2020, 18(11) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第18卷 第11期
Scaling law in nonsequential double ionization by counter-rotating two-color circularly polarized laser fields Download:857次
Download:857次
 Download:857次
Download:857次Nonsequential double ionization (NSDI) of noble gas atoms in counter-rotating two-color circularly polarized (CRTC) laser fields is investigated. A scaling law is concluded by qualitatively and quantitatively comparing the momentum distributions of two electrons from NSDI in CRTC laser fields for different atoms with different parameters. The scaling law indicates that the momentum distributions from an atom driven by CRTC laser frequency
scaling law two-color laser nonsequential double ionization Screen printing of upconversion NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ with Li+ doped for anti-counterfeiting application Download:811次
Download:811次
 Download:811次
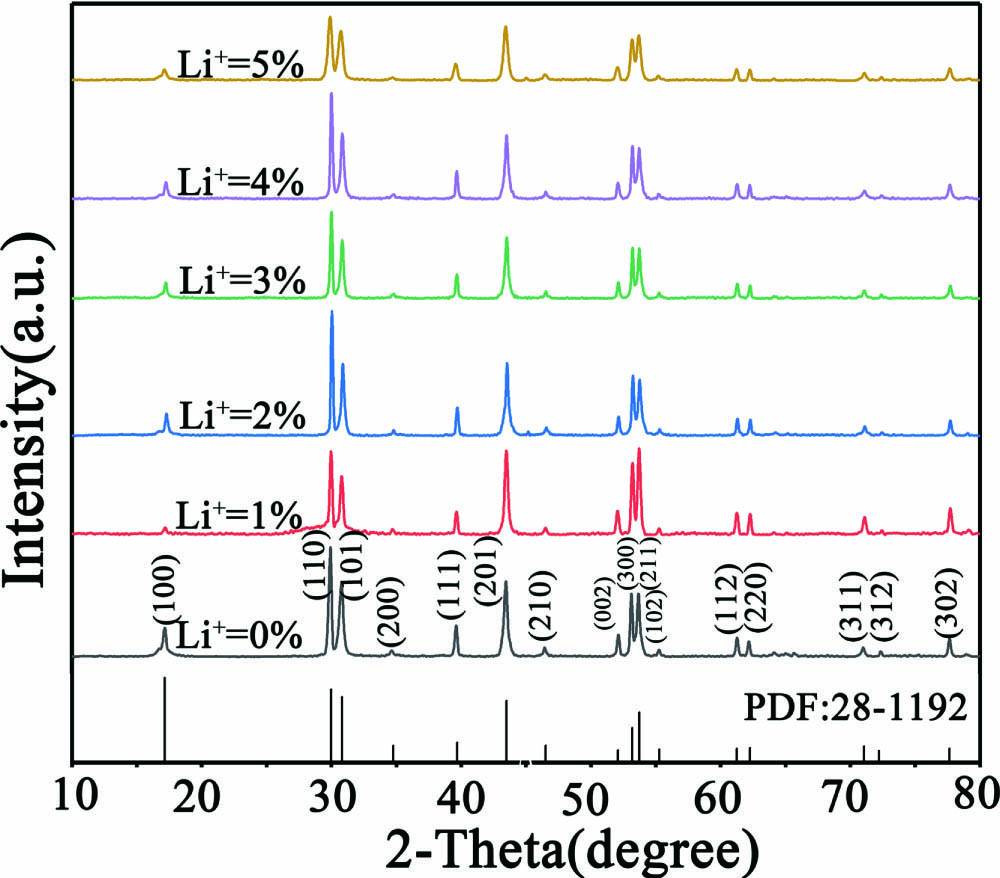
Download:811次Li ions affect the upconversion efficiency by changing the local crystal field of the luminescent center. Herein, in order to improve the upconversion efficiency of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+, a series of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ micro-particles with different Li+ doping concentrations were synthesized by the hydrothermal synthesis method, respectively. Firstly, the structure and morphology of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ upconversion micro-particles (UCMPs) with different doping concentrations were analyzed by X-ray diffraction and a scanning electron microscope (SEM). SEM results show that the UCMPs are not only highly crystallized, but also have hexagons with different Li+ concentrations of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+. X-ray diffraction shows that the crystal field around Eu3+ changes with the increase of Li+ concentration. Then, the fluorescence spectrum of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ was studied under the irradiation of a 980 nm laser. The results show that the fluorescence intensity of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ with 2% Li+ is the strongest, which is twice the intensity of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ without Li+. Finally, the fluorescence imaging analysis of NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ with 2% Li+ concentration was carried out. The UCMPs are used to screen printing to evaluate the imaging effect on different sample surfaces. The results show NaYF4:Yb3+/Eu3+ (with 2% Li+) has great application prospects in anti-counterfeiting recognition.
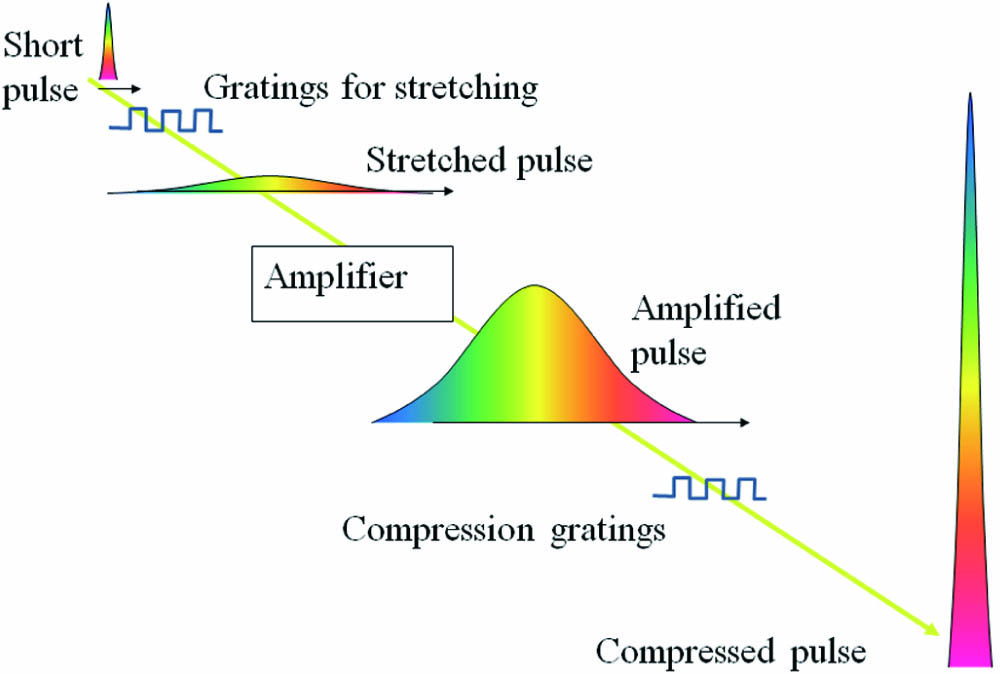
upconversion micro-particles hydrothermal synthesis anti-counterfeiting identification screen printing It is well-known that the chirped pulse amplification (CPA) technique won the award for the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physics to Mourou and Strickland. The compression and stretching using gratings is the essence of the CPA technique for amplifying femtosecond laser pulses. It seems the public is less aware that there are also other structures for compression and stretching of femtosecond laser pulses using other diffractive gratings, such as doubled-density gratings and deep-etched gratings. Therefore, from the view of diffractive optics, the CPA technique is reviewed with different approaches and experimental implementations that are not only useful for a more comprehensive retrospective overview of CPA, but also for the prospective of the CPA technique, which might lead us to new areas of picometer and femtometer optics in the future.
chirped pulse amplification femtosecond diffractive gratings We experimentally demonstrated an approach to generate arbitrary total angular momentum (TAM) states by using two liquid crystal devices. Photons’ TAM, the sum of spin and orbital angular momenta (SAM and OAM) under paraxial approximation, has found many applications in optics and attracted increasing attention in recent years. Our approach is based on the orthogonality of two eigen SAM components, that arbitrary TAM states will be produced through encoding different holograms in one system. The comparison with theoretical predications yields an excellent agreement, including both the separable state and the non-separable state. The proposed scheme takes a step forward for generating complex structured fields and broadens its application to various fields like laser processing and large capacity data transmission.
diffraction gratings polarization Flat transmitted serrated-phase high-contrast-index subwavelength grating beam splitter Download:632次
Download:632次
 Download:632次
Download:632次We proposed a method to form a flat transmitted serrated-phase (SP) high-contrast-index subwavelength grating (HCG) beam splitter (HBS) for all dielectric materials, which is to alternately arrange two kinds of grating bars with a phase difference of
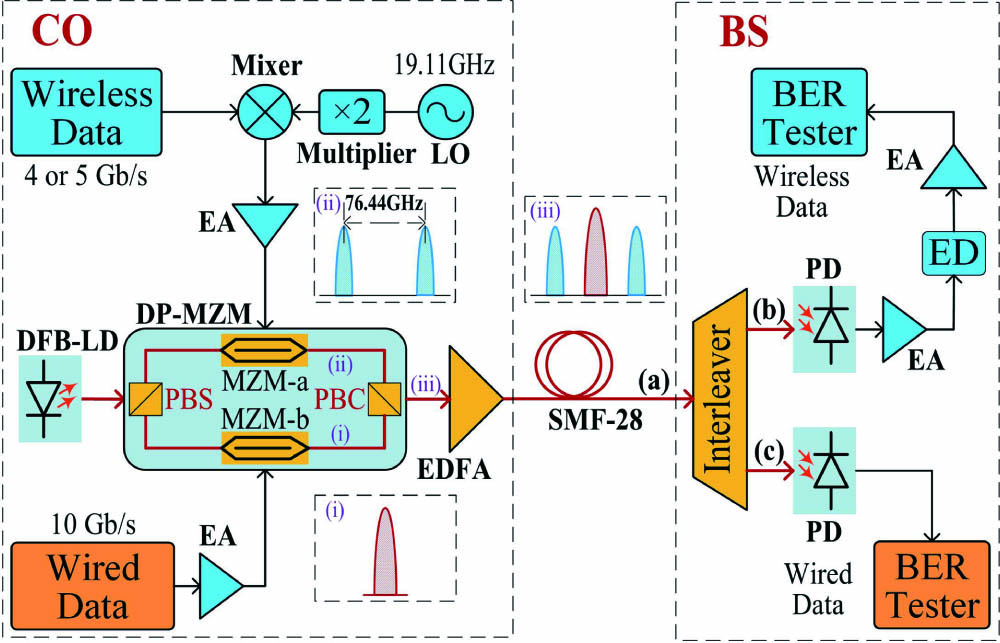
beam splitter high-contrast-index subwavelength grating serrated-phase profile splitting ability We proposed and demonstrated a new scheme for simultaneous generation of independent wired and wireless signals employing an integrated polarization multiplexing modulator. In the experimental system, a 10 Gb/s wired signal is imposed on the original optical carrier with one polarization, while a wireless signal with a bit rate larger than 4 Gb/s is carried on the generated millimeter wave of 76.44 GHz, which has polarization orthogonal to the wired signal. The dual services are successfully delivered over a 15 km standard single mode fiber; the power penalties of the wired and wireless signals are around 0.4 dB and 1.5 dB, respectively.
millimeter wave dual-parallel Mach–Zehnder modulator radio-over-fiber Visible light communication (VLC) shows great potential in Internet of Vehicle applications. A single-input multi-output VLC system for Vehicle to Everything is proposed and demonstrated. A commercial car headlight is used as transmitter. With a self-designed 2 × 2 positive-intrinsic-negative (PIN) array, four independent signals are received and equalized by deep-neural-network post-equalizers, respectively. Maximum-ratio combining brings high signal-to-noise ratio and data rate gain. The transmission data rate reaches 1.25 Gb/s at 1 m and exceeds 1 Gb/s at 4 m. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first-time demonstration of beyond 1 Gb/s employing a commercial car headlight.
visible light communication Internet of Vehicle Vehicle to Everything single-input multi-output deep neural networks maximum-ratio combining A continuous-wave Nd:YVO4/BaWO4 Raman laser generating simultaneous multi-wavelength first-Stokes and second-Stokes emissions is demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. Investigations concerning different pump spot sizes and crystal lengths were conducted to improve the thermal effect and pump absorption. Three first-Stokes lasers at 1103.6, 1175.9, and 1180.7 nm and two second-Stokes lasers at 1145.7 and 1228.9 nm are obtained simultaneously using the Raman shifts of 925 cm-1 and 332 cm-1 in BaWO4 and 890 cm-1 in YVO4. At the incident pump power of 23.1 W, 1.24 W maximum Raman output power is achieved, corresponding to an optical conversion efficiency of 5.4%. We also present a theoretical analysis of the competition between different Stokes lines.
multi-wavelength intracavity Raman laser continuous wave in-band pumping Design and analysis of a range-extended acidity detector based on a Nile red laser with tandem cuvette system Download:549次
Download:549次
 Download:549次
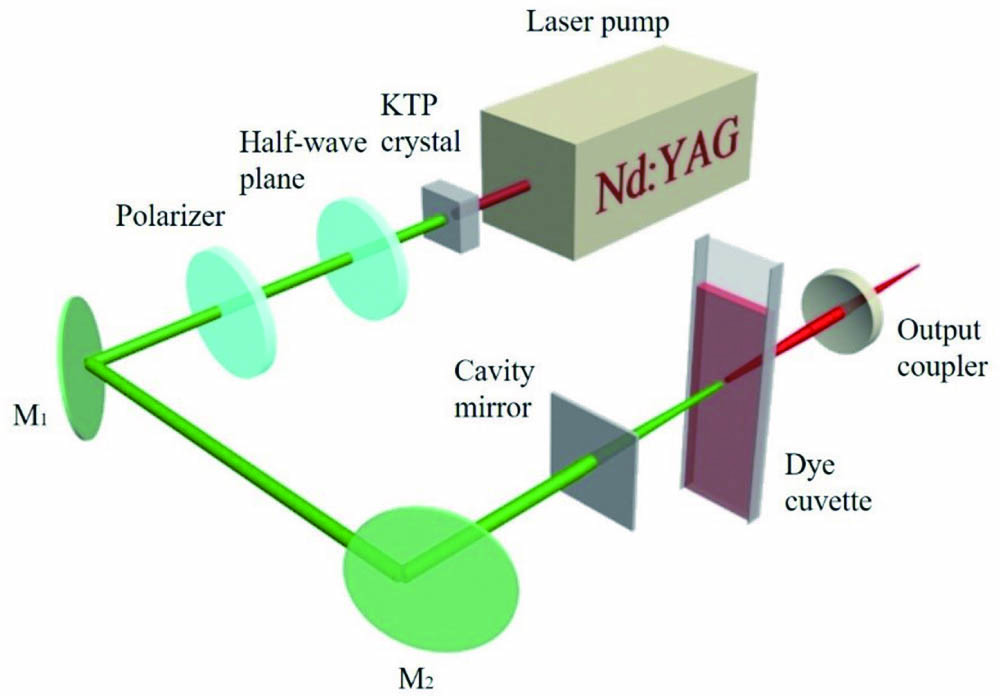
Download:549次A range-extended acidity detector based on Nile red was designed and analyzed in this work. In light of the good lasing property and solvatochromism characteristic of Nile red/ethanol solution, we have obtained laser spectra of sulfuric acid in different concentrations doped in this substrate. Moreover, to expand the acidity detection range, we proposed a tandem cuvette system containing rhodamine 6G/ethanol and Nile red/ethanol. Consequently, the detection range could be enlarged from 26 nm to 40 nm, by changing not only the wavelength peak but also by the intensity ratio of dual-wavelength laser output. In addition, by changing the detection and substrate materials, the whole detection range could be expanded, and therefore a wide range of applications in polarity and acidity detection could be implemented via this method.
acidity detector solvatochromism characteristic Nile red tandem cuvette system Impact of pre-pulse current and delay time on 46.9 nm laser with larger inner diameter alumina capillary Download:600次
Download:600次
 Download:600次
Download:600次In this Letter, we firstly, to the best of our knowledge, demonstrated the influence of pre-pulse current and delay time on the intensity of a discharge pumped Ne-like Ar soft X-ray laser operating at 46.9 nm by employing an alumina capillary having an inner diameter of 4.8 mm. Specifically, the delay time was changed from 8 to 520 μs in small intervals. The pre-discharge current was increased from 25 A to 250 A through small steps, while keeping the main discharge current constant. Usually, a small pre-discharge current is applied to an Ar-filled capillary to attain a plasma column having sufficient pre-ionization before the injection of the main current. The pre-discharge current of 140 A was declared the best current to obtain lasing with a 4.8 mm diameter capillary. The laser spots were captured at best time delays for the pre-discharge currents of 25, 45, 80, 140, and 250 A, which support the experimental results. We observed that by applying the pre-discharge current of 140 A, the laser spot exhibits small divergence, higher symmetry, and uniformity, which is clear evidence of strong amplification. The laser spot obtained at 140 A is cylindrically symmetric and has a better structure than those reported by all other groups in the literature. Hence, the laser spot indicates that the laser beam is highly focusable and beneficial for the applications of the 46.9 nm laser. Results of this Letter might open a new way to enhance applications of a 46.9 nm capillary discharge soft X-ray laser.
Z-pinch pre-discharge kink instabilities beam divergence No prior recognition method of modulation mode by partition-fractal and SVM learning method Download:619次
Download:619次
 Download:619次
Download:619次A modulation classification method in combination with partition-fractal and support-vector machine (SVM) learning methods is proposed to realize no prior recognition of the modulation mode in satellite laser communication systems. The effectiveness and accuracy of this method are verified under nine modulation modes and compared with other learning algorithms. The simulation results show when the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the modulated signal is more than 8 dB, the classifier accuracy based on the proposed method can achieve more than 98%, especially when in binary phase shift keying and quadrature amplitude shift keying modes, and the classifier achieves 100% identification whatever the SNR changes to. In addition, the proposed method has strong scalability to achieve more modulation mode identification in the future.
free-space optical communication pattern recognition modulation We demonstrated the efficient plasmon-induced nonlinear absorption of liquid metal GaInSn nanospheres prepared by a facile liquid-phase method. With GaInSn as saturable absorbers, a passively Q-switching operation was obtained at both 1.3 and 2 μm. The pulse width of 32 ns was achieved at 1.3 μm with repetition rate of 44 kHz, single pulse energy of 51.9 μJ, and output power of 425 mW. Meanwhile, 510 ns and 92 kHz pulses with energy of 36.1 μJ and output power of 2.48 W were obtained at 2 μm. This work provides the potential of liquid metal for improving metal functions and flexible optical devices.
GaInSn nanosphere passively Q-switched lasers saturable absorber Efficient 671 nm red light generation in annealed proton-exchanged periodically poled LiNbO3 waveguides Download:690次
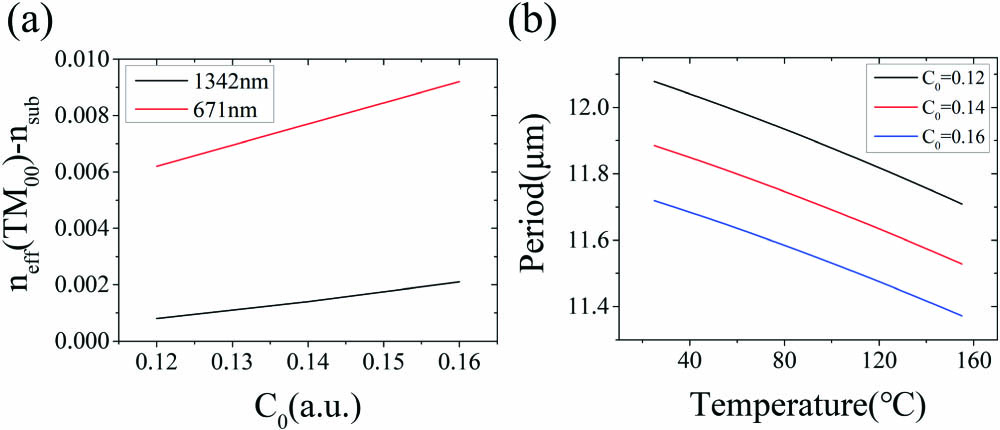
Download:690次
 Download:690次
Download:690次We report efficient generation of 671 nm red light based on quasi-phase-matched second harmonic generation of 1342 nm in LiNbO3 waveguides. The design method and fabrication process of the high-quality annealed proton-exchanged periodically poled channel waveguides were presented. A continuous-wave 1.71 mW red light was obtained with a single-pass conversion efficiency of 47%·W-1·cm-2, which is 88% that of the theoretical value. While for 1 mW quasi-continuous-laser input, the corresponding peak power being 2 W, the conversion efficiency reached up to 60%. Our results indicate that the annealed proton-exchanged periodically poled LiNbO3 waveguide is promising for high-efficiency and low power consumption nonlinear generation of visible light.
lithium niobate second-harmonic generation optical waveguides proton exchange Ultraviolet-infrared dual-color photodetector based on vertical GaN nanowire array and graphene Download:748次
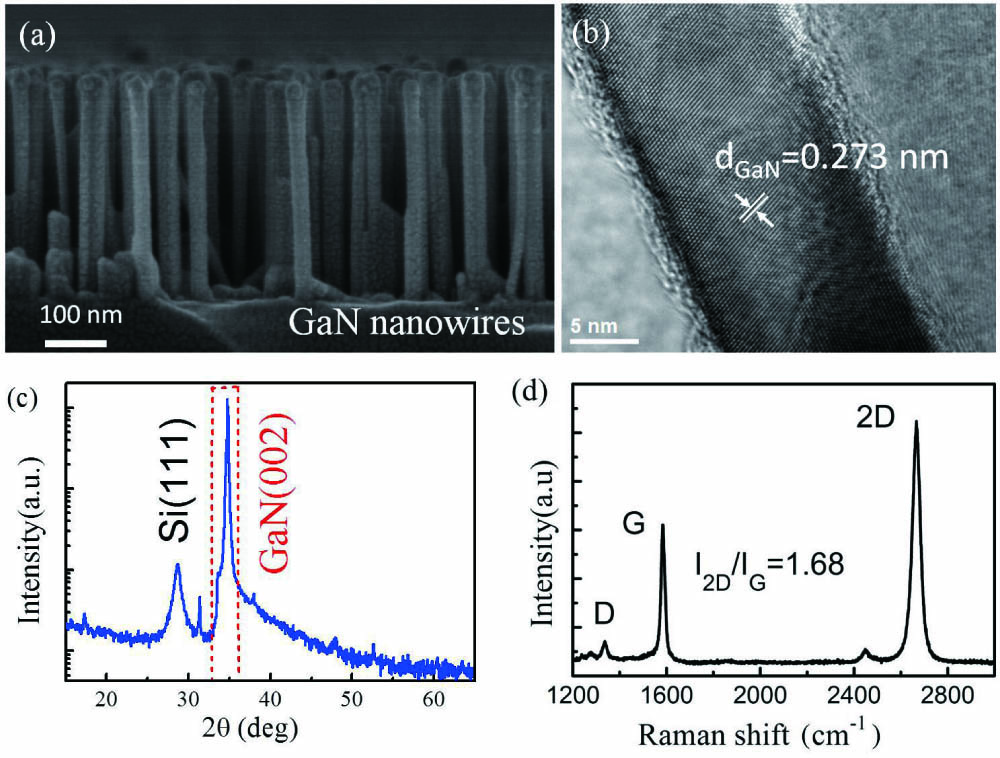
Download:748次
 Download:748次
Download:748次A monolithic integrated ultraviolet-infrared (UV-IR) dual-color photodetector based on graphene/GaN heterojunction was fabricated by vertically integrating a GaN nanowire array on a silicon substrate with monolayer graphene. The device detects UV and IR lights by different mechanisms. The UV detection is accomplished by the forbidden band absorption of GaN, and the IR detection is realized by the free electron absorption of graphene. At peak wavelengths of 360 nm and 1540 nm, the detector has responsivities up to 6.93 A/W and 0.11 A/W, detection efficiencies of 1.23 × 1012 cm·Hz1/2 ·W-1 and 1.88 × 1010 cm·Hz1/2 ·W-1, respectively, and a short response time of less than 3 ms.
UV-IR dual-color photodetector heterojunction GaN nanowire array graphene High efficiency X-ray diffraction diagnostic spectrometer with multi-curvature bent crystal Download:651次
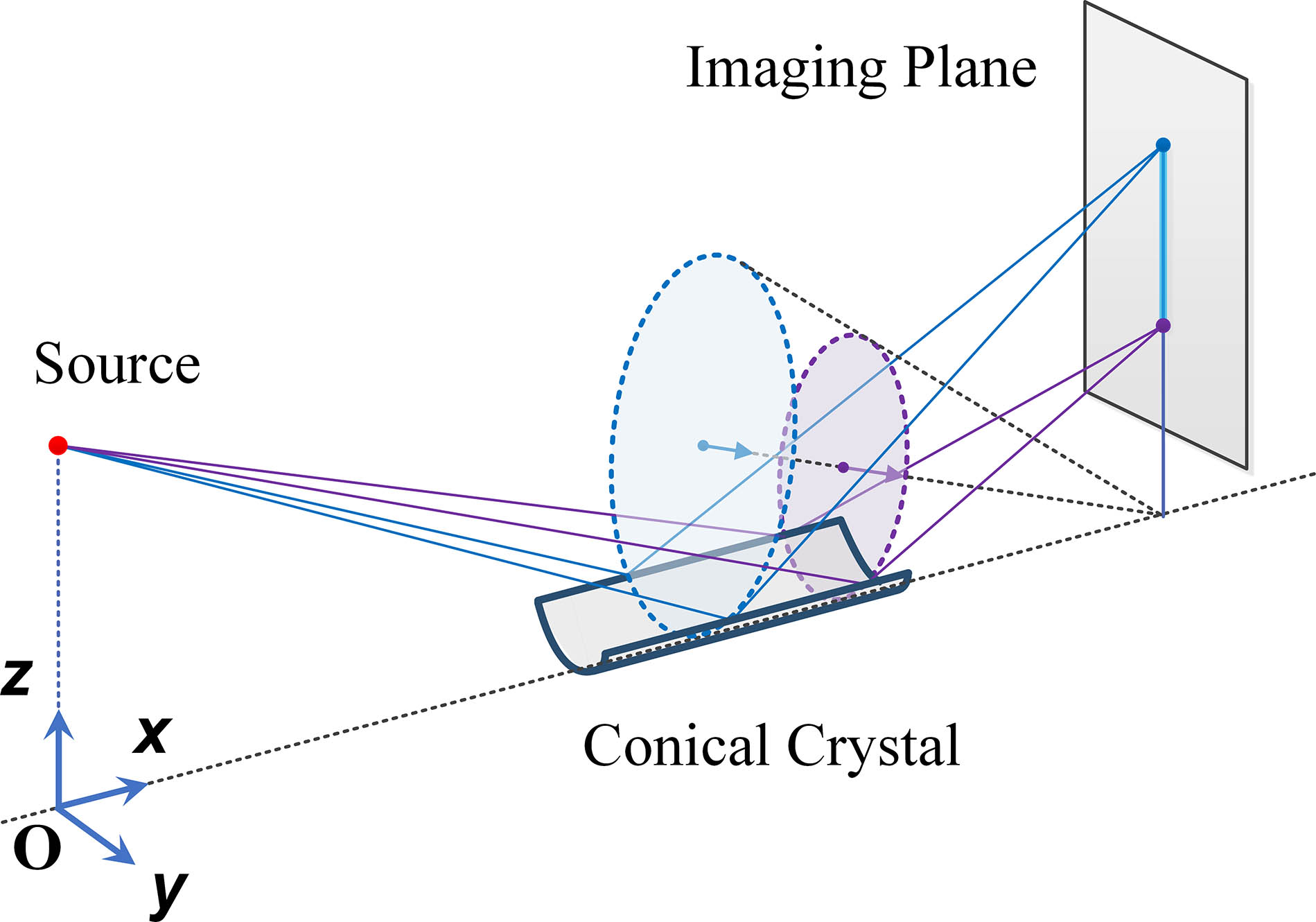
Download:651次
 Download:651次
Download:651次In spectral diagnostic physics experiments of inertial confinement fusion, the spectral signal is weak due to the low diffraction efficiency when using bent crystals. A spectral diagnostic instrument with high efficiency and wide spectral range is urgently needed. A multi-curvature bent crystal with multi-energy focusing ability is proposed based on the traditional conical crystal geometry. It has advantages of wide spectral range, strong focusing ability, and high spectral resolution. It also can eliminate the imaging aberration in principle due to rotational symmetry for the incoming X rays. A spectral diagnostic experiment based on a fabricated multi-curvature α-quartz crystal was accomplished using a titanium X-ray tube of the bent crystal, and the corresponding experimental data using a plane α-quartz crystal was also acquired to demonstrate the strong focusing ability. The result shows that the Kα intensity of the multi-curvature α-quartz crystal is 157 times greater than that of the plane crystal, and the corresponding energy range is about 4.51–5.14 keV. This diagnostic instrument could be combined with a streak camera at a vertical direction so as to intensify the diffracted X-ray signal with a wide spectral range.
inertial confinement fusion X-ray crystal spectrometer multi-curvature bent crystal X-ray diffraction Terahertz radiation enhancement in photoconductive antennas with embedded split-ring resonators Download:795次
Download:795次
 Download:795次
Download:795次This Letter proposes a novel method for enhancing terahertz (THz) radiation from microstructure photoconductive antennas (MSPCA). We present two types of MSPCA, which contain split-ring resonators (SRRs) and dipole photoconductive antennas (D-PCAs). The experimental results reveal that when the femtosecond laser is pumping onto the split position of the SRR, the maximum THz radiation power is enhanced by 92 times compared to pumping at the electrode edge of the D-PCA. Two
terahertz microstructure photoconductive antenna split-ring resonators 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦