1 江苏大学机械工程学院,江苏 镇江 212013
2 江苏大学微纳光电子与太赫兹技术研究院,江苏 镇江 212013
3 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所,上海 201800
基于空间光调制器外光路分束进行并行加工是提高超快激光加工效率的有效方法。高均匀度分束算法是实现外光路分束的关键。在实际光路中,由于光路不完全满足理论条件,经典的GS算法生成的多光束均匀度远低于理论值,不满足阵列化激光加工的要求。基于GS?GA算法的思想与图像处理技术,在程序设计中引入了实时反馈的功能,以达到提高分束均匀度的目的。并采用加载菲涅耳透镜相位的方式分离零级光,避免重建光场离轴带来的畸变。最终实现了均匀度接近94%的分束,并通过加工实验验证了高均匀度分束算法在精密加工中的应用效果。
激光技术 空间光调制 分束整形 超快激光精密加工 遗传算法 GS算法 中国激光
2023, 50(16): 1602401
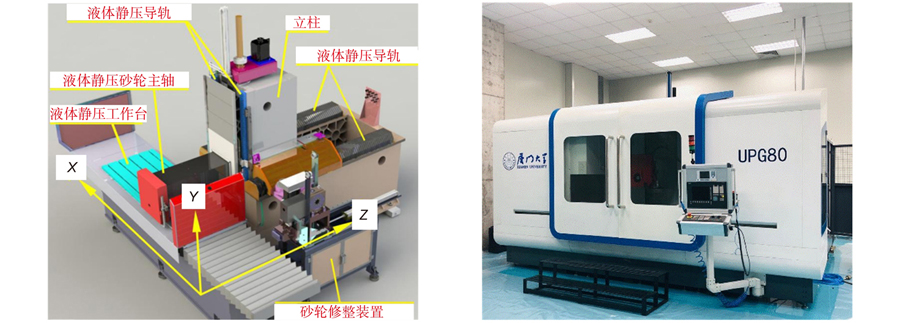
1 厦门大学航空航天学院,福建 厦门 361005
2 厦门大学深圳研究院,广东 深圳 518057
Overview: Driven by the rapid development of national optical projects such as laser nuclear fusion and aerospace telescopes, as well as high-end civilian fields such as advanced instruments and optical lenses, the requirements for full-frequency domain processing errors and surfaces of optical components are becoming more and more stringent. At this stage, the optical components generally need to go through rough grinding, fine grinding, polishing and coating, and other processes, and their surface quality mainly depends on the defect removal ability and error control level of the polishing process. Whether the fine grinding process can obtain better surface shape accuracy and low surface/subsurface damage suppression determines the processing efficiency, and the ultra-precision processing manufacturing equipment is the premise of the realization of ultra-precision machining of the optical components. So far, all countries in the world have invested in the research and development of optical ultra-precision grinding and polishing technology, and have developed more relatively mature high-precision grinding and polishing equipment, which can better meet the processing needs of most of the current optical components. For the core equipment and key technologies required for ultra-precision manufacturing, China has long relied on imports. In order to break through the bottleneck restricting the development of ultra-precision technology in China at this stage, under the traction and drive of the national large-scale engineering project, China has made remarkable progress in optical ultra-precision manufacturing equipment and technology. However, for the optical ultra-precision technology and equipment, there is still a certain gap between China and the international advanced level, and it is necessary to continue to strengthen the research. In addition to the high-end grinding and polishing equipment necessary for the ultra-precision machining of optical components, it is also necessary to strengthen the technical level of a series of key supporting units, such as ultra-precision grinding and polishing processing technology, high-end key functional components, intelligent monitoring technology of processing environment, efficient ultra-precision machining tools, processing and inspection path planning and compensation processing strategies, computer-aided manufacturing and testing software, etc. The research, development, and application of these technologies are related to the development of high-end manufacturing in the civilian fields and national defense fields, and are also the focus of the country. This paper mainly focuses on the ultra-precision machining of large-diameter optical aspherical components. Starting from the grinding and polishing process route, this paper introduces the long-term research progress of the Precision Engineering Laboratory of Xiamen University in the field of large-diameter optical aspherical component processing, and introduces in detail the technical and system achievements such as ultra-precision grinding and polishing equipment, robot-assisted grinding and polishing, equipment intelligent monitoring system, processing technology and control software.
超精密加工 磨抛装备 加工工艺 CAM软件 ultra-precision machining grinding and polishing equipment processing technology CAM software
天津大学精密测试技术及仪器国家重点实验室,微纳制造实验室,天津 300072
介绍了玻璃光学元件精密模压成形技术的原理、玻璃材料、模具制造、模具表面镀膜、结合有限元仿真的模压工艺优化和模压成形设备等核心技术的研究进展,并讨论了当前存在的问题。通过探讨玻璃模压成形技术在自由曲面、微结构、衍射结构表面和晶圆阵列等光学元件中的应用现状,对玻璃元件精密模压成形技术的发展趋势和挑战进行了展望。
光学设计 光学玻璃 非球面透镜 自由曲面透镜 超精密加工 玻璃精密模压 微结构制造
Author Affiliations
Abstract
EPSRC Future Metrology Hub, Centre for Precision Technologies, University of Huddersfield, Huddersfield HD1 3DH, United Kingdom
Freeform optics has become the most prominent element of the optics industry. Advanced freeform optical designs supplementary to ultra-precision manufacturing and metrology techniques have upgraded the lifestyle, thinking, and observing power of existing humans. Imaginations related to space explorations, portability, accessibility have also witnessed sensible in today’s time with freeform optics. Present-day design methods and fabrications techniques applicable in the development of freeform optics and the market requirements are focussed and explained with the help of traditional and non-traditional optical applications. Over the years, significant research is performed in the emerging field of freeform optics, but no standards are established yet in terms of tolerances and definitions. We critically review the optical design methods for freeform optics considering the image forming and non-image forming applications. Numerous subtractive manufacturing technologies including figure correction methods and metrology have been developed to fabricate extreme modern freeform optics to satisfy the demands of various applications such as space, astronomy, earth science, defence, biomedical, material processing, surveillance, and many more. We described a variety of advanced technologies in manufacturing and metrology for novel freeform optics. Next, we also covered the manufacturing-oriented design scheme for advanced optics. We conclude this review with an outlook on the future of freeform optics design, manufacturing and metrology.
freeform optics optical design optical fabrication ultra-precision machining surface metrology International Journal of Extreme Manufacturing
2022, 4(3): 032004
同济大学 物理科学与工程学院 精密光学工程技术研究所,先进微结构材料教育部重点实验室,上海市数字光学前沿科学研究基地,上海市全光谱高性能光学薄膜器件与 应用专业技术服务平台,上海200092
极紫外、X射线为微观物质认识、宏观空间探测提供了高精度的观测手段,但这类观测的实现需要大量高精度光学反射元件的支撑。由于极紫外、X射线在光学表面更易发生散射,其光学反射镜基底的精度需求和制作技术也明显区别于长波元件。近年来,同济大学精密光学工程技术研究所建立了极紫外、X射线反射元件基底的超精密加工与检测平台,研发了超光滑非球面的离子束修形技术,提出了基于泽尼克多项式的随机离轴旋转绝对检测方法,形成了极紫外、X射线光学用反射镜基底的高精度全流程研制技术,并将该技术成功地应用于国内和国际短波光学大科学装置中。本文综述了本课题组在极紫外、X射线用反射镜制作领域中的研究进展。
超精密加工 极紫外 X射线 反射镜基底 非球面元件 绝对检测 ultra-precision machining extreme ultraviolet X-ray reflector substrates aspheric surface absolute measurement 光学 精密工程
2022, 30(21): 2688
1 广东科技学院,广东东莞523083
2 华南理工大学 机械与汽车工程学院,广东广州510640
针对ITO玻璃表面线路激光刻蚀中因定位问题玻璃工件产生的微变形,采用微孔陶瓷对工件进行微气流阵列加压,确保高精度的激光刻蚀加工。分析不同加工工艺下的微气流压力分布,探究气流压力和刻蚀间隙对ITO玻璃刻蚀表面平面度的作用机制。结果表明:经微孔气流加压后,工件在气体流动的区域受到正压力,加工区域的压力分布较为均匀。由此可知,工件表面受到均布气压有利于刻蚀表面的定位,但过大的压力会导致工件微变形。实验结果显示:在合适的压力下,微孔气流加压可使得平面度低至8 μm,当压力在0.16~0.2 kPa,刻蚀间隙在1.8~1.9 mm时,工件表面压力为13.2~14.4 Pa,此时平面度最好,微米尺度的刻蚀线路清晰,不产生破损。最后,对微孔气流加压的ITO玻璃进行激光刻蚀加工,可得到8 μm以及25 μm的表面微细线路,解决了通常无微孔气流加压的刻蚀工艺导致局部断点或变形线路引起产品短路或开路等问题。
激光刻蚀 微孔气流 ITO玻璃 刻蚀工艺 高精密加工 laser etching microporous airflow ITO glass etching process high precision machining 光学 精密工程
2022, 30(13): 1564
1 中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所精密光学制造与检测中心, 上海 201800
2 中国科学院大学材料科学与光电技术学院, 北京 100049
传统的接触式加工不可避免地会在光学元件上产生亚表层损伤,而大气等离子体抛光(APPP)具有非接触、可定量去除、加工过程不受材料性能影响等优点,在光学加工领域有着巨大的应用潜力。但在实际加工过程中,光学元件加工后的收敛效果并不明显,经验证明去除量随驻留时间的变化呈非线性而导致了加工误差。针对这一问题,首先优化了加工参数;之后研究了加工原理以及加工残余物对后续加工的影响,分析了加工存在非线性效应的原因;提出了一种基于变去除函数的驻留时间算法,并进行了实验验证。结果显示,对尺寸为120 mm×65 mm×10 mm的熔石英光学元件进行变去除函数加工实验,面形峰谷值(PV)的平均收敛率由加工前的21.41%提升至加工后的60.52%,面形均方根值(RMS)的平均收敛率由加工前的24.13%提升至加工后的74.79%,实现了熔石英元件的高精度快速加工,验证了变去除函数加工的有效性。
材料 大气等离子体抛光 去除函数 超精密加工 熔石英 中国激光
2021, 48(24): 2403002
1 南昌航空大学无损检测教育部重点实验室, 江西 南昌 330063
2 中国科学技术大学精密机械与精密仪器系, 安徽 合肥 230026
氟化钙晶体微腔相比玻璃材料微腔,具有吸收系数小、缺陷少、纯度高、对周围环境湿度不敏感的优势,在微波光子学、陀螺仪和非线性光学等领域具有潜在的应用价值。通过超精密加工技术制备了回转椭球体氟化钙毫米晶体微腔。研发了一套精密加工系统来制备这种微腔,所制得的微腔形状为回转椭球体,微腔结构边缘表面粗糙度低至1.97 nm。使用光纤锥波导与氟化钙微腔实现了高效耦合,此耦合系统展现了高达~10 8的超高品质因子Q值和低至约0.03 nm的自由光谱范围。这些结果证明了针对氟化钙微腔的加工手段具有重要意义,将大大促进其应用。氟化钙微腔的特性也证明了它在光学滤波器、腔量子动力学、非线性光学和陀螺仪等应用中的潜力。
光学器件 光学微腔 超精密加工 光学谐振器 回音壁模式





