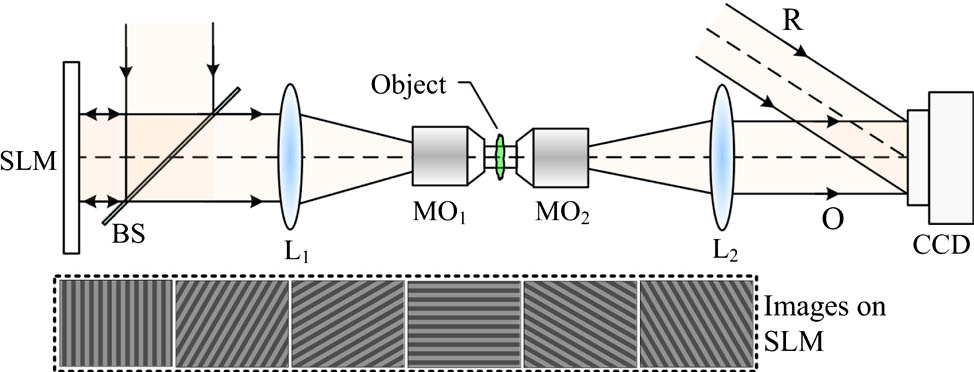
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 Institut fur Technische Optik, Universitat Stuttgart, Pfaffenwaldring 9, 70569 Stuttgart, Germany
3 Department of Bioengineering, Clemson University, Clemson-MUSC Bioengineering Program, Charleston, South Carolina 29425, USA
When structured illumination is used in digital holographic microscopy (DHM), each direction of the illumination fringe is required to be shifted at least three times to perform the phase-shifting reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a scheme for spatial resolution enhancement of DHM by using the structured illumination but without phase shifting. The structured illuminations of different directions, which are generated by a spatial light modulator, illuminate the sample sequentially in the object plane. The formed object waves interfere with a reference wave in an off-axis configuration, and a CCD camera records the generated hologram. After the object waves are reconstructed numerically, a synthetic aperture is performed by an iterative algorithm to enhance the spatial resolution. The resolution improvement of the proposed method is proved and demonstrated by both simulation and experiment.
Digital holography Holographic interferometry Interference microscopy Phase measurement Photonics Research
2014, 2(3): 03000087
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Quantitative phase imaging (QPI) of biological cells is an important developing technique. In this paper, a derivative method of phase extraction is put out under several typical blood cells' models, which is completed by numerically simulating the process of QPI. Furthermore, the first-order derivative of the phase is introduced to analyze the cell morphology, and a monocyte model is discussed as an example to demonstrate the method. It shows that the first-order derivative of the phase can be used as a tool for the identification of blood cells.
100.5070 Phase retrieval 180.3170 Interference microscopy 170.1530 Cell analysis Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s1): S11001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Quantitative interferometric microscopy is an important method for observing biological samples such as cells and tissues. As a key step in phase recovery, a fast phase unwrapping algorithm is proposed. By shifting mod 2\pi wrapped phase map for one pixel, then multiplying the original phase map and the shifted one, the phase discontinuities could be easily determined with high speed and efficiency. The method aims at enhancing phase retrieving efficiency without any background knowledge. We test our algorithm with both numerical simulation and experiments, by focusing our attentions on wrapped quantitative phase maps of cells. The results indicate that this algorithm features fast, precise and reliable.
180.3170 Interference microscopy 120.5050 Phase measurement Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(7): 071801
1 暨南大学光电工程系, 广东 广州 510632
2 光电信息传感技术广东省普通高校重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
相移误差在很大程度上影响着相移数字显微全息的测量精度。相移误差可大致分为数值误差和不均匀误差两类。相移器的标定错误和环境震动都能产生不可忽略的数值误差,因此自定标相移数字全息是值得探究的。提出了一种基于载频条纹分析方法的自定标相移数字全息显微术。利用傅里叶条纹解调分析方法,分别提取四幅全息图的载频条纹相位。通过对比载频条纹相位获得全息图间的相移量。实验装置设计的不合理导致了不均匀误差。提出一种基于改进型Linik干涉仪的相移数字全息显微装置。实验结果证明了自定标算法和改进型的Linik干涉仪具有更好的重建结果。
全息 数字全息 全息干涉仪 相位测量 干涉显微镜 中国激光
2013, 40(12): 1209001





