
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Hangzhou Institute for Advanced Study, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou 310024, China
High-precision angle measurement of pulsars is critical for realizing pulsar navigation. Compared to visible light and radio waves, the wavelength of X-rays is incredibly short, which provides the possibility of achieving better spatial resolution. However, due to the lack of applicable X-ray apparatus, extracting the angle information of pulsars through conventional X-ray methods is challenging. Here, we propose an approach of pulsar angle measurement based on spatially modulated X-ray intensity correlation (SMXIC), in which the angle information is obtained by measuring the spatial intensity correlation between two radiation fields. The theoretical model for this method has been established, and a proof-of-concept experiment was carried out. The SMXIC measurement of observing angles has been demonstrated, and the experimental results are consistent with the theoretical values. The potential of this method in future applications is discussed, and theoretically, the angular measurement at the level of micro-arcsecond can be expected. The sphere of pulsar navigation may benefit from our fresh insights.
pulsar measurement X-ray measurement intensity correlation spatial modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 043401
1 国防科技大学理学院, 湖南 长沙 410073
2 国防科技大学量子信息学科交叉中心, 湖南 长沙 410073
3 北京邮电大学电子工程学院, 北京 100876
光学成像是人们获取信息最重要的技术手段之一。关联成像作为一种基于光场高阶关联发展起来的新技术, 利用单个点探测器就可以实现对面目标的成像, 具有物像分离、探测灵敏度高、抗干扰能力强等优点, 为光学成像技术的发展带来了新的机遇。但关联成像以时间换空间的多帧累积成像模式, 严重限制了图像的获取效率。为了解决该问题, 除了进行系统结构、光源和探测方法优化设计外, 研究高效的图像重构算法也是提高成像质量和成像速度最有效的方法之一。好的图像重构算法不仅能大大降低成像所需的测量次数, 提高信息提取效率和重构图像质量, 还能降低对成像系统硬件的要求, 是关联成像技术走向实用的关键。近年来, 关联成像图像重构算法不断演变, 发展出很多不同类型的重构算法。本文简要回顾了关联成像的原理机制, 进而在此基础上系统介绍了几种主要关联成像算法的基本原理, 并分析了其优缺点和适用场景。
量子光学 关联成像 强度关联 伪逆算法 深度学习 quantum optics ghost imaging intensity correlation pseudo-inverse algorithm deep-learning
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所量子光学重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 国科大杭州高等研究院, 浙江 杭州 310024
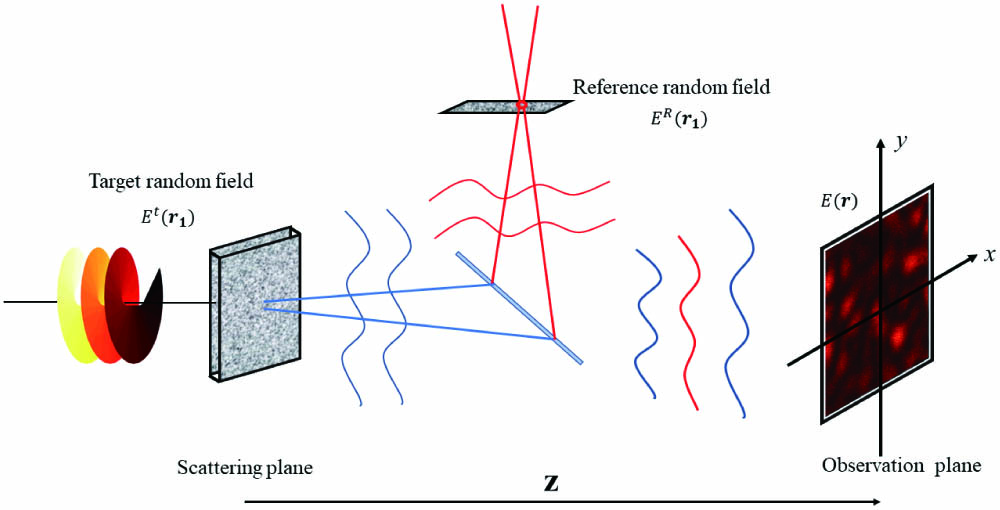
强度关联干涉测量利用光场的高阶关联特性获取星体空间角度信息,有望实现脉冲星角位置的高精度测量。然而常规的强度关联测量需要满足相干探测条件,这对探测器的时间分辨提出了极高的要求。提出基于空间调制的星体观测张角强度关联干涉测量方法,在探测器前放置调制屏以对光场进行空间调制,通过旋转调制屏获取二阶干涉条纹。理论推导了当两条光路的调制屏存在角度差时二阶关联函数的表达式,并基于理论推导结果设计双反射镜实验方案并进行相关可见光实验验证,所得实验结果与理论分析结果相符。该方法大幅降低了探测器的时间分辨要求,对于我国未来实现航天器的自主导航具有重要意义。
测量 干涉测量 强度关联 X射线
1 三峡大学, 理学院, 湖北 宜昌 443002
2 上海理工大学上海出版印刷高等专科学校 上海 200093
本文在三能级级联结构的非对称半导体量子阱中研究了荧光的高阶量子关联效应。利用三个激光场同时驱动三个偶极允许的跃迁时, 研究结果发现强度- 强度关联函数和强度- 振幅关联函数依赖于驱动场的相对相位及拉比频率。在三个驱动场拉比频率相等的条件下, 相对相位为0时, 二阶关联呈现出强关联; 相位不为0时, 二阶关联为一般关联。不仅如此, 我们发现改变相位可以调节三阶关联函数时间不对称性程度, 相位为π/2或3π/2正时和负时关联函数表现了较好的对称性。另外, 我们发现通过调节拉比频率的大小可以实现二阶关联由强关联向一般关联效应转换, 三阶强度- 幅度关联的值得到极大增强。最后, 利用修饰态绘景我们分析了上述现象内在的物理机制为多重量子干涉效应。这些结果可能对于高精度测量和产生单光子源具有潜在的应用价值。
半导体量子阱 强度- 强度关联 强度- 振幅关联 Semiconductor Quantum Well Intensity-Intensity Correlation Intensity-Amplitude Correlation

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Optoelectronics System Laboratory, Institute of Semiconductors, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100083, China
2 College of Materials Science and Opto-Electronics Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 School of Electronic, Electrical and Communication Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
An enhancement method of rapid lifetime determination is proposed for time-resolved fluorescence imaging to discriminate substances with approximate fluorescence lifetime in forensic examination. In the method, an image-exclusive-OR treatment with filter threshold adaptively chosen is presented to extract the region of interest from dual-gated fluorescence intensity images, and then the fluorescence lifetime image is reconstructed based on the rapid lifetime determination algorithm. Furthermore, a maximum and minimum threshold filtering is developed to automatically realize visualization enhancement of the lifetime image. In proof experiments, compared with traditional fluorescence intensity imaging and rapid lifetime determination method, the proposed method automatically distinguishes altered and obliterated documents written by two brands of highlighters with the same color and close fluorescence lifetime.
time-resolved fluorescence imaging fluorescence lifetime image visualization enhancement dual-gated intensity-correlation forensic examination Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(4): 041101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Information Science and Engineering, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 361021, China
2 Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU), Varanasi 221005, Uttar Pradesh, India
3 CREOL, College of Optics and Photonics, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL 32816-2700, USA
4 Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Light Propagation and Transformation, Huaqiao University, Xiamen 361021, China
Encoding information using the topological charge of vortex beams has been proposed for optical communications. The conservation of the topological charge on propagation and the detection of the topological charge by a receiver are significant in these applications and have been well established in free-space. However, when vortex beams enter a diffuser, the wavefront is distorted, leading to a challenge in the conservation and detection of the topological charge. Here, we present a technique to measure the value of the topological charge of a vortex beam obscured in the randomly scattered light. The results of the numerical simulations and experiments are presented and are in good agreement. In particular, only a single-shot measurement is required to detect the topological charge of vortex beams, indicating that the method is applicable to a dynamic diffuser.
intensity correlation vortex beam scattering Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(2): 022603
在相位敏感的改良Hanbury Brown-Twiss(HBT)方案中,热光散斑图包含样本的复透射系数的振幅信息和相位信息。基于此特性,本文提出了一种测量样本的复透射系数及样本厚度的方法。研究结果表明,在样本粗糙程度较小的情况下,通过加入厚度已知的定标层以增加约束条件,就可以从散斑图中提取样本不同位置处的复透射系数,尤其是其相位信息,从而可以计算相对应的样本厚度。计算精度取决于从散斑图中提取的信息量,提取越多,测量越精确。
HBT实验 强度关联 散斑测量 相位测量 HBT scheme intensity-intensity correlation speckle measurement phase measurement
1 中国科学院半导体研究所 光电系统实验室, 北京 100083
2 中国科学院大学 材料与光电研究中心, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院大学 电子电气与通信工程学院, 北京 100049
相比传统水下摄像机, 水下距离选通成像的作用距离可提高两三倍, 同时基于该技术可实现快速高分辨率三维成像, 在水底详查、避障导航、海洋科学研究、矿藏开发等方面具有广泛应用前景。虽然距离选通成像可通过空间切片的方式抑制水体的后向散射噪声, 实现感兴趣区较高质量的成像, 但是, 在选通图像中仍不可避免地存在空间切片水体的后向散射噪声, 导致图像信噪比和对比度降低, 尤其是对于远距离目标或低反射率目标。介绍了针对水下距离选通二维成像及三维成像去噪方面的技术研究。在二维成像方面, 一是采用双平台自适应增强算法提高图像对比度, 更好地满足人眼视觉要求; 二是采用参考水体去噪算法实现含目标图像的水体去噪, 提高信噪比。在三维成像方面, 针对距离能量相关三维成像, 一是利用参考水体去噪算法实现去噪三维重建, 二是采用双边滤波法对三维图像中数据空洞进行修复, 提高三维图像质量。所述四种方法可独立或联合用于水下距离选通成像的去噪增强, 提高水下距离选通成像技术的性能。
水下成像 距离选通成像 三维成像 距离能量相关 图像增强 去噪 underwater imaging range-gated imaging three-dimensional imaging range-intensity correlation image enhancement deblurring 红外与激光工程
2020, 49(2): 0203002
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所量子光学重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
实现脉冲星导航首先需要对脉冲星进行高精度测量,而脉冲星辐射的X射线相干时间极短,到达卫星探测器的光通量极低,必须在极弱光条件下实现强度关联探测来获取脉冲星信息。针对这一问题,使用可见光模拟源进行了强度关联干涉测量实验研究,获取二阶干涉条纹并得到了对应的角直径,分析了符合计数对测量误差的影响,以及探测系统的空间和时间分辨率对强度关联干涉测量结果的影响,为脉冲星X射线强度关联探测系统硬件参数的选取提供了依据。
成像系统 干涉测量 强度关联 X射线 极弱光
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所量子光学重点实验室, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学, 北京 100049
X射线强度关联干涉测量为实现高分辨率脉冲星信息获取提供一条可行的技术途径,但现有的X射线探测器能量分辨率有限,探测到的X射线信号有一定能谱展宽,从而导致测量精度降低。为解决这一问题,基于不同能量相干曲线之间的缩放关系,提出一种强度关联干涉测量能谱展宽校正方法。通过仿真分析了校正前后的测量误差,探讨噪声对该校正方法的影响,并进行了可见光波段的模拟干涉测量实验,结果表明校正后的测量值与理论值相符,从而验证了该方法的有效性。
X射线光学 干涉测量 强度关联 能谱展宽 光学学报
2019, 39(10): 1034001





