
“天琴计划”教育部重点实验室,天琴中心 & 物理与天文学院,天琴前沿科学中心,国家航天局引力波研究中心,中山大学(珠海校区),广东 珠海 519082
Overview: The space gravitational wave detection telescope is one of the core payloads of the gravitational wave detection satellite, simultaneously expanding and contracting the transmitted beam. Optical path stability is one of the core indices for the telescope, closely related to its structural stability. To meet the ultra-high path stability and structural stability requirements posed by the gravitational wave detection mission, it is essential to study the structural deformation measurement of the telescope. Currently, there are still several shortcomings in the research of multi-degree-of-freedom deformation measurement methods for gravitational wave detection telescopes, such as inaccurate selection of measurement points, inability to decouple multi-degree-of-freedom coupling, and unclear identification of error sources in multi-degree-of-freedom measurement. This paper deeply investigates the high-precision measurement of structural deformation of space-borne telescopes designed for space gravitational wave detection. It preliminarily establishes a framework and method system for measuring the structural deformation of space-borne telescopes, theoretically describing the measurement principle of the method. The feasibility of this method applied to space gravitational wave detection is verified through simulation analysis and error decomposition. The paper focuses on resolving the issue of decoupling multiple degrees of freedom, establishing a mathematical model using analytical methods, and conducting preliminary validation using Zemax. Finally, noise analysis of the measurement system is carried out, with experimental testing of the main noise components in the measurement system, validating the correctness of the theoretical noise model proposed in this paper. The experimental results show that near 1 Hz, the displacement noise background of the single-link interferometer is 100 pm/Hz1/2. At 1 mHz in the low-frequency range, the displacement noise background reaches 10 nm/Hz1/2. The noise level of the measurement system below 1 mHz is mainly limited by environmental temperature noise, while above 10 mHz, it is primarily constrained by laser frequency noise, phase acquisition background noise, and vibration noise. During the development phase of the space gravitational wave detection telescope, the research on this measurement method is expected to fulfill the telescope's multi-degree-of-freedom deformation measurement needs. It also provides data feedback for telescope design and offers guidance for the study of the telescope's optical path stability.
空间引力波探测望远镜 形变测量 多自由度 解耦研究 噪声分析 the space gravitational wave detection telescope deformation measurement multi-degree-of-freedom decoupling study noise analysis 
1 北京空间机电研究所,北京 100094
2 首都师范大学数学科学学院,北京 150001
3 兰州大学物理科学与技术学院,甘肃 兰州 730000
Overview: In order to achieve the measurement of gravitational wave signals in the millihertz frequency band, the space-based gravitational wave detection projects such as LISA, TianQin, and Taiji projects, which are based on laser interference systems, require the hardware noise floor of the interferometers to be lower than the interstellar weak light shot noise limit. This imposes stringent engineering specifications on the optical-mechanical design and the corresponding interferometer payload. This paper approaches the issue from the perspective of detection mode selection and derives the expressions of readout noise and stray light noise in the interference signal under the single detector mode and the balanced mode. Furthermore, a detailed discussion is provided on the weak-light interference process of the scientific interferometer. The results demonstrate that the balanced mode is capable of suppressing the interference phase noise caused by laser power fluctuations and backscattered stray light across multiple orders of magnitude. However, the suppression capability is constrained by the unequal splitting property of the beam combiner. To address this, a relative gain factor is introduced to compensate for the unequal splitting property of the beam combiner. Further analysis reveals that electronic gain compensation can only eliminate the impact of unequal splitting on one of the two noises rather than both simultaneously. Therefore, a balance must be struck in selecting gain compensation between the suppression of laser power fluctuation noise and stray light noise. Even with this consideration, the balanced mode still offers significant noise suppression capabilities at a magnitude difference, thus potentially reducing the engineering requirements for laser power fluctuations and telescope backscattered stray light.
引力波探测 平衡探测模式 读出噪声 杂散光分析 gravitational wave observation balanced detection mode read out noise straylight analysis
核酸检测方法可快速鉴定特异基因指标,但其广泛应用受限于多种仪器设备串行使用以及对操作人员的高专业技术要求。本团队开发了一套注射式微流控芯片全集成核酸分析系统,该系统主要包含两大模块,分别是可以为不同类型临床样本提供多种核酸提取方法的全自动注射式核酸提取模块,以及基于微流控芯片的微纳体系多指标联合并行检测等温扩增核酸检测模块。这两大模块既可以单独发挥各自的功能,也可以组合成全集成注射式微流控芯片核酸分析系统,形成全集成自动化、微纳反应体系、快速、多指标联合并行检测的核酸检测分析平台。采用本团队开发的注射式微流控芯片全集成核酸分析系统,分别对热带念珠菌标准株培养菌液和64例外阴阴道念珠菌感染疾病的临床拭子样本进行检测。结果显示:本系统对菌液的最低检测限为3.95×102 CFU/mL,而且样品制备更方便快捷,仅需1次加样操作,核酸提取时间为10 min;64例临床样本检测效果与金标准培养法相比,卡方检验为1,Kappa值为0.950,说明两种方法无显著差异,且一致性很高。本团队开发的注射式微流控芯片全集成核酸分析系统,可以为临床多指标微纳体系核酸快速检测提供一个可靠的平台,为临床医疗应用提供精准快检技术与便捷分析仪器支撑。
医用光学 注射式 微流控芯片 全集成核酸分析系统 精准医疗应用
辽宁工程技术大学 电子与信息工程学院,辽宁 葫芦岛 125105
针对现有图像重定向方法视觉效果差和处理速度慢的问题,提出一种基于主成分分析法和分块的内容感知图像重定向方法。首先,利用主成分分析法融合梯度图和显著图来提取更加丰富的图像特征,避免主体信息失真;其次,相邻裁缝线由均值代替,避免像素不连贯;最后,根据能量图中列能量值的大小将图像分为显著区域和非显著区域,并行缩放分块,更加注重图像特征并提高运行效率。在MIT RetargetMe、DUT-OMRON和NJU2000数据集上进行实验分析,以主观感受和客观因子运行时间、SIFT-flow作为评价指标,与几种常用算法对比。实验结果表明,该方法保证了图像主体信息的完整性,平均运行时间为线裁剪算法的1/3。本文提出的方法不仅具有较优的视觉效果,而且可降低运算量。
主成分分析法 能量图 分块 裁缝线 缩放 principal component analysis energy map blocking seams scaling
1 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所上海 201800
2 中国科学技术大学合肥 230026
3 中国科学院大学北京 100049
4 中国科学院上海高等研究院上海 201204
为了研究高能电子加速器储存环中的注入瞬态过程及束流不稳定性问题,上海光源束测组开发了可实现逐束团三维位置和电荷量的精确测量的宽带示波器信号处理软件包HOTCAP。但该软件包未特别针对数据处理速度进行算法和代码执行效率的优化,完成单次测量数据的处理分析所需时间达到数十分钟量级,不能完全满足实时测量的需要。为解决这一问题,对HOTCAP软件包各功能模块进行了运行效率测试及算法优化,优化后单次测量数据处理时间缩短10倍以上,可满足高能电子储存环状态的实时监控与数据在线发布需求。
逐束团测量 HOTCAP 数据分析 高速示波器 Bunch-by-bunch measurement HOTCAP software package Data analysis High-speed oscilloscope
强激光与粒子束
2024, 36(4): 043010
强激光与粒子束
2024, 36(4): 043016
Wei Yin 1,2,3†Yuxuan Che 1,2,3†Xinsheng Li 1,2,3Mingyu Li 1,2,3[ ... ]Chao Zuo 1,2,3,****
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Smart Computational Imaging Laboratory (SCILab), School of Electronic and Optical Engineering, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China
2 Smart Computational Imaging Research Institute (SCIRI) of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210019, China
3 Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Spectral Imaging & Intelligent Sense, Nanjing 210094, China
4 Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, The University of Hong Kong, Pokfulam, Hong Kong SAR 999077, China
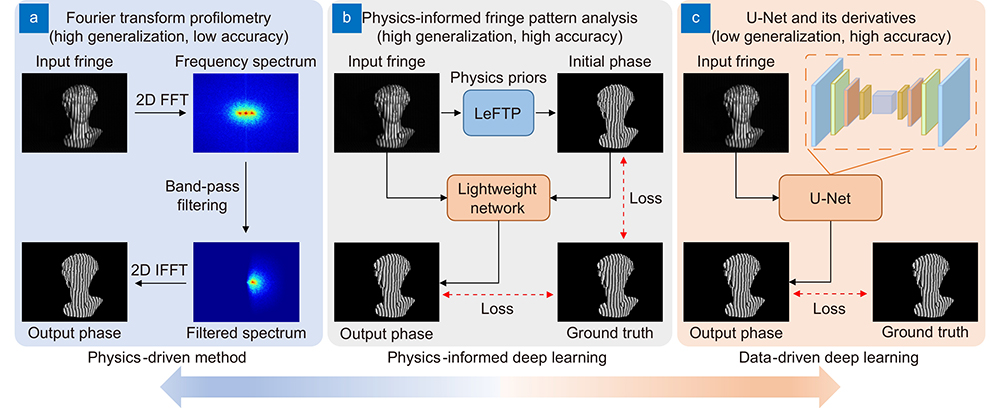
Recently, deep learning has yielded transformative success across optics and photonics, especially in optical metrology. Deep neural networks (DNNs) with a fully convolutional architecture (e.g., U-Net and its derivatives) have been widely implemented in an end-to-end manner to accomplish various optical metrology tasks, such as fringe denoising, phase unwrapping, and fringe analysis. However, the task of training a DNN to accurately identify an image-to-image transform from massive input and output data pairs seems at best na?ve, as the physical laws governing the image formation or other domain expertise pertaining to the measurement have not yet been fully exploited in current deep learning practice. To this end, we introduce a physics-informed deep learning method for fringe pattern analysis (PI-FPA) to overcome this limit by integrating a lightweight DNN with a learning-enhanced Fourier transform profilometry (LeFTP) module. By parameterizing conventional phase retrieval methods, the LeFTP module embeds the prior knowledge in the network structure and the loss function to directly provide reliable phase results for new types of samples, while circumventing the requirement of collecting a large amount of high-quality data in supervised learning methods. Guided by the initial phase from LeFTP, the phase recovery ability of the lightweight DNN is enhanced to further improve the phase accuracy at a low computational cost compared with existing end-to-end networks. Experimental results demonstrate that PI-FPA enables more accurate and computationally efficient single-shot phase retrieval, exhibiting its excellent generalization to various unseen objects during training. The proposed PI-FPA presents that challenging issues in optical metrology can be potentially overcome through the synergy of physics-priors-based traditional tools and data-driven learning approaches, opening new avenues to achieve fast and accurate single-shot 3D imaging.
optical metrology deep learning physics-informed neural networks fringe analysis phase retrieval Opto-Electronic Advances
2024, 7(1): 230034
提出一种基于三芯结构空芯反谐振光纤的太赫兹耦合器。采用有限元分析法对太赫兹光纤的模式特性进行分析,并基于耦合理论得到其耦合特性曲线。仿真结果表明,三芯结构模式具有比单芯结构更低的传输损耗,其耦合长度可通过改变纤芯间隔和隔离包层管的间隙进行调节。采用长度为223.2 mm的三芯结构空芯光纤可以实现插入损耗小于3.5 dB、带宽达到0.52 THz的宽带、均匀分束。
光学器件 空芯太赫兹光纤 反谐振 模式耦合 损耗特性 带宽分析





