Author Affiliations
Abstract
Indian Institute of Information Technology-Allahabad, Prayagraj 211015, India
The impulse response for a phase-change material Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST)-based photodetector integrated with a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) waveguide is simulated using finite difference time domain method. The current is calculated by solving the drift-diffusion model for short pulse (~10 fs) excitation for both of the stable phases. Full width at half-maximum values of less than 1 ps are found in the investigation. The crystalline GST has higher 3 dB bandwidth than the amorphous GST at a 1550 nm wavelength with responsivities of 21 A/W and 18.5 A/W, respectively, for a 150 nm thick GST layer biased at 2 V. A broad spectrum can be utilized by tuning the device using the phase-change property of material in the near infrared region.
040.3060 Infrared 160.4670 Optical materials 230.5160 Photodetectors 320.7080 Ultrafast devices Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(10): 100401
中国科学院上海光学精密机械研究所, 上海 201800
上海超强超短激光实验装置(SULF)是上海建设具有全球影响力的科创中心、打造世界级重大科技基础设施集群的首批重大项目之一。结合国内外超强超短激光研究现状和趋势, 简单介绍了SULF的研制背景、建设现状和未来主要应用和发展方向。
激光技术 超快器件 超强超短激光
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics and Department of Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (MoE) and School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
4 SUPA, Department of Physics, University of Strathclyde, Glasgow G4 0NG, United Kingdom
The temporal profiles of high-power short-pulse lasers reflected from self-induced plasma mirrors (PMs) were measured with high temporal resolution in the sub-picosecond window. The leading front shape of the laser pulse is found to depend sensitively on the laser fluence on the PM surface. Spectral modulation plays a key role in pulse profile shaping. Our findings will extend our knowledge on properly using PMs.
320.5540 Pulse shaping 320.7080 Ultrafast devices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(10): 103202

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Surface Physics and Department of Physics, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
2 Key Laboratory for Laser Plasmas (MoE) and School of Physics and Astronomy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
3 Collaborative Innovation Center of IFSA (CICIFSA), Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
The femtosecond laser pulses reflected from the self-induced plasma mirror (PM) surface are characterized. More than two orders of magnitude improvement on intensity contrast both in nanosecond and picosecond temporal scales are measured. The far-field distribution, i.e., focusability, is measured to degrade in comparison with that without using a PM. Experiments on proton accelerations are performed to test the effect of the balance between degraded focusability and increased reflectivity. Our results show that PM is an effective and robust device to improve laser contrast for applications.
320.5540 Pulse shaping 320.7080 Ultrafast devices Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 013201

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of California—Davis, Davis, California 95618, USA
2 W&WSens Devices, Inc., 4546 El Camino, Suite 215, Los Altos, California 94022, USA
3 Electrical Engineering, Baskin School of Engineering, University of California, Santa Cruz, California 95064, USA
4 e-mail: sislam@ucdavis.edu
In this paper, high-speed surface-illuminated Ge-on-Si pin photodiodes with improved efficiency are demonstrated. With photon-trapping microhole features, the external quantum efficiency (EQE) of the Ge-on-Si pin diode is >80% at 1300 nm and 73% at 1550 nm with an intrinsic Ge layer of only 2 μm thickness, showing much improvement compared to one without microholes. More than threefold EQE improvement is also observed at longer wavelengths beyond 1550 nm. These results make the microhole-enabled Ge-on-Si photodiodes promising to cover both the existing C and L bands, as well as a new data transmission window (1620–1700 nm), which can be used to enhance the capacity of conventional standard single-mode fiber cables. These photodiodes have potential for many applications, such as inter-/intra-datacenters, passive optical networks, metro and long-haul dense wavelength division multiplexing systems, eye-safe lidar systems, and quantum communications. The CMOS and BiCMOS monolithic integration compatibility of this work is also attractive for Ge CMOS, near-infrared sensing, and communication integration.
Photodiodes Ultrafast devices Photonics Research
2018, 6(7): 07000734
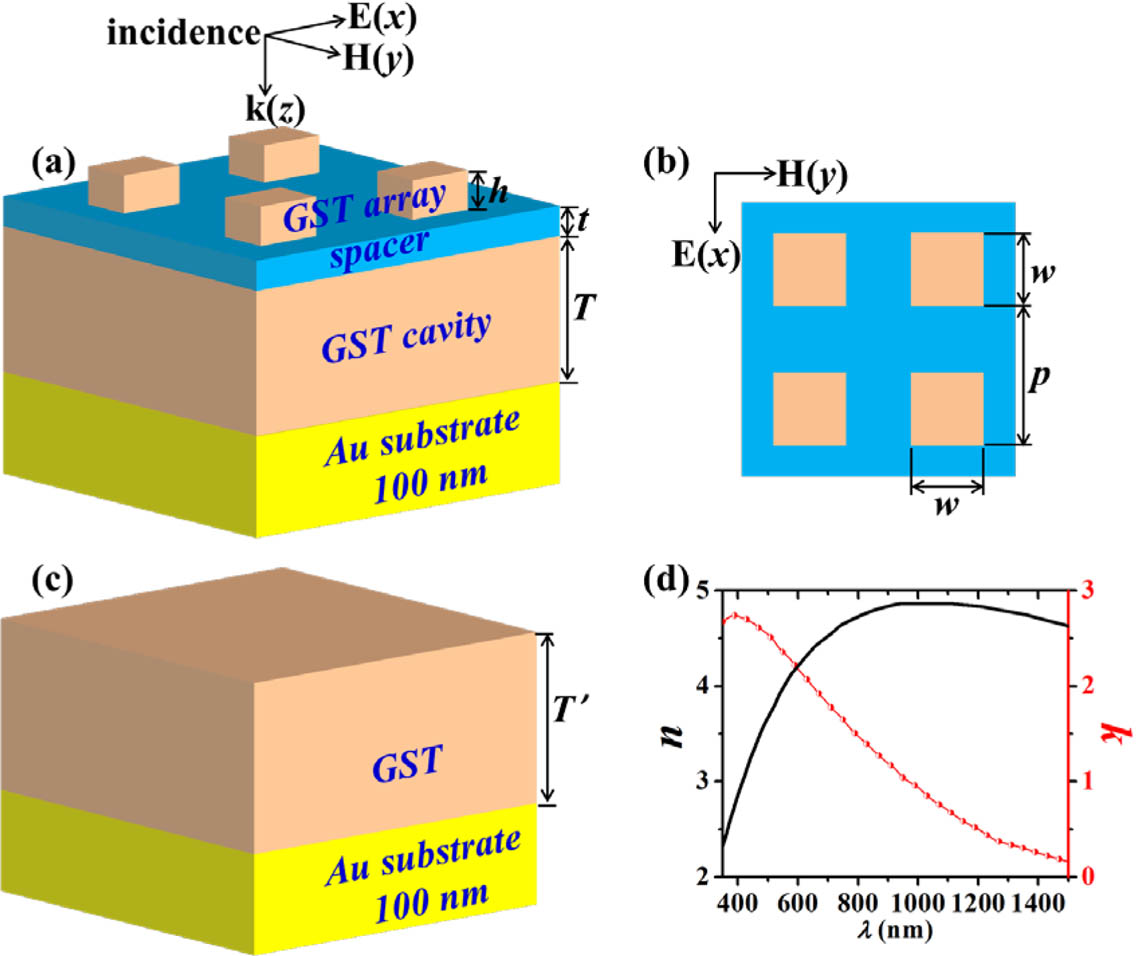
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Laboratory of Optical Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, P.O. Box 603, Beijing 100190, China
We numerically demonstrate a novel ultra-broadband polarization-independent metamaterial perfect absorber in the visible and near-infrared region involving the phase-change material Ge2Sb2Te5 (GST). The novel perfect absorber scheme consists of an array of high-index strong-absorbance GST square resonators separated from a continuous Au substrate by a low-index lossless dielectric layer (silica) and a high-index GST planar cavity. Three absorption peaks with the maximal absorbance up to 99.94% are achieved, owing to the excitation of plasmon-like dipolar or quadrupole resonances from the high-index GST resonators and cavity resonances generated by the GST planar cavity. The intensities and positions of the absorption peaks show strong dependence on structural parameters. A heat transfer model is used to investigate the temporal variation of temperature within the GST region. The results show that the temperature of amorphous GST can reach up to 433 K of the phase transition temperature from room temperature in just 0.37 ns with a relatively low incident light intensity of 1.11 × 108 W∕m2, due to the enhanced ultra-broadband light absorbance through strong plasmon resonances and cavity resonance in the absorber. The study suggests a feasible means to lower the power requirements for photonic devices based on a thermal phase change via engineering ultra-broadband light absorbers.
Metamaterials Metamaterials Photothermal effects Photothermal effects Surface plasmons Surface plasmons Microcavities Microcavities Absorption Absorption Ultrafast devices Ultrafast devices Photonics Research
2016, 4(4): 04000146
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Joint Laboratory on High Power Laser and Physics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, Shanghai 201800, China
2 Shanghai Institute of Laser Plasma, China Academy of Engineering Physics, Shanghai 201800, China
Pulse contrast is an important parameter for ultrafast pulses. It shall be 108 or higher in order to avoid effect from noise before main pulse. Diagnostics with cross-correlation can achieve high temporal resolution such as ~7fs. Cross-correlation has advantage in pulse contrast measurement than autocorrelation because it can distinguish noise before or after main pulse. High dynamic range is also essential in pulse contrast measurement. Cross-correlation signal from a single shot is converted into a signal series through fiber array, which can be analyzed by a set of a PMT and an oscilloscope. Noise from nonlinear crystal and scatter needs decrease to improve dynamic range. And pulse power is also discussed in pulse contrast experiments. Time delay τ is generated by travel stage in measurement for repetition pulses. Then energy instability will generate error in this measurement. In measurement for single shot pulse, time delay τ is generated by slant angle of beams. The scanning procession is completed with thousands parts of beam section within a single shot, and error will generated from no uniformity in near field. Performance test of pulse contrast measurement is introduced in subsequent sections. Temporal resolution is testified by self-calibration. Dynamic range is judged by a parallel flat. At last pulse contrast of petawatt laser is diagnosed by a single shot cross-correlator with high confidence. The ratio is 10-6 at 50ps before main pulse, and 10-4 at 10ps before main pulse.
ultrafast lasers petawatt laser high power laser pulse contrast measurement cross-correlation optical instruments ultrafast measurements ultrafast devices Collection Of theses on high power laser and plasma physics
2015, 13(1): 93450R
Author Affiliations
Abstract
An all-optical serial-to-parallel converter (SPC) utilizing two cascaded phase modulators and optical band-pass filters (OBPFs) is experimentally investigated and applied to demultiplex an 80-GBd optical time-division multiplexing (OTDM) return-to-zero (RZ) differential quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) signal. Two 40-GBd OTDM tributaries are error-free demultiplexed with a power penalty of approximately 4 dB in the worst case. With its advantages of compact structure, high speed, low power penalty, simultaneous two-tributary operation, and no assistance from a light source, the SPC has potential for use in future OTDM networks. However, the performance of the SPC still needs improvement.
320.7080 Ultrafast devices 320.1590 Chirping 060.5060 Phase modulation Chinese Optics Letters
2012, 10(11): 113201
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Devices and Systems of Ministry of Education and Guangdong Province, Institute of Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
Streak camera has high temporal resolution and high sensitivity, and is a powerful tool in biomedical study to measure fluorescence lifetime and perform fluorescence lifetime imaging. However, nonuniformity of the gain in the streak tube and nonlinearity of the sweeping speed limit the precision of fluorescence lifetime measurement, particularly when fluorescence lifetimes are short. We have constructed a twophoton excitation fluorescence lifetime measurement system that is based on a synchroscan streak camera and have developed accordingly a method to correct the effect of gain nonuniformity and nonlinearity of sweeping speed on the measurement precision. A continuous-wave laser of high stability is used to calibrate the gain of the streak camera, and a Fabry-Perot etalon is used to calibrate the nonlinearity of the sweeping speed. Fitting algorithms are used to correct the gain of the streak camera and nonlinearity of the sweeping speed respectively, which significantly improves the measurement precision of the system, as characterized through the fluorescence lifetime of the short-lived fluorescence dye, Rose Bengal. Experimental results show that the measurement fluctuation of the lifetime has been improved from more than 10% to 2% after correcting the effects of gain nonuniformity and sweeping speed nonlinearity.
荧光寿命成像 扫描相机 扫描速度 非线性 非均匀性 170.0110 Imaging systems 170.0180 Microscopy 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging 170.6920 Time-resolved imaging 320.7080 Ultrafast devices Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(10): 934
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Physics, Changchun University of Science and Technology, Changchun 130022, China
2 Department of Physics and Center of Applied Photonics, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany
Ultrafast spectroscopy of semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) is measured using a femtosecond pump-probe experiment. This allows dynamic responses of SESAM in the cavity to be concluded by ultrafast spectroscopy. Change in reflection is measured as a function of pump-probe delay for different pump excitation fluences. Change of nonlinear reflection of SESAM is measured as a function of incident light energy density. When the excitation fluence increases, nonlinear change in ultrafast spectroscopy of SESAM becomes increasingly significant. When SESAM is pumped by an ultrahigh excitation fluence, the energy density of which is approximately 1400 \mu J/cm2, two-photon absorption can be observed visibly in its ultrafast spectroscopy.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 320.7080 Ultrafast devices Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(7): 676





