强激光与粒子束
2022, 34(1): 011007
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Space Laser Communication and Detection Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
3 Shanghai Key Laboratory of All Solid-State Laser and Applied Techniques, Shanghai 201800, China
4 Key Laboratory of Materials for High Power Laser, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
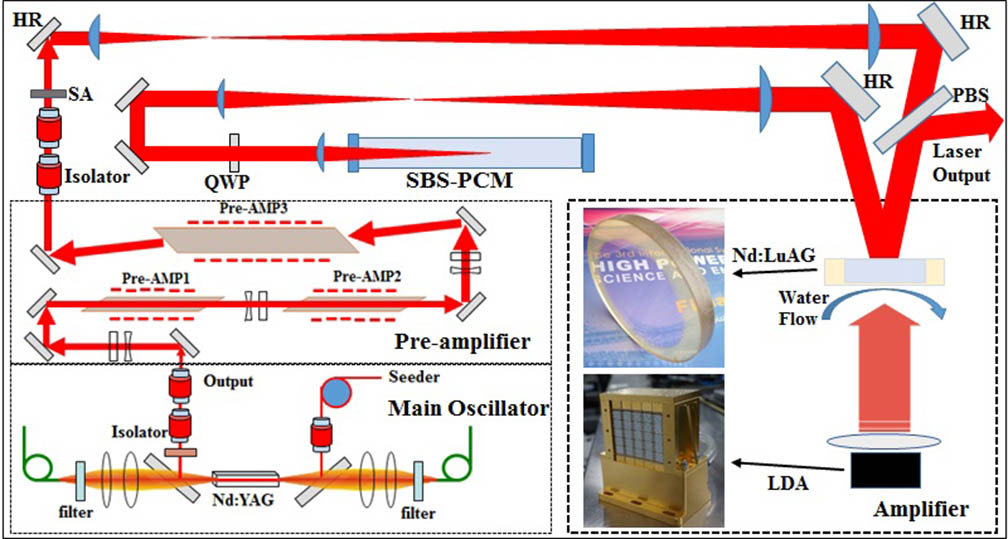
A 1.5 J Nd:LuAG ceramic active mirror laser amplifier with a high beam quality is demonstrated in which a 0.8% (atomic fraction) Nd-doped Nd:LuAG ceramic disk with a diameter of 64 mm and a thickness of 5.5 mm is used as a laser gain medium. A maximum single-pass small-signal gain of 2.59 is measured when the pump energy is 11.5 J, with an injected seed energy of 0.4 J; a maximum output energy of 1.5 J is obtained at the repetition rate of 10 Hz. A far-field beam spot 1.25 times the diffraction limit (DL) is achieved by using a stimulated Brillouin scattering phase conjugation mirror (SBS-PCM) for wavefront correction.
high energy lasers disk laser amplifiers Nd:LuAG ceramic high beam quality Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(2): 021401
Author Affiliations
Abstract
HiLASE Centre
,
Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences
,
Za Radnicí 828/5
,
25241
,
Dolní Břežany
,
Czech Republic
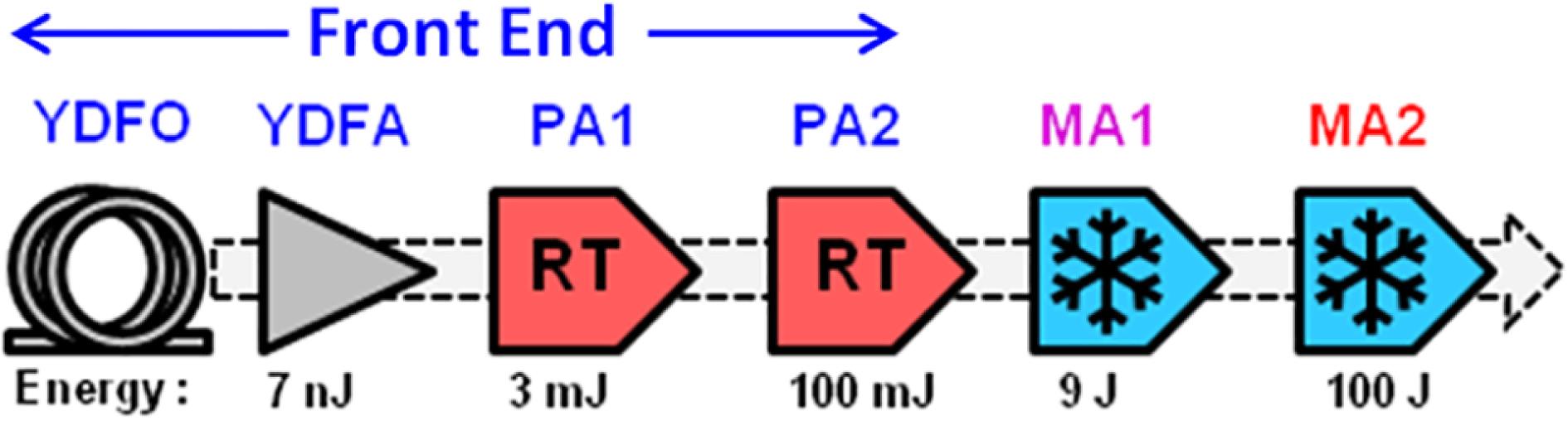
Development of high energy laser sources with nanosecond pulses at several hertz values for repetition rate has been very attractive in recent years due to their great potential for practical applications. With the recent advancement in fabricating large size laser quality transparent ceramics, diode pumped solid-state laser generating pulse energy of 100 J at 10 Hz has been recently realized at HiLASE center using Yb:YAG ceramic with Cr:YAG cladding. This review discusses Yb based high energy lasers, specific laser geometries for efficient thermal management and the role of transparent ceramics in such diode pumped high-energy-class solid-state lasers around the world.
diode pumped solid-state lasers high energy lasers laser materials transparent ceramics High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(4): 04000e62
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Central Laser Facility
,
STFC Rutherford Appleton Laboratory
,
Didcot
,
OX11 0QX
,
UK
2 Institute for Radiation Physics
,
Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf e.V.
,
D-01328 Dresden
,
Germany
In this paper we review the design and development of a 100 J, 10 Hz nanosecond pulsed laser, codenamed DiPOLE100X, being built at the Central Laser Facility (CLF). This 1 kW average power diode-pumped solid-state laser (DPSSL) is based on a master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) design, which includes two cryogenic gas cooled amplifier stages based on DiPOLE multi-slab ceramic Yb:YAG amplifier technology developed at the CLF. The laser will produce pulses between 2 and 15 ns in duration with precise, arbitrarily selectable shapes, at pulse repetition rates up to 10 Hz, allowing real-time shape optimization for compression experiments. Once completed, the laser will be delivered to the European X-ray Free Electron Laser (XFEL) facility in Germany as a UK-funded contribution in kind, where it will be used to study extreme states of matter at the High Energy Density (HED) instrument.
cryogenic lasers diode-pumped solid-state laser high energy lasers laser amplifiers Yb:YAG High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2018, 6(4): 04000e65
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
高能拍瓦激光的高精度脉宽测量对离轴抛物面镜焦斑功率密度的诊断以及光栅损伤阈值的分析都具有重要意义。分析了光束指向性和近场分布的周期性调制这两方面的误差影响。结果表明, 当反射镜稳定性在5 μrad时,光束指向性的误差最大为0.03%。当近场调制周期增加时, 误差降低; 而调制度增加时, 误差增大。另外, 采用镜像结构能降低近场缺陷导致的测量误差。当调制深度为1.5、调制周期大于10时, 综合误差小于20%, 最小可降至10%。镜像结构的误差均小于15%, 最小可降至0。在拍瓦级激光脉宽测量实验中, 证实了近场调制对于脉宽测量的影响及改善效果。
激光器 超短脉冲 单次自相关 高能激光 超短脉冲测量 中国激光
2017, 44(11): 1104001

Author Affiliations
Abstract
Sandia National Laboratories, P.O. Box 5800 MS 1197, Albuquerque, NM 87185, USA
The Z-backlighter laser facility primarily consists of two high energy, high-power laser systems. Z-Beamlet laser (ZBL) (Rambo et al., Appl. Opt. 44, 2421 (2005)) is a multi-kJ-class, nanosecond laser operating at 1054 nm which is frequency doubled to 527 nm in order to provide x-ray backlighting of high energy density events on the Z-machine. Z-Petawatt (ZPW) (Schwarz et al., J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 112, 032020 (2008)) is a petawatt-class system operating at 1054 nm delivering up to 500 J in 500 fs for backlighting and various short-pulse laser experiments (see also Figure 10 for a facility overview).With the development of the magnetized liner inertial fusion (MagLIF) concept on the Z-machine, the primary backlighting missions of ZBL and ZPW have been adjusted accordingly. As a result, we have focused our recent efforts on increasing the output energy of ZBL from 2 to 4 kJ at 527 nm by modifying the fiber front end to now include extra bandwidth (for stimulated Brillouin scattering suppression). The MagLIF concept requires a well-defined/behaved beam for interaction with the pressurized fuel. Hence we have made great efforts to implement an adaptive optics system on ZBL and have explored the use of phase plates. We are also exploring concepts to use ZPW as a backlighter for ZBL driven MagLIF experiments. Alternatively, ZPW could be used as an additional fusion fuel pre-heater or as a temporally flexible high energy pre-pulse. All of these concepts require the ability to operate the ZPW in a nanosecond long-pulse mode, in which the beam can co-propagate with ZBL. Some of the proposed modifications are complete and most of them are well on their way.
adaptive optics adaptive optics high energy lasers high energy lasers MagLIF MagLIF OPCPA OPCPA petawatt lasers petawatt lasers SBS suppression SBS suppression High Power Laser Science and Engineering
2016, 4(4): 04000e36
国防科学技术大学光电科学与工程学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
高能激光系统中,反射镜镜面热变形会使系统的输出光强和波前分布不均匀性加剧,从而导致输出光束质量的下降。建立了复杂镜面光线追迹的模型,使用Fresnel衍射公式和光线追迹的方法,研究了高能激光系统内通道不同数量22.5°反射镜对输出光束质量的影响。该方法和部分结果对高能激光系统激光器的优化设计,激光内通道冷却方式以及自适应光学校正能力设计参数的选取具有一定的参考价值。
激光技术 高能激光 热变形 光束质量 laser technology high energy lasers thermal distortion beam quality
使用积分方法和差分方法结合的快速计算方法,在实际燃烧驱动氟化氢化学激光器增益介质沿径向分布不均匀的情况下,考虑在光束变换环形孔径激光谐振腔的紧束段引入光束旋转90°对其输出性能的影响.计算结果显示:在无腔失调的情况下,在紧束段引入光束旋转对束变换环孔激光谐振腔输出功率及光束质量的改善并不显著;在存在腔失调的情况下,紧束段光束旋转对于输出功率和光束质量的改善有显著效果.
激光技术 高能激光 化学激光 光束变换环形孔径谐振腔 环形增益介质 光束旋转 Laser technology High energy lasers Chemical lasers Beam-converting annular resonator Annular gain medium Beam rotation 强激光与粒子束
2004, 16(10): 1245
1 国防科技大学,理学院,定向能技术研究所,湖南,长沙,410073
2 北京跟踪与通信技术研究所,北京,100094
通过对高能激光器气动窗口的研究现状和应用需求的分析,指出建立一套气动窗口光束质量的评价方法是十分必要的.在分析气动窗口工作机理和现有激光光束质量评价因子的基础上,提出一种评价气动窗口光束质量的方法,即用斯特列尔比来评价气动窗口的光束质量,并辅以相对衍射极限因子进行远场直观说明.分析表明,此种评价方法是可行的,并达到了不受限于气动窗口类别的光束质量评价的要求.
高能激光器 气动窗口(ADW) 光束质?科兰鄯椒?斯特列尔比 high energy lasers aerodynamic windows methods of evaluating beam quality Strehl ratio





