Author Affiliations
Abstract
College of Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
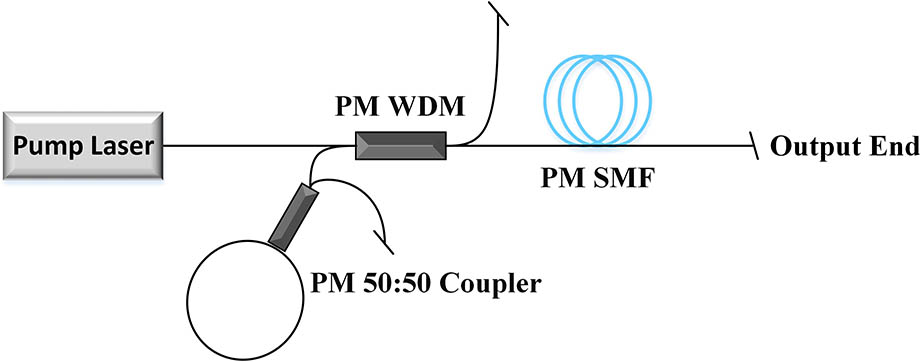
A high power linearly polarized tunable Raman random fiber laser (RFL) was studied theoretically and experimentally. The parameters required for the system design were obtained through numerical simulation, based on which a hundred-watt-level linearly polarized tunable RFL was successfully demonstrated. The central wavelength can be continuously tuned from 1113.76 to 1137.44 nm, and the output power exceeds 100 W for all of the lasing wavelengths with the polarization extinction ratio (PER) exceeding 20 dB at the maximum output power. Besides, the linewidth, spectral evolution, and temporal dynamics of a specified wavelength (1124.72 nm) were investigated in detail. Moreover, the theoretical results and the experimental results fit well. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time for a hundred-watt-level linearly polarized tunable RFL ever reported.
140.3490 Lasers, distributed-feedback 060.2420 Fibers, polarization-maintaining 290.5870 Scattering, Rayleigh Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(6): 061402
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shanghai Key Laboratory of All Solid-state Laser and Applied Techniques, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Shanghai Synet Optics Technology Corporation, Shanghai 200135, China
4 Bandweaver Technologies Co. Ltd., Shanghai 201203, China
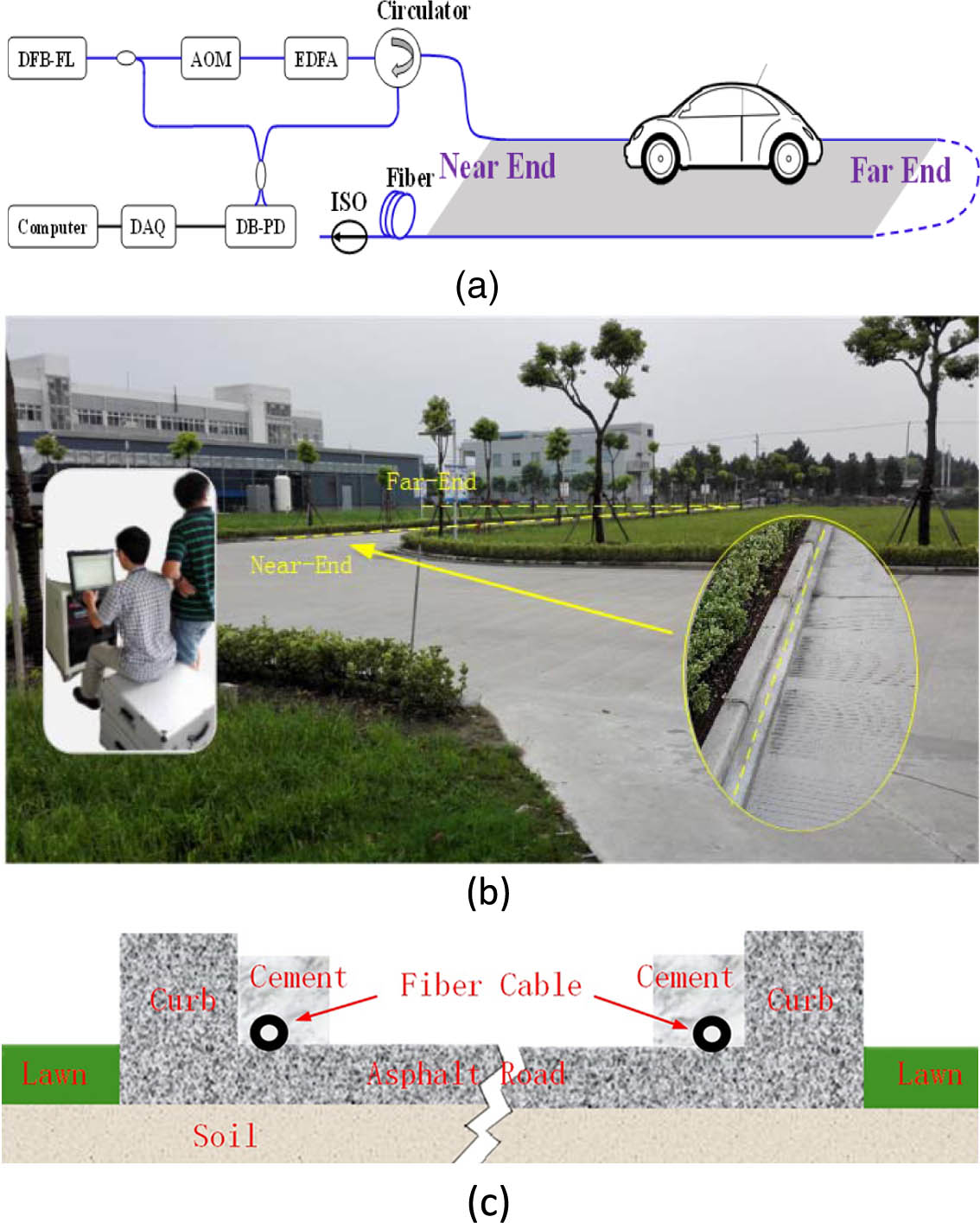
A novel distributed passive vehicle tracking technology is proposed and demonstrated. This technology is based on a phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (Φ-OTDR) that can sense and locate vibrations. Two algorithms, dynamic frequency-space image and 2D digital sliding filtering, are proposed to distinguish a car’s moving signals from severe environmental noises and disturbances. This technology is proved effective by field experiments for tracking a single car and multiple cars. This work provides a new distributed passive way for real-time vehicle tracking and this technology will be extremely important for traffic controlling and public safety in modern society.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 230.0250 Optoelectronics 290.5870 Scattering, Rayleigh Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(10): 100603
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Department of Information and Electronic Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 4300742 Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan 430074
We make a detailed analysis on the linearity and accuracy of the relationship between the full-width at half-height (FWHH) of the atmosphere molecules Rayleigh scattering spectrum and the square root of the atmospheric temperature. A simulation of the FWHH of the atmosphere molecules Rayleigh scattering spectrum is made based on the S6 Atmosphere Model and U.S. Standard Atmosphere Model. The calculated temperature is compared with the initial simulation temperature. The result shows that the FWHH of the atmosphere molecules Rayleigh scattering spectrum is nearly proportional to the atmospheric temperature. The goodness-of-fit index of the fitting curve is 0.9977 and the maximum absolute error of measured atmospheric temperature is about 2 K.
大气光学 激光雷达 瑞利散射 温度 精度 010.1290 Atmospheric optics 010.3640 Lidar 290.5870 Scattering, Rayleigh 120.6780 Temperature 300.0300 Spectroscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2009, 7(3): 03173
Author Affiliations
Abstract
P. N. Lebedev Physical Institute of RAS, Leninsky pr.53, Moscow 119991, Russia
By the 90 deg. elastic light scattering investigation and far field observation in the range of 20-800 centigrade, the relation between behavior of light scattering anomalies and evolution of nanodomain structures in lattice of barium sodium niobate (Ba2NaNb5O15, BSN) crystal was clarified. The correlation between anomalies on the temperature curves of the elastic light scattering intensity and temperature transformations of nanodomains was studied by X-ray and electron microscope methods. Phase transition near 500 centigrade and movement in field of scattering light could be explained by appearance of a new incommensurate phase.
非线性光学 材料 散射 190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials 290.5870 Scattering, Rayleigh Chinese Optics Letters
2008, 6(2): 02143
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Atomic and Molecular Physics, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900
3 Department of Science, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044
4 State Key Laboratory of High Field Laser Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800
A deuterium cluster jet produced in the supersonic expansion into vacuum of deuterium gas at liquid nitrogen temperature and moderate backing pressures is studied by Rayleigh scattering techniques. The experimental results show that deuterium clusters can be created at moderate gas backing pressures ranging from 8 to 23 bar, and a maximum average cluster size of 350 atoms per cluster is estimated. The temporal evolution of the cluster jet generated at the backing pressure of 20 bar demonstrates a two-plateau structure. The possible mechanism responsible for this structure is discussed. The former plateau with higher average atom and cluster densities is more suitable for the general laser-cluster interaction experiments.
290.5870 Scattering, Rayleigh 320.4240 Nanosecond phenomena 020.2070 Effects of collisions Chinese Optics Letters
2006, 4(5): 05249
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Institute of Near-Field Optics and Nanotechnology, Department of Physics, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian 116024
Optical trapping is an increasingly important technique for manipulating and probing matter ranging from nanometers to millimeters. In this paper, the theories of optical trapping to date are reviewed briefly. The typical conventional far field trapping design is introduced. A 5-micron yeast cell is trapped and manipulated with a 1.25 numerical aperture (NA) oil-immersion, 100X magnification objective by a 780 nm trapping beam at 16 mW in our experiment. Furthermore, the development of near-field optical trapping associated with evanescent wave is also discussed. Several proposed near-field trapping schemes, respectively using laser-illuminated metal tip, metal-coated fiber probe in the scanning near-field optical microscopy (SNOM) and focused evanescent wave, are also described.
140.7010 Trapping 290.4210 Multiple scattering 290.5870 Scattering, Rayleigh 170.5810 Scanning microscopy Chinese Optics Letters
2005, 3(0s): 71





