光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42 (5): 1439, 网络出版: 2022-11-10
基于一维卷积神经网络和拉曼光谱的肺炎支原体菌株分类
Classification of Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Strains Based on One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network and Raman Spectroscopy
肺炎支原体 拉曼光谱 定性分类 一维卷积神经网络 Mycoplasma pneumoniae Raman spectroscopy Qualitative classification One dimensional convolution neural network
摘要
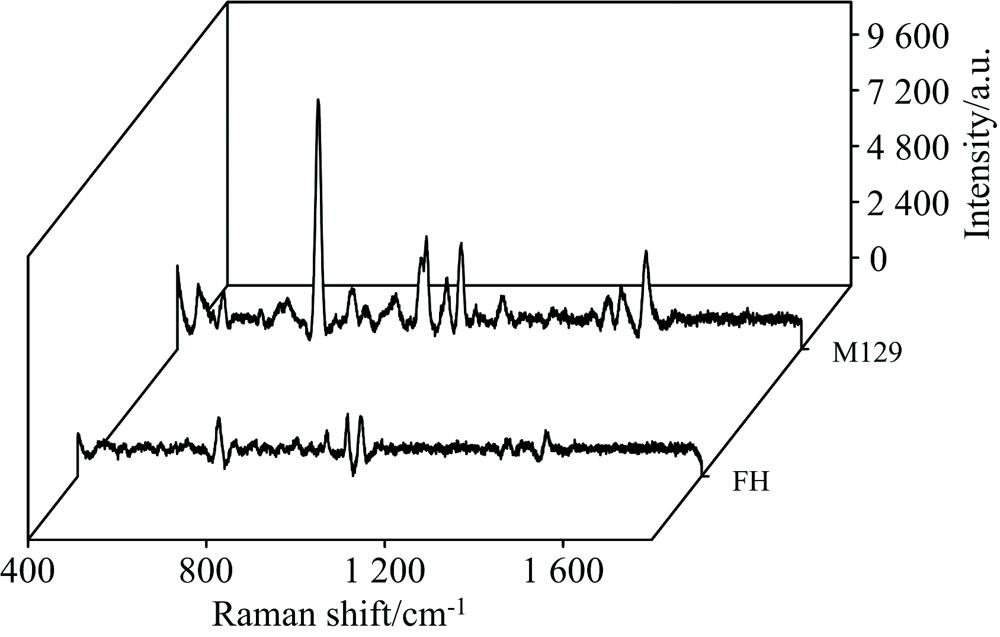
肺炎支原体是造成人类呼吸系统疾病的主要原因。 临床中, 患者感染不同肺炎支原体症状极为相似, 很难根据症状判别肺炎支原体类型并对症给药。 因此, 准确判别肺炎支原体菌株类型对于发病机理和疾病流行病学研究以及临床精准治疗具有重要意义。 拉曼光谱具有快速、 高效、 无污染等优点, 在生物医学领域逐渐得到越来越多研究者们的关注。 一维卷积神经网络(1D-CNN)是一类包含卷积运算且具有深度结构的前反馈网络, 在语音信号和振动信号分析等方面取得成功应用。 提出一维卷积神经网络与拉曼光谱技术结合, 针对肺炎支原体主要基因型M129型和FH型样本的拉曼光谱数据集, 实现肺炎支原体菌株分类。 利用光谱数据增强方法扩充原光谱数据集作为模型输入, 训练一维卷积神经网络模型, 解决由于小样本导致卷积神经网络数据饥渴问题; 为了得到最好的肺炎支原体分类效果并加速学习过程, 优化模型结构并确定最佳模型参数; 拉曼光谱测量时常混有高斯噪声、 泊松噪声和乘性噪声, 为优化模型抗噪能力, 将原光谱分别叠加高斯噪声、 泊松噪声和乘性噪声, 训练一维卷积神经网络模型并和LDA, KNN和SVM等传统算法进行比较。 实验结果表明基于1D-CNN方法, 对于叠加高斯噪声的光谱数据所建模型分类正确率为98.0%, 叠加泊松噪声的光谱数据分类正确率为97.0%, 叠加乘性噪声的光谱数据分类正确率为97.0%, 分类正确率远高于基于LDA, KNN和SVM等传统算法所建模型分类正确率; 同时构造叠加5, 15, 25, 35, 45和55 dBW不同强度噪声的光谱数据集, 当噪声达到55 dBW时, 1D-CNN模型仍能取得92.5%的分类正确率。 因此, 一维卷积神经网络结合拉曼光谱技术应用于肺炎支原体菌株类型分类是可行的, 具有抗噪声能力强和分类正确率高的优点, 该研究为肺炎支原体肺炎快速诊断提供新思路。
Abstract
Mycoplasma pneumoniae is the main cause of human respiratory diseases. Clinically, the symptoms of patients infected with different mycoplasma pneumoniae are very similar, so it is difficult to distinguish the type of mycoplasma pneumoniae according to the symptoms and give medication. Therefore, the accurate identification of mycoplasma pneumoniae strain type is of great significance for the pathogenesis and epidemiological research of the disease, and accurate clinical treatment. Raman spectrum has been paid more and more attention because of its advantages of fast-speed, high efficiency, pollution-free and non-destructive analysis. One-dimensional Convolution Neural Network (1D-CNN) is a kind of pre-feedback network with a deep structure, including Convolution operation. It has been successfully applied in the analysis of speech and vibration signals. The combination of the One-Dimensional Convolution Neural Network and the Raman spectral data of the main genotypes of mycoplasma pneumoniae M129 and FH were used as the research objects to realize mycoplasma classification pneumoniae strains. The spectral data enhancement method expands the original spectral data set, and the one-dimensional convolution neural network model was trained, and the problem of data hunger of convolutional neural network caused by small samples was solved. In order to obtain the best classification effect of mycoplasma pneumoniae and accelerate the learning process, the model structure was optimized, and the best model parameters were determined. Gaussian noise, Poisson noise and multiplicative noise are often mixed in Raman spectral measurement. Gaussian noise, Poisson noise and multiplicative noise are often mixed in Raman spectral measurement. In order to optimize the anti-noise ability of the model, Gaussian noise, Poisson noise and multiplicative noise were superimposed on the original spectrum respectively, and the 1D-CNN model was trained and compared with the models built by traditional algorithms such as LDA, KNN and SVM. The experimental results show that for the Raman spectra superimposed with Gaussian noise, Poisson noise and multiplicative noise, the classification accuracy of the models based on 1D-CNN method has achieved 98.0%, 97.0% and 97.0%, respectively, which are all much higher than those of the models based on LDA, KNN and SVM algorithms. At the same time, the 1D-CNN model can achieve 92.5% classification accuracy when the noise reacheds the 55 dBW interference factor, aiming at the noise with different intensities of 5, 15, 25, 35, 45 and 55 dBW.Therefore, it is feasible to apply a one-dimensional convolutional neural network combined with Raman spectrum technology to the classification of mycoplasma pneumoniae strain types, which has the advantages of strong anti-noise ability and high classification accuracy. This study provides a new idea for the rapid diagnosis of mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia.
赵勇, 何梦园, 王泊林, 赵荣, 孟宗. 基于一维卷积神经网络和拉曼光谱的肺炎支原体菌株分类[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42(5): 1439. Yong ZHAO, Men-yuan HE, Bo-lin WANG, Rong ZHAO, Zong MENG. Classification of Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Strains Based on One-Dimensional Convolutional Neural Network and Raman Spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022, 42(5): 1439.