2018, 16(7) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第7期
We present the long-term stability of the integrating sphere cold atom clock (ISCAC) and analyze its systematic limitations. The relative frequency instability of 2.6 × 10 15 2 × 10 5 s
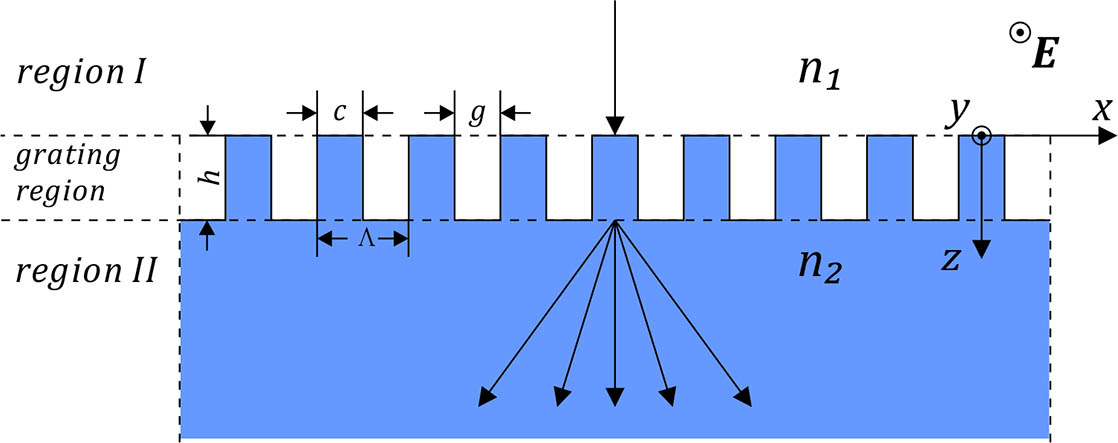
020.1335 Atom optics 020.3320 Laser cooling 020.7490 Zeeman effect A single-groove grating for five-port TE-polarization beam splitting under normal incidence at the wavelength of 1550 nm is presented. The transmitted diffraction efficiency of the gratings is over 94.5% with uniformity better than 2%. A physical view of diffraction inside the grating is presented by the simplified modal method (SMM). Initial parameters of the grating profiles are obtained by use of SMM and then optimized by employing rigorous coupled-wave analysis and the simulated annealing algorithm.
050.1950 Diffraction gratings 050.1970 Diffractive optics Impact of the self-steepening effect on soliton spectral tunneling in PCF with three zero dispersion wavelengths Download:586次
Download:586次
 Download:586次
Download:586次This work presents a numerical investigation of the self-steepening (SS) effect on the soliton spectral tunneling (SST) effect in a photonic crystal fiber (PCF) with three zero dispersion wavelengths. Interestingly, the spectral range and flatness can be flexibly tuned by adjusting the SS value. When the SS coefficient increases, the energy between solitons and dispersion waves is redistributed, and the red-shifted soliton forms earlier in the region of long wavelength anomalous dispersion. As a consequence, the SST becomes more obvious. The findings of this work provide interesting insights in regard to the impact of the SST effect on tailored supercontinuum generation.
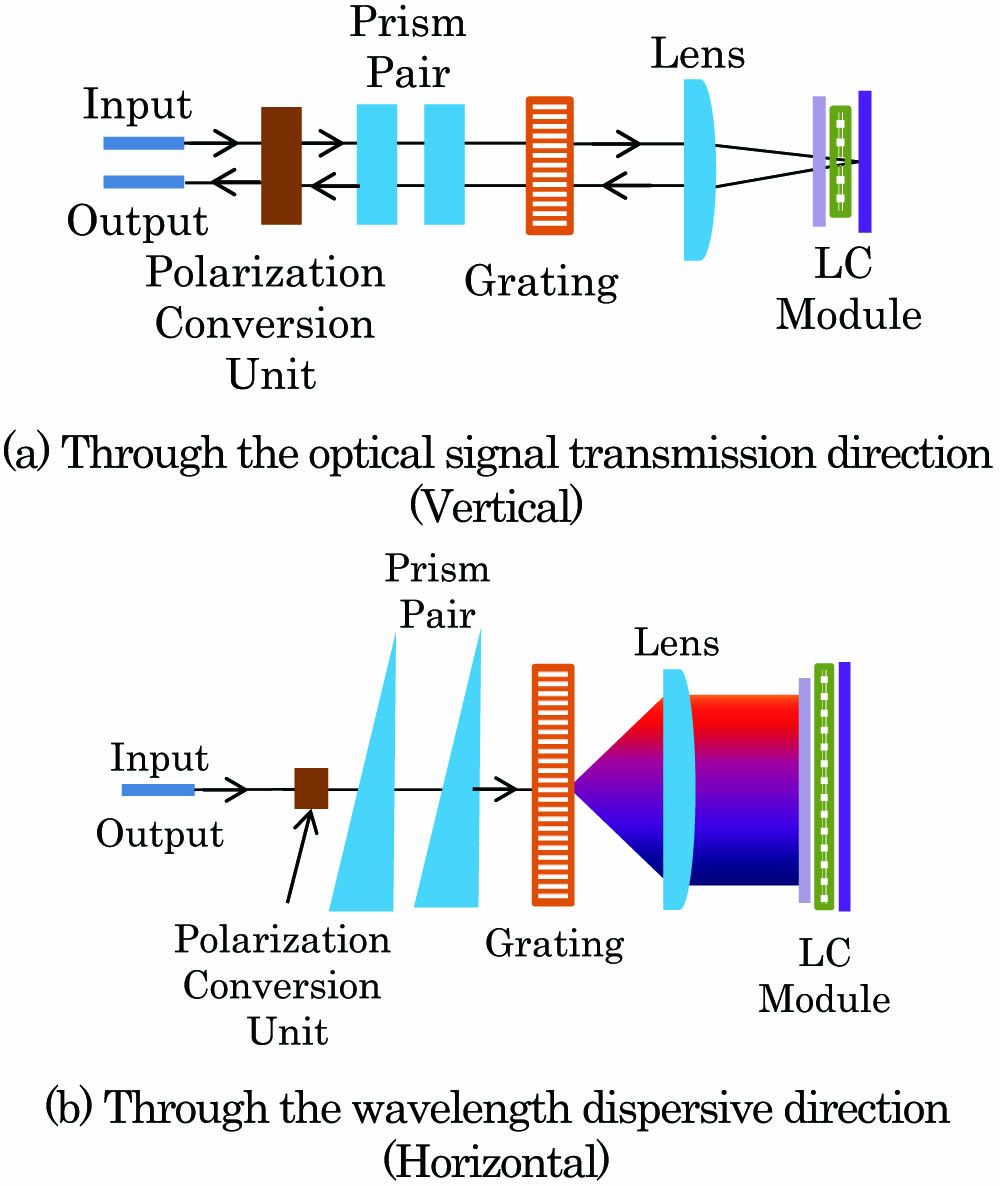
060.5295 Photonic crystal fibers A bandwidth-tunable optical passband filter with tunable attenuation is proposed. The filter, composed of a transmission liquid crystal array and high-resolution diffraction grating, was successfully demonstrated based on the compact spatial light design. Experimental results showed that the bandwidth, wavelength, and attenuation could be tuned by controlling the voltage applied on the liquid crystal array. The insertion loss was less than 3 dB; the attenuation tuning range was from 0 to 15 dB. The bandwidth tuning range was from 50 to 5000 GHz, which covered the full C band. The filter can meet the technical requirements of colorless-directionless-contentionless-flexible reconfigurable optical add/drop multiplexer.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 130.7408 Wavelength filtering devices We modify the pulse-reference-based compensation technique and propose a low-noise and highly stable optical fiber temperature sensor based on a zinc telluride film-coated fiber tip. The system noise is measured to be 0.0005 dB, which makes it possible for the detection of the minor reflectivity change of the film at different temperatures. The temperature sensitivity is 0.0034 dB/°C, so the resolution can achieve 0.2°C. The maximum difference of the temperature output values of the sensor at 20°C at different points in time is 0.39°C. The low cost, ultra-small size, high stability, and good repeatability of the sensor make it a promising temperature sensing device for practical application.
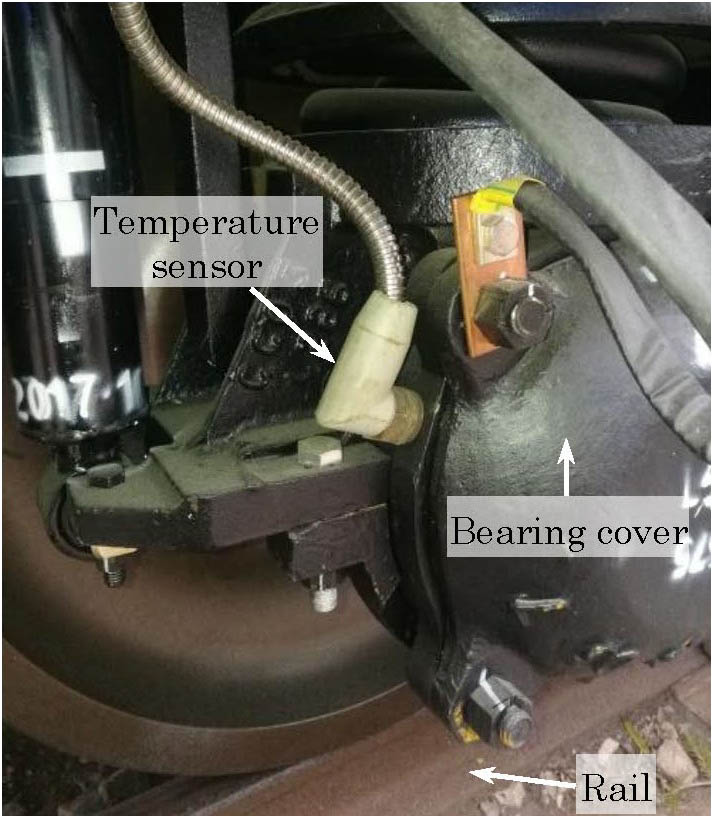
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.4080 Modulation Hybrid fiber Bragg grating sensor for vibration and temperature monitoring of a train bearing Download:627次
Download:627次
 Download:627次
Download:627次We report a fiber Bragg grating (FBG)-based sensor for the simultaneous measurement of a train bearing’s vibration and temperature. A pre-stretched optical fiber with an FBG and a mass is designed for axial vibration sensing. Another multiplexed FBG is embedded in a selected copper-based alloy with a high thermal expansion to detect temperature. Experiments show that the sensor possesses a high resonant frequency of 970 Hz, an acceleration sensitivity of 27.28 pm/g , and a high temperature sensitivity of 35.165 pm/°C. A resonant excitation test is also carried out that demonstrates the robustness and reliability of the sensor.
060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Mode division multiplexed holography by out-of-plane scattering of plasmon/guided modes Download:573次
Download:573次
 Download:573次
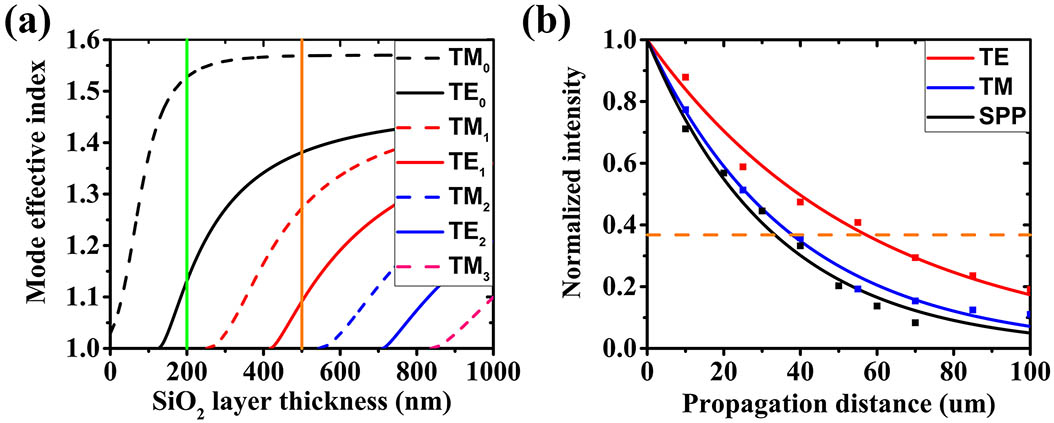
Download:573次We design and demonstrate a type of multiplexed hologram by nanoscatterers inside a dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguide with guided-wave illuminations. The mode division multiplexed hologram (MDMH) is fulfilled by the scattering of guided waves to free space with respect to different modes. According to different mode numbers, these guided modes have different responses to the multiplexed hologram, and then give rise to different holographic images in reconstructions. In experiments, we show two kinds of MDMHs based on TM 0 / TE 0 TE 0 / TE 1
090.4220 Multiplex holography 050.1970 Diffractive optics Detecting and tracking multiple targets simultaneously for space-based surveillance requires multiple cameras, which leads to a large system volume and weight. To address this problem, we propose a wide-field detection and tracking system using the segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optical reconnaissance. This study realizes two operating modes by changing the working paired lenslets and corresponding waveguide arrays: a detection mode and a tracking mode. A model system was simulated and evaluated using the peak signal-to-noise ratio method. The simulation results indicate that the detection and tracking system can realize wide-field detection and narrow-field, multi-target, high-resolution tracking without moving parts.
110.3175 Interferometric imaging 110.2970 Image detection systems 100.4999 Pattern recognition, target tracking Electronic speckle pattern interferometry (ESPI) and digital speckle pattern interferometry are well-established non-contact measurement methods. They have been widely used to carry out precise deformation mapping. However, the simultaneous two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) deformation measurements using ESPI with phase shifting usually involve complicated and slow equipment. In this Letter, we solve these issues by proposing a modified ESPI system based on double phase modulations with only one laser and one camera. In-plane normal and shear strains are obtained with good quality. This system can also be developed to measure 3D deformation, and it has the potential to carry out faster measurements with a high-speed camera.
120.6160 Speckle interferometry 120.5060 Phase modulation 120.5050 Phase measurement Faraday-rotation self-interference method for electron beam duration measurement in the laser wakefield accelerator Download:732次
Download:732次
 Download:732次
Download:732次Real-time single-shot measurement of the femtosecond electron beam duration in laser wakefield accelerators is discussed for both experimental design and theoretical analysis that combines polarimetry and interferometry. The probe pulse polarization is rotated by the azimuthal magnetic field of the electron beam and then introduced into a Michelson-type interferometer for self-interference. The electron beam duration is obtained from the region size of the interference fringes, which is independent of the pulse width of the probe laser. Using a larger magnification system or incident angle, the measurement resolution can be less than 1 fs.
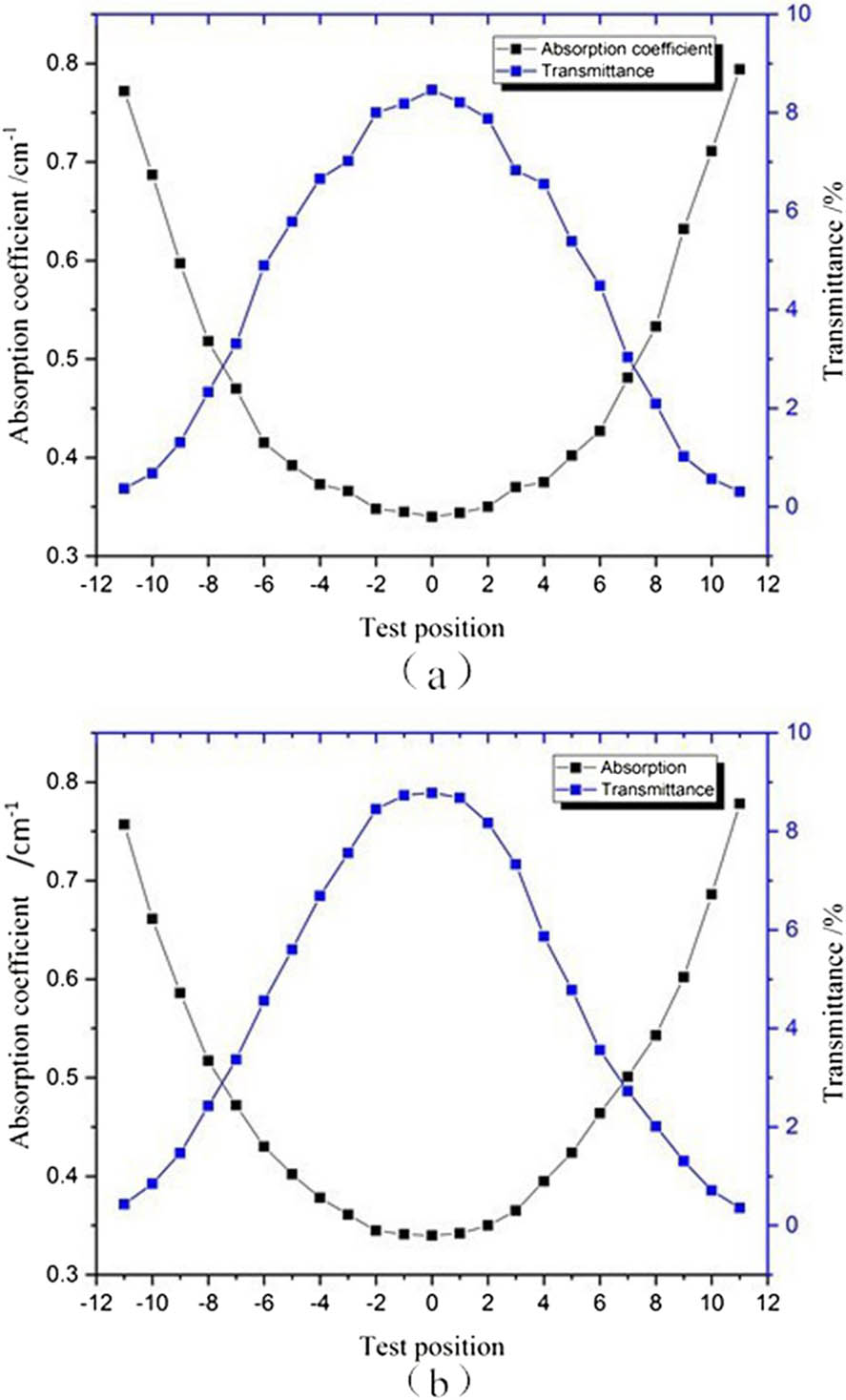
120.5410 Polarimetry 350.5400 Plasmas 120.3180 Interferometry A Ti:sapphire crystal with a diameter of 235 mm and thickness of 72 mm was grown by the heat exchange method (HEM). The absorption intensity of the crystal at 532 nm averaged at 91%. The figures of merit (FOMs) at different positions of the crystal were measured and the FOM value in the central region was found to reach 90. The transmittance laser beam was intact with no obvious distortions and had only a small deformation compared with the incident laser beam. A small-signal amplification experiment was performed on the Ti:sapphire crystal and a gain of more than 6 times was achieved with a pump energy density of 1.98 J / cm 2
140.3280 Laser amplifiers 140.3590 Lasers, titanium 140.5560 Pumping Narrow-wavelength-spread spectral combining laser with a reflector for a double pass with a single grating Download:628次
Download:628次
 Download:628次
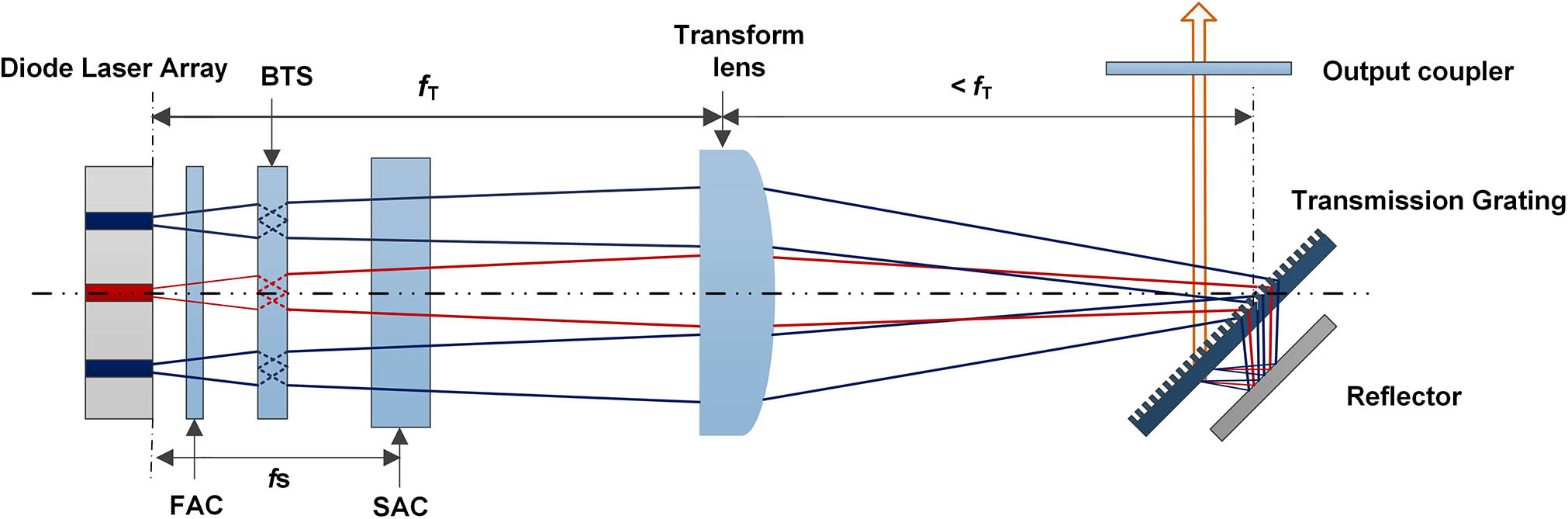
Download:628次We proposed a novel wavelength-spread compression technique for spectral beam combining of a diode laser array. A reflector, which is parallel to the grating, is introduced to achieve a double pass with a single grating. This facilitated the reduction of the wavelength spread by half and doubled the number of combined elements in the gain range of the diode laser. We achieved a power of 26.1 W under continuous wave operation using a 19 element single bar with a wavelength spread of 6.3 nm, which is nearly half of the original wavelength spread of 14.2 nm, demonstrating the double-compressed spectrum capability of this structure. The spectral beam combining efficiency was 63.7%. The grating efficiency and reflector reflectance were both over 95%; hence, the efficiency loss of the double-pass grating with a reflector is acceptable. In contrast to double-grating methods, the proposed method introduces a reflector that efficiently uses the single grating and shows significant potential for a more efficient spectral beam combining of diode laser arrays.
140.2010 Diode laser arrays 140.3290 Laser arrays 140.3298 Laser beam combining Simultaneous blood flow and oxygenation measurements using an off-the-shelf spectrometer Download:533次
Download:533次
 Download:533次
Download:533次Blood oxygenation and flow are both important parameters in a living body. In this Letter, we introduce a simple configuration to simultaneously measure blood flow and oxygenation using an off-the-shelf spectrometer. With the integration time of 10 ms, flow phantom measurements, a liquid blood phantom test, and an arm cuff occlusion paradigm were performed to validate the feasibility of the system. We expect this proof-of-concept study would be widely adopted by other researchers for acquiring both blood flow and oxygenation changes due to its straightforward configuration and the possibility of multimodal measurement.
170.2655 Functional monitoring and imaging 170.3890 Medical optics instrumentation 170.7050 Turbid media Myopia has become a noteworthy issue due to the increasing use of our eyes. We propose a continuous power variation vision-training device based on Alvarez lenses with the power ranging from 10 D + 2 D
220.3620 Lens system design 220.1250 Aspherics 330.7333 Visual optics, refractive anomolies Optical properties and dynamic process in metal ions doped on CdSe quantum dots sensitized solar cells Download:583次
Download:583次
 Download:583次
Download:583次In recent years, the nanostructure for solar cells have attracted considerable attention from scientists as a result of a promising candidate for low cost devices. In this work, quantum dots sensitized solar cells with effective performance based on a co-sensitized
250.4745 Optical processing devices 260.2160 Energy transfer Optical saturation characteristics of dual- and single-injection Ge-on-Si photodetectors Download:634次
Download:634次
 Download:634次
Download:634次The optical saturation characteristics in the germanium-on-silicon (Ge-on-Si) photodetector are studied for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The relationship between the optical saturation characteristics and the optical field distribution in the Ge layer is illustrated by the simulation. This theory is verified by comparative experiments with single-injection and dual-injection structures. The dual-injection photodetector with a more balanced and uniform optical field distribution has a 13% higher responsivity at low optical power and 74.4% higher saturation current at 1550 nm. At higher optical power, the bandwidth of the dual-injection photodetector is five times larger than that of the single-injection photodetector.
250.0040 Detectors 040.5160 Photodetectors We report on a systematic study of the laser polarization effect on a femtosecond laser filamentation in air. By changing the laser’s ellipticity from linear polarization to circular polarization, the onset position of laser filament formation becomes farther from the focusing optics, the filament length is shorter, and less laser energy is deposited. The laser polarization effect on air filaments is supported by a simulation and analysis of the polarization-dependent critical power and ionization rates in air.
320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 260.5430 Polarization The effect of material surface morphology on the periodic subwavelength of nano-structures induced by a femtosecond (fs) laser was investigated systematically from the initial surface roughness, the different scratches, the pre-formed ripples, and the “layer-carving” technology experiments. The results of the comparative experiments indicate that the initial surface conditions of the target surface have no obvious effects on the spatial structured periods (SSPs) and the ripple orientation of the periodic nano-structures induced by a fs laser, which agreed well with the foretold present surface two-plasmon resonance (STPR) model. Furthermore, different shapes of nano-grids with high regularity and uniformity were obtained by fs-laser fabrication.
320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 240.5770 Roughness 220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦