
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Physics and Electronic Engineering, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices and Institute of Opto-Electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
An experimental investigation of two-color polarization spectroscopy (TCPS) is presented based on the cesium 6S1/2 – 6P3/2 – 8S1/2 (852.3 nm + 794.6 nm) ladder-type system in a room-temperature vapor cell. The dependency of line shapes of TCPS on the power of a 852.3 nm pump and a 794.6 nm probe laser is measured in detail, and we confirm that the linewidth of TCPS in a counter-propagating configuration between the pump and probe laser beams is obviously narrower than that of a co-propagating configuration, due to the atomic coherence effect. It is helpful for laser stabilization of the excited state transition using TCPS without frequency modulation.
300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic 020.1670 Coherent optical effects 020.3690 Line shapes and shifts 300.3700 Linewidth Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(9): 093001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center for Advanced Measurement Science, National Institute of Metrology, Beijing 100029, China
2 College of Metrology & Measurement Engineering, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou 310018, China
3 School of Optoelectronics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
Atomic Doppler broadening thermometry (DBT) is potentially an accurate and practical approach for thermodynamic temperature measurement. However, previous reported atomic DBT had a long acquisition time and had only been proved at the triple point of water, 0°C, for the purpose of determination of the Boltzmann constant. This research implemented the cesium atomic DBT for fast room temperature measurement. The Cs133 D1 (6S1/2 → 6p1/2 transition) line was measured by direct laser absorption spectroscopy, and the quantity of thermal-induced linewidth broadening was precisely retrieved by the Voigt profile fitting algorithm. The preliminary results showed the proposed approach had a 4 min single-scan acquisition time and 0.2% reproducibility. It is expected that the atomic DBT could be used as an accurate, chip-scale, and calibration-free temperature sensor and standard.
020.1335 Atom optics 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic 120.6780 Temperature Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 060201
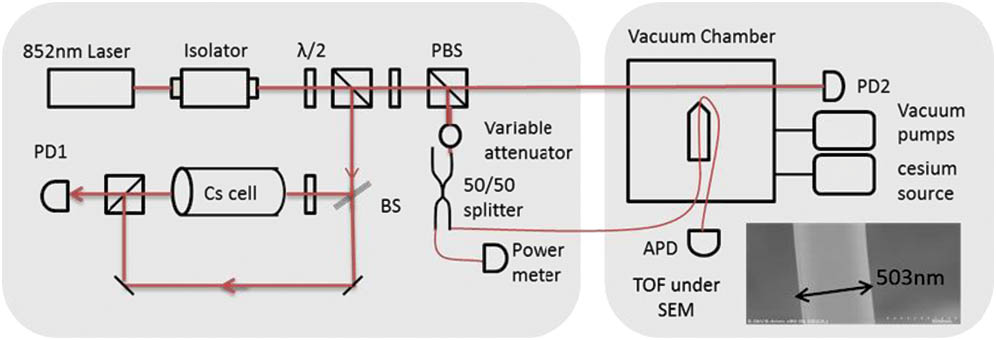
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices, Institute of Laser Spectroscopy, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
2 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
3 College of Physics and Electronics Engineering, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
We report the observation of ultralow-power absorption saturation in a tapered optical fiber (TOF) mounted in a hot cesium (Cs) vapor in a vacuum chamber. The small optical mode area of TOF produces a great influence on optical properties, allowing optical interactions with nanowatt-level power. The comparison of transmission characteristics for the TOF system and free-space vapor is investigated at different input power and atomic density. The unique performance of the Cs-TOF system makes it a promising candidate in resonant nonlinear optical applications with ultralow power.
190.4360 Nonlinear optics, devices 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(3): 031901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Artificial Structures and Quantum Control (Ministry of Education), Shanghai 200240, China
2 School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Advanced Microstructures, Nanjing 210000, China
We propose an optical weighing technique with a sensitivity down to a single atom through the coupling between a surface plasmon and a suspended graphene nanoribbon resonator. The mass is determined via the vibrational frequency shift on the probe absorption spectrum while the atom attaches to the nanoribbon surface. We provide methods to separate out the signals of the ultralow frequency vibrational modes from the strong Rayleigh background, first based on the quantum coupling with a pump-probe scheme. Owing to the spectral enhancement in the surface plasmon and the ultralight mass of the nanoribbon, this scheme results in a narrow linewidth (~GHz) and ultrahigh mass sensitivity (~30 yg). Benefitting from the low noises, our optical mass sensor can be achieved at room temperature and reach ultrahigh time resolution.
Optomechanics Surface plasmons Nanophotonics and photonic crystals Spectroscopy, atomic Photonics Research
2018, 6(9): 09000867
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication System and Network, School of Electronics Engineering and Computer Science, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
The intensities of fluorescence spectral lines of Ca atoms and Sr atoms in two different hollow cathode lamps (HCLs) are measured by element-balance-detection technology. In the wavelength range of 350–750 nm in the visible spectral region, using the individual strongest line (Ca 422.67 nm, Sr 460.73 nm) as the bench mark, the population ratios between the excited states of Ca atoms and Sr atoms are calculated by rate equations and the spontaneous transition probabilities. The HCLs with populations at excited states can be used to realize the frequency stabilization reference of the laser frequency standard.
300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic 020.1335 Atom optics Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(3): 033001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Quantum Information and Quantum Optoelectronic Devices, School of Science, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
Vector beams with spatially variant polarization have attracted much attention in recent years, with potential applications in both classical optics and quantum optics. In this work, we study a polarization selection of spatial intensity distribution by utilizing a hybridly polarized beam as a coupling beam and a circularly polarized beam as a probe beam in Rb87 atom vapor. We experimentally observe that the spatial intensity distribution of the probe beam after passing through atoms can be modulated by the hybridly polarized beam due to the optical pumping effect. Then, the information loaded in the probe beam can be designedly filtrated by an atomic system with a high extinction ratio. A detailed process of the optical pumping effect in our configurations and the corresponding absorption spectra are presented to interpret our experimental results, which can be used for the spatial optical information locally extracted based on an atomic system, which has potential applications in quantum communication and computation.
Atom optics Polarization Spectroscopy, atomic Photonics Research
2018, 6(5): 05000451
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics and Quantum Optics Devices, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
2 Institute of Opto-Electronics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of Extreme Optics, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China
A 1470 nm+852 nm two-color (TC) cesium (Cs) magneto-optical trap (MOT) with a 6S1/2-6P3/2-7S1/2 ladder-type system is proposed and experimentally investigated. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first report about the 1470 nm+852 nm Cs TC-MOT. One of the three pairs of the 852 nm cooling and trapping beams (CTBs) in a conventional Cs MOT is replaced with a pair of the 1470 nm CTBs. Thus, the TC-MOT partially employs the optical radiation forces from photon scattering of the 6P3/2 (F′=5) 7S1/2 (F′′=4) excited-state transition (1470 nm). This TC-MOT can cool and trap Cs atoms on both the red- and blue-detuning sides of the two-photon resonance. This work may have applications in cooling and trapping of atoms using inconvenient wavelengths and background-free detection of cold and trapped Cs atoms.
020.3320 Laser cooling 270.4180 Multiphoton processes 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(5): 050203
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing 100049, China
3 Center for Cold Atom Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
We experimentally observe polarization spectroscopy (PS) of the S01-P31 transition of mercury atom gases at 253.7 nm. The PS signal can be observed in all six richly abundant isotopes and the PS signal of six transitions for laser cooling are all clear and of a dispersive line shape. The optimized pump power and probe power are found for the PS of Hg202. We find the linearly polarized component in the pump beam will distort the original PS signal due to the use of linear PS. Consequently, the purity of the pump beam is crucial to laser frequency stabilization by PS.
300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic 300.6310 Spectroscopy, heterodyne Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(7): 073001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Science, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
2 Key Laboratory of Chemical Lasers, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, Dalian 116023, China
Pulsed collimated blue light at 420.3 nm is generated in hot Rb vapor by upconverting the 778.10 nm pumping beam through four wave mixing process. The energy conversion efficiency exceeds 1% when a 45 cm-long, 170°C heated Rb cell is used. The influence of cell temperature, wavelength, and energy of a pumping laser are fully examined. The efficiency of the photon conversion is found to be more sensitive to the blue detuning of the pump light and less sensitive to the red detuning of the pump light. This phenomenon can be explained by stimulated hyper-Raman scattering involved in the four-wave mixing process.
190.4380 Nonlinear optics, four-wave mixing 190.4180 Multiphoton processes 190.7220 Upconversion 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(12): 121903
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences – Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Wuhan 430071, China
2 Center for Cold Atom Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 430071, China
We report the experimental demonstration of an ultranarrow bandwidth atomic filter by optically induced polarization rotation in multilevel electromagnetically induced transparency systems in hot Rb vapor. With a coupling intensity of 2.3 W/cm2, the filter shows a peak transmission of 33.2% and a bandwidth of 10 MHz. By altering the coupling frequency, a broad tuning range of several Doppler linewidths of the D1 line transitions of 87Rb atoms can be obtained. The presented atomic filter has useful features of ultranarrow bandwidth, and the operating frequency can be tuned resonance with the atomic transition. Such narrowband tunable atomic filter can be used as an efficient noise rejection tool in classical and quantum optical applications.
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 020.1670 Coherent optical effects 300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(12): 121404





