Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Laser Polarization and Information Technology, Department of Physics, School of Physics and Engineering, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, China
2 College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Qufu Normal University, Qufu 273165, China
3 College of Precision Instrument & Opto-electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
4 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronics Information and Technical Science, Ministry of Education, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
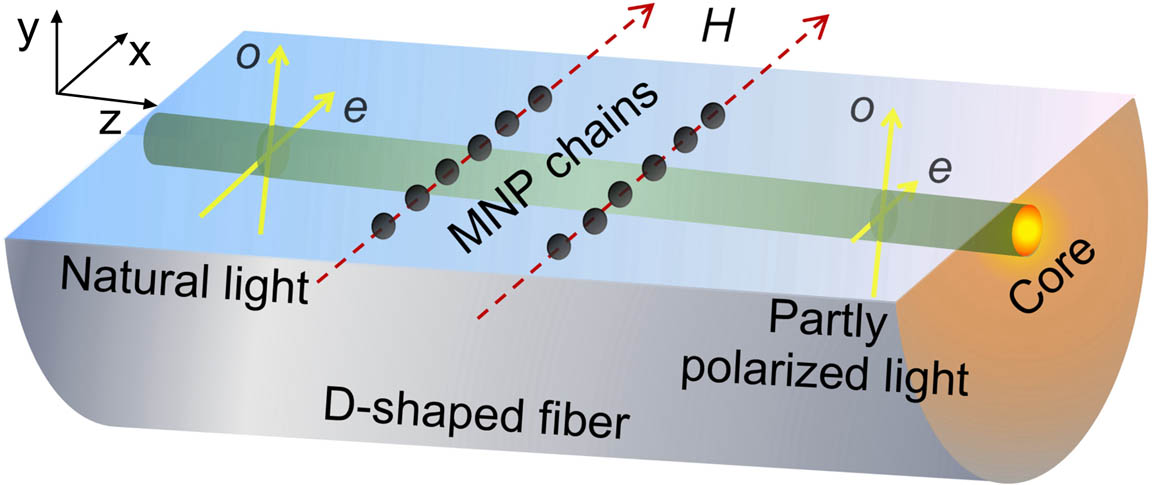
The polarization of a D-shaped fiber is modulated after immersing it in magnetic fluid (MF) and applying a magnetic field. Theoretical analysis predicts that magneto-optical dichroism of MF plays a key role in light polarization modulation. During light polarization modulation, the evanescent wave polarized parallel to the magnetic field has greater loss than its orthogonal component. Light polarization of a D-shaped fiber with a wide polished surface can be modulated easily. High concentration MF and a large magnetic field all have great ability to modulate light polarization.
fiber optics components polarization-selective devices magneto-optic systems magneto-optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2020, 18(1): 010601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Material Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai 200062, China
2 Department of Physics, Shanghai University, Shanghai 200444, China
3 Shanghai Engineering Research Center of Ultra-Precision Optical Manufacturing and Key Laboratory of Micro and Nano Photonic Structures (Ministry of Education), Department of Optical Science and Engineering, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
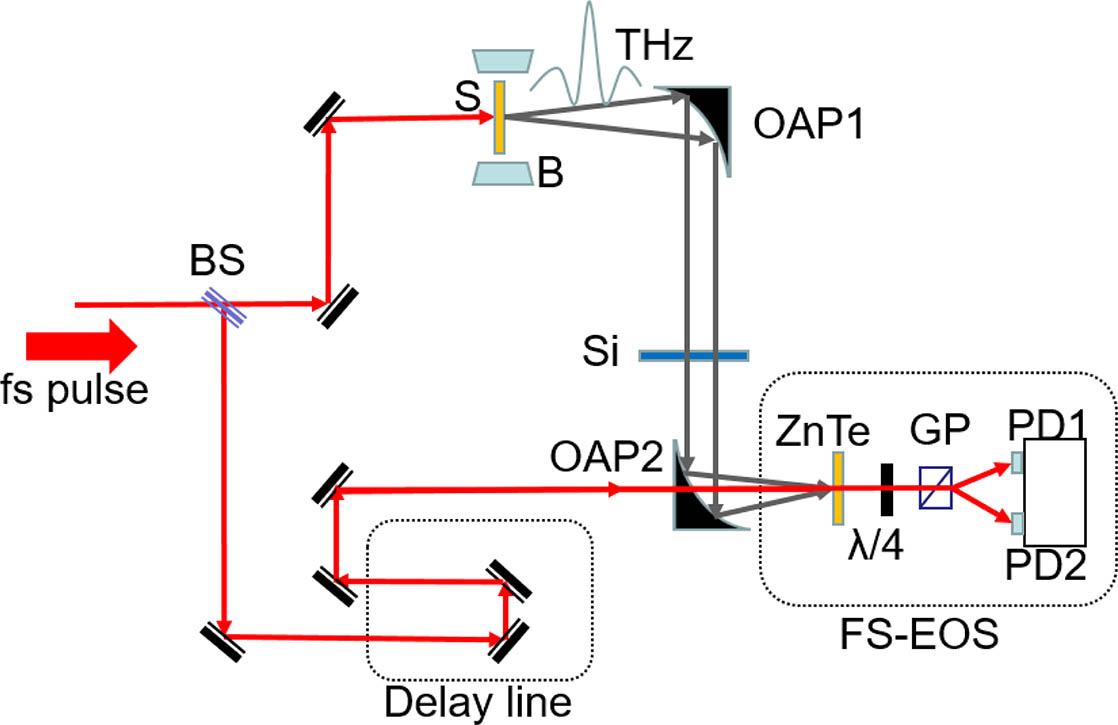
The ultrafast spin dynamic of in-plane magnetized Fe/Pt films was investigated by terahertz emission spectroscopy. The amplitude of the emitted terahertz wave is proportional to the intensity of the exciting laser beams. Both the amplitude and polarity of the terahertz wave can be adjusted by modifying the external magnetic field. The dependency of the amplitude on external magnetic fields is coincident to the hysteresis loops of the sample. Also, the polarity of the terahertz wave is reversed, as the magnetization orientation is reversed. The super-diffusive transient spin current with an inverse spin Hall effect is attributed to the main mechanism of the terahertz emission.
160.3820 Magneto-optical materials 310.6845 Thin film devices and applications 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(8): 081601
朱银龙 1,2,3秦俊 1,2,3张燕 1,2,3梁潇 1,2,3[ ... ]毕磊 1,2,3,*
1 电子科技大学国家电磁辐射控制材料工程技术研究中心, 四川 成都 610054
2 电子科技大学电子薄膜与集成器件国家重点实验室, 四川 成都 610054
3 电子科技大学微电子与固体电子学院, 四川 成都 610054
在室温下实现了全固态Au/Ti/Y2CeFe5O12多层结构的电阻和磁光克尔效应的电场调控。在635 nm波长处,1.5 V的操作电压使饱和磁光克尔旋转角的变化幅度达58.1 μrad,对应的能耗为0.66 nJ/μm2,响应时间为300 s,且该调控具有可逆性与非易失性。以Au/Y2CeFe5O12作为对照,揭示了Ti层对该调控的关键影响。通过表征多层结构的电阻在电场作用下的变化,证实了氧离子迁移的发生。氧离子迁移是电场调控磁光效应的机制,该原型器件为发展电场可调的磁光器件提供了一种新途径。
材料 磁光材料 磁光开关 氧离子迁移 钇铁石榴石 电场调控磁性 激光与光电子学进展
2018, 55(7): 071602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Engineering Research Center of Electromagnetic Radiation Control Materials, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
2 School of Microelectronics and Solid State Electronics, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu 610054, China
Magnetoplasmonic sensors are attractive candidates for ultrasensitive chemical and biomedical sensor applications. A variety of ferromagnetic metal thin films have been used for magnetoplasmonic device applications, yet the dependence of sensor performance on the optical and magneto-optical properties of ferromagnetic metal materials has been rarely studied. In this work, we report the study of enhanced magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE) and sensing performance in Au/FexCo1?x bilayer magneto-optical surface plasmon resonance (MOSPR) transducers. The optical constants of FexCo1?x (x=0, 0.29, 0.47, 0.65, and 1) in a sputter-deposited Au/FexCo1?x device are characterized by the attenuated total internal reflection (ATR) method. FexCo1?x thin films show different MOKEs as a function of the chemical concentration, with the highest transverse MOKE signal observed in Fe0.7Co0.3. Index sensing performance is closely related to the material’s optical and magneto-optical constants. By studying the sensing performance in the parameter space of the Au/FexCo1?x bilayer thicknesses, the highest sensitivity is found to be 0.385 (theoretical) and 0.306 RIU?1 (experimental) in the Au/Fe0.7Co0.3 MOSPR devices. Our research highlights the influence of the optical properties of ferromagnetic material to device sensitivity in MOSPR transducers. The high sensitivity in Au/FexCo1?x MOSPR devices make these structures attractive candidates for chemical and biomedical sensing applications.
(280.0280) Remote sensing and sensors (240.6680) Surface plasmons (160.3820) Magneto-optical materials. Photonics Research
2017, 5(5): 05000385
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Lab of All Optical Network and Advanced Telecommunication Network of Ministry of Education, Institute of Lightwave Technology, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing 100044, China
A high sensitivity magnetic fluid (MF) filled side-hole fiber magnetic field sensor based on surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is designed and investigated. Within the side-hole fiber, the water-based MF is injected into the two side holes, and both of the holes are coated with gold to realize the measurement of the magnetic field by using the SPR effect. The refractive index of the MF changes with different external magnetic fields, resulting in the resonant wavelength moving to other wavelengths. Furthermore, when the external magnetic field increases from 30 to 210.9 Oe, the magnetic field sensitivity can reach to 1.063 nm/Oe.
240.6680 Surface plasmons 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 160.3820 Magneto-optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2016, 14(11): 110603

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 College of Precision Instrument and Opto-Electronics Engineering, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
2 Department of Mechanical Engineering, Columbia University, New York 10027, USA
3 Key Laboratory of Opto-electronics Information Technology (Tianjin University) Ministry of Education, Tianjin 300072, China
4 e-mail: tgliu@tju.edu.cn
A novel magnetic field sensing system based on the fiber loop ring-down technique is proposed in this paper. In the fiber loop, a U-bent single-mode-fiber structure coated with magnetic fluid (MF) serves as the sensing head, and an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is introduced to compensate for the intrinsic loss of the cavity. The ring-down time of the system varies with the change of applied magnetic field due to the tunable absorption coefficient and refractive index of the MF. Therefore, measurement of the magnetic field can be realized by monitoring the ringdown time. The experimental results show that the performance of the system is extremely dependent on the interrogation wavelength, because both the gain of the EDFA and the loss of the sensing head are wavelength dependent. We found that at the optimal wavelength, the ratio of the gain to loss attained its maximum. The sensing system was experimentally demonstrated and a sensitivity of ?0.5951 μs∕Oe was achieved.61107035).
Fiber optics Fiber optics Fiber optics sensors Fiber optics sensors Magneto-optical materials Magneto-optical materials Spectroscopy Spectroscopy time-resolved time-resolved Photonics Research
2016, 4(6): 06000322
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
Tb3Ga5O12 (TGG) is an excellent material for magneto-optical applications, and is the key component in Faraday isolators (FIs). The preparation process of transparent TGG ceramics is experimentally studied. The optical quality and the microstructure of the samples are investigated. The results show that the transmittance of the sample sintered at 1550°C is close to 72% in the region of 500–1500 nm. The Verdet constant at 632.8 nm measured at room temperature is 125.01 rad T 1 m 1, which is almost the same as that of a single crystal.
160.3820 Magneto-optical materials 140.3380 Laser materials 160.4670 Optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(3): 031602

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Ludong University, Yantai 264025, China
2 Engineering Research Center of Optical Instruments and Systems, Ministry of Education, Shanghai Key Lab of Modern Optical Systems, School of Optical-Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai 200093, China
Based on the inverse Faraday effect, a super-long longitudinal magnetization needle can be induced by a transversely polarized needle-shaped electric field. This needle-shaped electric field can be obtained in the focal volume of the objective by focusing an azimuthally polarized vortex beam that is modulated both radially and azimuthally by a specifically designed annular phase filter. The numerical calculation shows that the full widths at half-maximums in longitudinal direction and in transverse direction of the magnetization needle are 28λ and 0.27λ. The corresponding needle aspect ratio of 103 is more than ten times larger than that of the magnetization needle fabricated by electron beam lithography.
210.3820 Magneto-optical materials 260.5430 Polarization 350.5500 Propagation 060.5060 Phase modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2015, 13(5): 052101
Author Affiliations
Abstract
In this study, based on magnetic tunable characteristics of nanoparticle magnetic fluid, we design the photonic crystals' defect-localized modes with a defect layer of nanoparticle magnetic fluids. The transmission spectrum of one-dimensional photonic crystals with a defect layer of nanoparticle magnetic fluid is calculated numerically using the transfer matrix method. The results indicate that the wavelength of defect localized modes moves to short wave with the increasing of magnetic field intensity. The maximum variation is 7 nm. When the thickness deviation of defect layer is in the range of 5 nm, the variation of the wavelength is 6 nm. The bandwidth of the defect localized modes is 0.2 nm and its quality factor is of the order of 103. Therefore, the variation of the wavelength of defect-localized modes, which is caused by the thickness deviation of a defect layer, could be compensated by changing the magnetic field. In this study, the defect-localized modes with a certain wavelength are realized.
160.0160 Materials 160.2260 Ferroelectrics 160.3820 Magneto-optical materials 160.5298 Photonic crystals Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(s1): S11602
1 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所, 上海 200050
2 中国科学院研究生院, 北京 100039
3 上海应用技术学院材料工程系, 上海 200235
采用光学浮区法生长了钙钛矿结构的YFeO3磁光晶体, 研究了影响晶体质量的关键工艺条件。结果表明, 原料棒的直径、均匀性和致密度直接影响晶体生长过程中熔体的稳定性,从而影响晶体的质量。在适当温度下多次预烧结和反复混料, 并通过最后的烧结可获得纯相、均匀和致密的原料棒; 原料棒直径一般控制在10 mm以内; 3~5 mm/h的生长速度适合晶体生长; 生长结束时缓慢降温和退火处理可抑制YFeO3晶体的开裂。在上述优化的工艺参数下, 成功地生长了Φ10 mm×40 mm的YFeO3晶体, 并测试了YFeO3晶体折射率和消光系数在可见光和近红外波段随波长的变化曲线。YFeO3磁光晶体具有较高的折射率。
磁光材料 YFeO3晶体 光学浮区法 折射率





