
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Sun Yat-Sen University, State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, School of Physics, Guangzhou, China
2 Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Quantum Metrology and Sensing, School of Physics and Astronomy, Zhuhai, China
3 Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory, Zhuhai, China
Scattered light imaging through complex turbid media has significant applications in biomedical and optical research. For the past decade, various approaches have been proposed for rapidly reconstructing full-color, depth-extended images by introducing point spread functions (PSFs). However, because most of these methods consider memory effects (MEs), the PSFs have angular shift invariance over certain ranges of angles. This assumption is valid for only thin turbid media and hinders broader applications of these technologies in thick media. Furthermore, the time-variant characteristics of scattering media determine that the PSF acquisition and image reconstruction times must be less than the speckle decorrelation time, which is usually difficult to achieve. We demonstrate that image reconstruction methods can be applied to time-variant thick turbid media. Using the time-variant characteristics, the PSFs in dynamic turbid media within certain time intervals are recorded, and ergodic scattering regimes are achieved and combined as ensemble point spread functions (ePSFs). The ePSF traverses shift-invariant regions in the turbid media and retrieves objects beyond the ME. Furthermore, our theory and experimental results verify that our approach is applicable to thick turbid media with thickness of 1 cm at visible incident wavelengths.
scattered light imaging memory effect thick turbid media image reconstruction Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(2): 026010
1 中国科学技术大学环境科学与光电技术学院,安徽 合肥 230022
2 中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院安徽光学精密机械研究所中国科学院大气光学重点实验室,安徽 合肥 230031
3 先进激光技术安徽省实验室,安徽 合肥 230037
基于混浊大气表观调制传递函数的光谱特征,提出一个新的成像质量评价因子作为波段优选的依据,得到了不同波段的成像效果。同时分析了优选波段的影响因素,给出了典型大气条件、典型带宽下的成像优选波段,即在1036~1046 nm、1620~1630 nm波段可得到典型区域相对普适的、良好的成像质量。最后通过成像实验对优选方法的有效性进行了初步验证。
光谱学 调制传递函数 混浊介质中的成像 图像质量分析 光学学报
2022, 42(24): 2430003
朱京平 1,2,3邓金鑫 1,2,3李浩翔 1,2,3郭奉奇 1,2,3侯洵 1,2,3
1 西安交通大学 电子与信息学部电子科学与工程学院,西安
2 电子物理与器件教育部重点实验室,西安
3 陕西省信息光子技术重点实验室,西安
在浑浊介质中进行光学成像时,由于受介质吸收与散射影响,目标信号被淹没在背景噪声中,导致图像的清晰度严重下降。利用光的偏振信息可显著提升浑浊介质中目标的探测能力,其中偏振差分作为代表性偏振成像技术,充分挖掘介质光与场景光的偏振特性差异对背向散射噪声实现偏振共模抑制。由于其系统结构简单、可移植性好、适用领域广泛、凸显边缘等优势备受关注。该技术不仅可以作为物理光学成像方法对水下浑浊环境、生物组织、大气雾霾散射环境中目标进行高对比度成像,还可作为光学传感器件抑制杂散光的有效手段,从提出至今已积累了大量优秀的研究成果,从偏振差分成像技术的基本原理出发,根据成像应用场景的不同从两方面介绍了该技术一系列最新的研究进展,并对偏振差分成像未来可能的发展方向进行了展望,期望为该领域的后续研究提供指引。
偏振差分成像 浑浊介质 偏振共模抑制 成像对比度 polarization differential imaging turbid media polarization common-mode suppression imaging contrast
1 中国医学科学院,北京协和医学院生物医学工程研究所,天津 300192
2 首都医科大学附属北京友谊医院,北京 100050
3 中国医学科学院,北京协和医学院北京协和医院,北京 100730
本研究的目的在于获得Nd∶YAG激光在血液中传播的几何尺寸损耗与血液厚度的关系,从而获得适用于Nd∶YAG激光在血液中传播的修正朗伯比尔定律的准确表达式。通过所建立的Nd∶YAG激光在离体血液中透过的光检测实验系统,检测得到激光在穿透目标厚度为1.0~2.5 mm(临床脉管性病变的常见血层厚度)的圆柱形血层后的光衰减情况,并基于R语言和统计学方法,建立了几何尺寸损耗与血液厚度之间的线性、对数、指数和乘幂回归模型。其中,线性回归模型的拟合效果最好,R2值可达0.9219,由此获得适用于Nd∶YAG激光在血液中传播的修正朗伯比尔定律表达式。
激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(6): 0617023
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Sharif University of Technology, Tehran 11365-9161, Iran
2 Biomedical Engineering Department, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI 48201, USA
3 Department of Dermatology, Wayne State University, School of Medicine, Detroit, MI 48202, USA
4 Barbara Ann Karmanos Cancer Institute, Detroit, MI 48202, USA
By manipulating the phase map of a wavefront of light using a spatial light modulator, the scattered light can be sharply focused on a specific target. Several iterative optimization algorithms for obtaining the optimum phase map have been explored. However, there has not been a comparative study on the performance of these algorithms. In this paper, six optimization algorithms for wavefront shaping including continuous sequential, partitioning algorithm, transmission matrix estimation method, particle swarm optimization, genetic algorithm (GA), and simulated annealing (SA) are discussed and compared based on their e±ciency when introduced with various measurement noise levels.
Wave front shaping algorithms optimization turbid media wavefront shaping Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2019, 12(4): 1942002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Foshan University, Foshan 528000, P. R. China
2 Department of Physics, College of Science, Shantou University, Shantou 515063, P. R. China
3 School of Physics, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, P. R. China
Visual perception of humans penetrating turbid medium is hampered by scattering. Various techniques have been prompted recently to recover optical imaging through turbid materials. Among them, speckle correlation based on deconvolution is one of the most attractive methods taking advantage of high imaging quality, robustness, ease-of-use, and ease-of-integration. By exploiting the point spread function (PSF) of the scattering system, large Field-of-View, extended Depth-of-Field, noninvasiveness and spectral resoluation are now available as successful solutions for high quality and multifunctional image reconstruction. In this paper, we review the progress of imaging through a scattering medium based on deconvolution method, including the principle, the breakthrough of the limitation of the optical memory effect, the improvement of the deconvolution algorithm and innovative applications.
Speckle correlation deconvolution scattering medium imaging through turbid media Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2019, 12(4): 1930005
山东理工大学物理与光电工程学院, 山东 淄博 255000
基于HSI(Hue, Saturation and Intensity)颜色空间提出一种快速偏振光学去雾方法。利用HSI颜色空间中强度与颜色无关的优势,在强度通道中利用偏振光学去雾方法进行去雾处理,然后利用颜色恒常性校正方法对图像的颜色畸变进行校正。该技术不仅具有良好的图像细节恢复能力,还有效地提高了偏振光学去雾方法的计算效率。与目前流行的去雾方法进行对比后可知,该技术可以得到更好或者相同的实验效果,但其执行效率更高。所提出的方法在图像实时去雾和视频去雾领域有广阔的应用前景。
成像系统 偏振成像 图像增强 能见度 浑浊介质成像 激光与光电子学进展
2019, 56(14): 141103
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Center of Materials Science and Optoelectronics Engineering, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
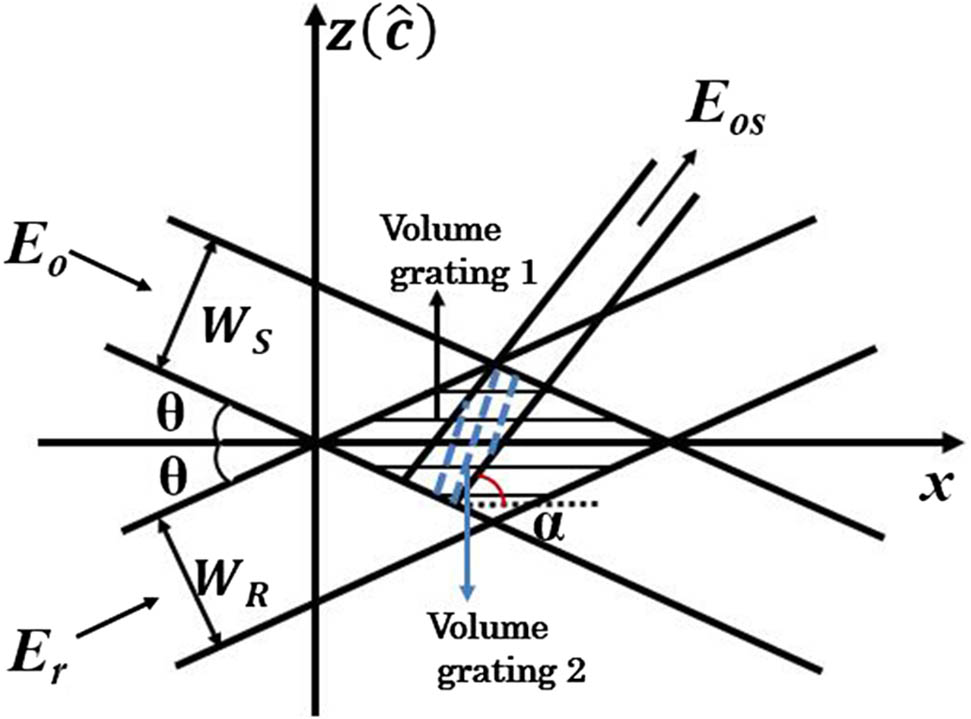
A method is proposed to optimize the recording structure of the photorefractive volume grating to compensate high spatial frequency in the distorted wavefront by optical phase conjugation. Based on the coupled-wave equation, the diffraction efficiency of the recorded grating formed by the scattered beams in different recording structures is simulated. The theoretical results show that the recorded modulations with high spatial frequency can be significantly improved in the small recording angle. In the experiment, three recording structures with the recording angles of 7.5°, 30°, and 45° are chosen to verify the compensation effect. Compared with the reconstructed image in the large recording angle of 45°, the signal to noise ratio of the image recorded at 7.5° increases to 3.2 times of that at 45°.
090.7330 Volume gratings 110.0113 Imaging through turbid media 070.5040 Phase conjugation Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(7): 070901

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Biomedical Science and Engineering, Institute of Integrated Technology, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju 61005, Korea
2 School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju 61005, Korea
3 School of Undergraduate Studies, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, Daegu 42988, Korea
Blood oxygenation and flow are both important parameters in a living body. In this Letter, we introduce a simple configuration to simultaneously measure blood flow and oxygenation using an off-the-shelf spectrometer. With the integration time of 10 ms, flow phantom measurements, a liquid blood phantom test, and an arm cuff occlusion paradigm were performed to validate the feasibility of the system. We expect this proof-of-concept study would be widely adopted by other researchers for acquiring both blood flow and oxygenation changes due to its straightforward configuration and the possibility of multimodal measurement.
170.2655 Functional monitoring and imaging 170.3890 Medical optics instrumentation 170.7050 Turbid media Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(7): 071701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Research Department of Information Photonics, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an 710119, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China
3 Department of Electronics Science and Technology, School of Electronic & Information Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
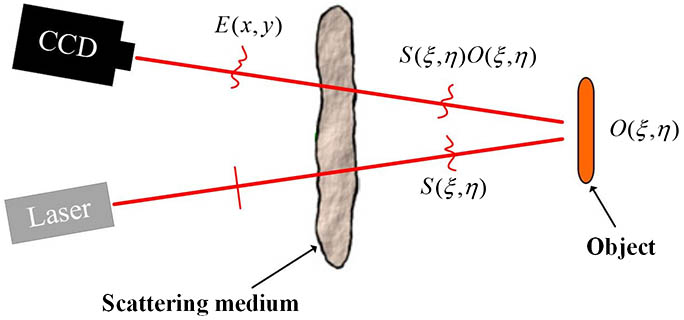
Traditional one-way imaging methods become invalid when a target object is completely hidden behind scattering media. In this case, it has been much more challenging, since the light wave is distorted twice. To solve this problem, we propose an imaging method, so-called round-trip imaging, based on the optical transmission matrix of the scattering medium. We show that the object can be recovered directly from the distorted output wave, where no scanning is required during the imaging process. We predict that this method might improve the imaging speed and have potential application for real-time imaging.
110.0113 Imaging through turbid media 110.1650 Coherence imaging 110.1758 Computational imaging Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(4): 041102





