
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden – Rossendorf, Dresden, Germany
2 Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
3 OncoRay – National Center for Radiation Research in Oncology, Faculty of Medicine and University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus, TUD Dresden University of Technology, Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden – Rossendorf, Dresden, Germany
4 Current affiliation: Institut Curie, Université PSL, CNRS UMR3347, Orsay, France
5 Current affiliation: Universitätsklinikum Freiburg, Freiburg, Germany
Laser plasma accelerators (LPAs) enable the generation of intense and short proton bunches on a micrometre scale, thus offering new experimental capabilities to research fields such as ultra-high dose rate radiobiology or material analysis. Being spectrally broadband, laser-accelerated proton bunches allow for tailored volumetric dose deposition in a sample via single bunches to excite or probe specific sample properties. The rising number of such experiments indicates a need for diagnostics providing spatially resolved characterization of dose distributions with volumes of approximately 1 cm ${}^3$ for single proton bunches to allow for fast online feedback. Here we present the scintillator-based miniSCIDOM detector for online single-bunch tomographic reconstruction of dose distributions in volumes of up to approximately 1 cm ${}^3$ . The detector achieves a spatial resolution below 500 $\unicode{x3bc}$ m and a sensitivity of 100 mGy. The detector performance is tested at a proton therapy cyclotron and an LPA proton source. The experiments’ primary focus is the characterization of the scintillator’s ionization quenching behaviour.
beam monitoring detectors laser-driven proton beams scintillator-based diagnostics ultra-high dose rate High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2024, 12(2): 02000e17
1 中国科学技术大学国家同步辐射实验室,安徽 合肥 230029
2 中国科学院大学物理科学学院,北京 101408
3 合肥工业大学物理学院,安徽 合肥 230009
4 安徽大学化学化工学院,安徽 合肥 230601
红外光谱有着广泛的应用。合肥红外自由电子激光装置能够为用户提供高亮度的中/远红外辐射,为高水平的红外研究提供基础条件。自由电子激光和实验站之间需要用光束线连接起来,以便在完成红外辐射高效输送的同时进行聚焦、诊断等。本文介绍了合肥红外自由电子激光装置红外光束线的设计与性能,主要包括光束线的总体要求、设计方案和布局、光学设计、光斑演化、光束传输、激光的分束取样、激光宏脉冲的在线同步测量、激光光谱的在线同步测量等。调试结果表明,设计达到了预期指标,整个光束线可以稳定运行。
激光光学 光束线 自由电子激光 中/远红外 激光诊断
1 南京理工大学能源与动力工程学院, 先进燃烧实验室, 江苏 南京 210094
2 西安近代化学研究所, 燃烧与爆炸技术重点实验室, 陕西 西安 710065
金属燃料的添加不仅能够提高推进剂的能量密度, 还能缓解冲压发动机高频燃烧的不稳定现象。 硼具有较高的质量热值和体积热值, 受到了广泛关注。 然而由于硼自身熔点高、 沸点高且表面存在氧化层, 导致点火困难, 燃烧性能差。 铝和铁的存在会使得氧化过程表面反应的放热增加, 提高温度, 促进硼的点火和燃烧。 同时由于铝和铁具有较高的燃烧热和较快的能量释放速率, 理论燃烧热利用率高, 可引入铝和铁来提高硼的燃烧效率和实际燃烧热值。 针对硼点火困难和燃烧性能差的问题, 将硼分别和铝、 铁掺混得到兼具较好点火性能和较高能量密度的复合金属燃料。 采用弥散燃烧系统研究了纳米硼基复合金属颗粒云的弥散燃烧特性, 利用高速相机获得硼及硼基复合金属颗粒云的燃烧过程, 并利用双色法测量了其温度分布变化, 应用光纤光谱仪、 扫描透射电镜、 X射线衍射和元素分析对硼基复合金属颗粒的燃烧特性及机理进行分析。 结果表明, 铝和铁的加入缩短了硼的点火延迟时间和燃烧时间, 并且使得同一时间内被点燃的硼颗粒数量增加, 硼的燃烧过程更加剧烈。 铝的加入提高了复合燃料的燃烧温度; 铁的加入降低了复合燃料的燃烧温度。 硼基复合金属颗粒弥散燃烧测温过程中观察到明显的绿光, 结合光谱图, 分析该绿光来自于硼燃烧生成的中间产物BO2。 硼基复合金属颗粒弥散燃烧后团聚物主要为氧化产物, 其中也含有少量的氮元素。 硼基复合金属颗粒弥散燃烧后产物团聚现象更为明显, 且不规则块状硼的破裂更加严重。 硼基复合金属颗粒进入管式炉后, 受到热辐射后在短时间内快速升温, 铝和铁颗粒率先达到着火温度开始燃烧, 燃烧释放的热量积聚在颗粒内部, 被硼颗粒吸收, 硼表面氧化层破裂, 内部硼与空气接触, 继而温度上升至硼的着火点, 硼开始燃烧, 从而促进了硼的燃烧。
纳米颗粒 硼基复合金属 弥散燃烧 燃烧诊断 Nanoparticles Boroncomposite metal Dispersion combustion Combustion diagnostics 光谱学与光谱分析
2023, 43(10): 3252
1 重庆工商大学 制造装备机构设计与控制重庆市重点实验室,重庆 400067
2 重庆工商大学 机器人与激光智能制造研究所,重庆 400067
3 中国工程物理研究院 激光聚变研究中心,四川 绵阳 621900
强激光加载下金属材料产生的微喷射现象及其内在的机理分析是冲击压缩科学与工程领域研究的前沿问题,相关研究对于认识材料在极端载荷条件下的动力学行为具有重要意义。近年来国内外科学家们基于各大激光装置开展了大量微喷射诊断实验研究,在喷射物性质、金属界面不稳定性增长以及微喷混合问题等方面取得了一系列重要进展。通过回顾微喷静态和动态诊断实验的研究历程,对微喷诊断实验研究方法的重要应用作了详细介绍,同时对微喷产生的主要作用机制、影响因素以及微喷混合等问题进行回顾、梳理和总结。根据当前国内外微喷诊断实验发展趋势,归纳总结目前微喷诊断实验研究结果中仍存在的不足,并对微喷射实验研究未来发展方向进行展望。
微喷射 冲击波 回收 动态诊断 X射线成像 micro-ejection shock wave recovery dynamic diagnostics X-ray radiography 强激光与粒子束
2023, 35(10): 101001
1 上海理工大学能源与动力工程学院/上海市动力工程多相流动与传热重点实验室, 上海 200093
2 上海航天动力技术研究所, 上海 201109
火焰燃烧参数能直接反映火焰燃烧状态, 并对燃烧过程进行诊断、 预测和优化。 火焰温度及辐射率是燃烧状态的重要表征参数, 火焰温度及辐射率的准确测量对于建立燃烧模型、 优化燃烧过程和控制污染物排放有着非常重要的意义。 随着数字图像技术与光谱学的发展, 多光谱成像技术逐步应用于火焰燃烧温度及辐射率测量。 针对光谱仪空间分辨率低和RGB彩色相机光谱分辨率低的问题, 多光谱成像技术能获得兼顾空间分辨率及光谱分辨率的火焰光谱图像, 实现火焰温度及辐射率分布测量, 具有高时空分辨率、 响应快速及测温范围宽等优点。 因此, 提出了基于多光谱成像技术的火焰温度及辐射率测量方法, 搭建标准高温黑体辐射实验测量系统, 对多光谱相机665~960 nm波段开展高温黑体辐射响应系数标定实验, 获得多光谱相机25波段光谱响应标定系数, 通过四阶多项式拟合建立多光谱相机各波段下仪器响应值与理论辐射强度之间的关系, 并开展多光谱成像技术测量验证实验, 结果显示温度与辐射率测量的相对偏差分别小于1%与4%。 在此基础上, 以蜡烛火焰为研究对象, 建立了火焰多光谱成像测量系统, 获得了蜡烛火焰多光谱辐射图像, 基于普朗克辐射定律参数拟合方法, 实现了蜡烛火焰温度与辐射率分布测量。 测量结果表明: 火焰竖直平面上火焰中心区温度及辐射率均高于火焰上部和底部; 蜡烛火焰温度测量结果范围约为1 350~2 050 K, 火焰中心区最高温度约为2 050 K; 蜡烛火焰辐射率测量结果范围约为0.04~0.36, 火焰中心区最高辐射率为0.36。 测量结果与蜡烛火焰燃烧过程及辐射特性分布规律一致。
多光谱成像 燃烧诊断 辐射测温法 蜡烛火焰 火焰辐射率分布 Multispectral imaging Combustion diagnostics Radiation temperature measurement Candle flame Flame emissivity distribution 光谱学与光谱分析
2023, 43(11): 3644
1 西北核技术研究所激光与物质相互作用国家重点实验室,陕西 西安 710028
2 上海交通大学四川研究院,四川 成都 610200
基于羟基标记示踪速度测量技术,研究了基于该技术中激光光解水产生的OH-进行温度测量的双色平面激光诱导荧光(PLIF)方法和荧光强度测温方法,进而开发了一种新的速度、温度同时测量技术,并在电加热流场及超燃冲压发动机流场进行了测量验证。在室温至900 K的温度范围内,与热电偶温度测量结果比,基于光解OH-的双色PLIF温度测量的平均标准偏差为12.1 K,基于光解OH-荧光强度的温度测量最大偏差为16.8 K,速度测量不确定度在1%以内。在超燃冲压发动机流场中,利用CARS温度测量数据作为温度测量标定点,获得了标记线上温度、速度的同时测量结果,其中所得温度与CARS温度测量结果的最大偏差为44 K。
测量 速度温度同时测量 羟基示踪 光解离 激光诊断 光学学报
2023, 43(17): 1712001
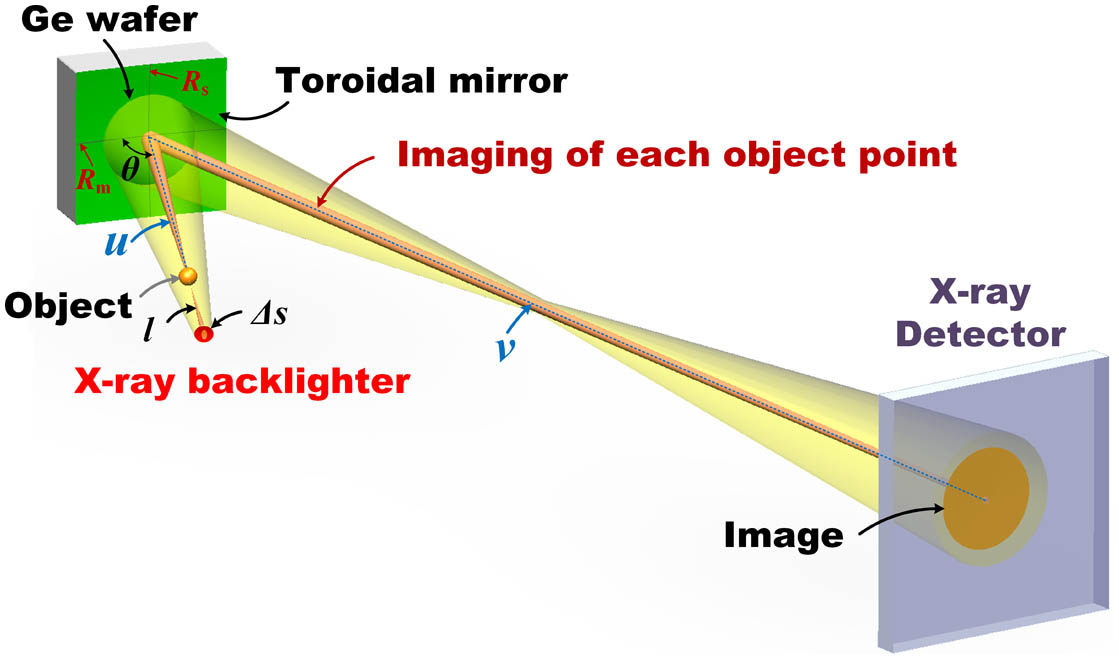
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute of Precision Optical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Advanced Micro-Structured Materials, Shanghai Frontiers Science Center of Digital Optics, Shanghai Professional Technical Service Platform for Full-Spectrum and High-Performance Optical Thin Film Devices and Applications, School of Physics Science and Engineering, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China
2 Research Center of Laser Fusion, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Mianyang 621900, China
Curved crystal imaging is an important means of plasma diagnosis. Due to the short wavelengths of high-energy X rays and the fixed lattice constant of the spherical crystal, it is difficult to apply the spherical crystal in high-energy X-ray imaging. In this study, we have developed a high-energy, high-resolution X-ray imager based on a toroidal crystal that can effectively correct astigmatism. We prepared a Ge toroidal crystal for backlighting Mo Kα1 characteristic lines ( keV) and verified its high-resolution imaging ability in high-energy X-ray region, achieving a spatial resolution of 5–10 µm in a field of view larger than 1.0 mm.
laser plasma diagnostics toroidal crystal monochromatic X-ray imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2023, 21(10): 103401
1 上海交通大学 机械与动力工程学院, 上海 200240
2 西北核技术研究所, 西安 710613
为了对激光光强分布进行准确测量,本文提出基于层析成像技术的激光光强分布测量方法。首先,通过数值仿真计算,对采用的成像模型的准确性以及重建算法的收敛性进行验证。对不同激光光强分布模型以及不同随机噪声等级时的重建精度进行评估。经计算,采用不同典型激光光强模型时其重建误差均小于等于7.02%;在施加10%以内随机噪声时,重建误差均小于8.5%。设计并搭建了层析成像系统,采用定制的一分七光纤束实现7七个角度信号的测量。7个角度分布在垂直于激光光束平面内的近半圆周内,各个角度距重建区域的距离约为160 mm,且7个角度的角度覆盖范围约为150°。实验通过探测激光光束穿过若丹明-乙醇溶液之后的体激光诱导荧光信号,结合后续的数据处理过程间接实现激光光强三维分布的反演。在数据处理过程中,采用交替迭代重建算法对探测信号进行吸收矫正的三维重建,可间接地获得激光光强分布。为了定量评估测量精度,在进行重建时仅采用其中6个角度,将余下一角度的重建反投影以及投影数据间的相关性用来间接证明此重建方法的可行性。计算结果表明,该角度投影以及反投影之间的相关性系数为0.9802,可间接的验证该方法的可行性。可以预见,本工作提出的激光光强三维测量方案在激光应用领域具有广泛的前景。
光学诊断 计算成像 层析成像 三维重建 激光诱导荧光 optical diagnostics computational imaging tomographic imaging three-dimensional reconstruction laser-induced fluorescence 
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 ELI Beamlines Facility, The Extreme Light Infrastructure ERIC, Dolní Břežany, Czech Republic
2 Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering, Czech Technical University in Prague, Prague, Czech Republic
An optical probing of laser–plasma interactions can provide time-resolved measurements of plasma density; however, single-shot and multi-frame probing capabilities generally rely on complex setups with limited flexibility. We have demonstrated a new method for temporal resolution of the rapid dynamics ( $\sim 170$ fs) of plasma evolution within a single laser shot based on the generation of several consecutive probe pulses from a single beta barium borate-based optical parametric amplifier using a fraction of the driver pulse with the possibility to adjust the central wavelengths and delays of particular pulses by optical delay lines. The flexibility and scalability of the proposed experimental technique are presented and discussed.
off-harmonic optical probing plasma diagnostics ultrafast imaging High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(4): 04000e45

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, Garching, Germany
The Centre for Advanced Laser Applications in Garching, Germany, is home to the ATLAS-3000 multi-petawatt laser, dedicated to research on laser particle acceleration and its applications. A control system based on Tango Controls is implemented for both the laser and four experimental areas. The device server approach features high modularity, which, in addition to the hardware control, enables a quick extension of the system and allows for automated data acquisition of the laser parameters and experimental data for each laser shot. In this paper we present an overview of our implementation of the control system, as well as our advances in terms of experimental operation, online supervision and data processing. We also give an outlook on advanced experimental supervision and online data evaluation – where the data can be processed in a pipeline – which is being developed on the basis of this infrastructure.
data processing high-power laser experiments laser–plasma acceleration online diagnostics High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2023, 11(4): 04000e44





