微柱镜面周期性纹理结构衍射杂散光研究
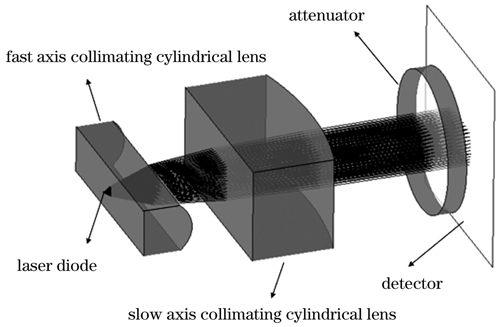
In the field of optics, micro-cylindrical lenses and cylindrical lens arrays are commonly used optical devices usually processed by traditional mechanical grinding, ultraprecision turning, and die forming. In the process of diamond lathe machining, the tool machining step often has a constant period, resulting in the formation of a periodic texture structure corresponding to the knife pattern on the lens surface. This structure causes an obvious diffraction phenomenon under strong laser irradiation and produces stray light that interferes with the optical path in the optical system, seriously affecting the function of the optical system. However, there are few reports on this phenomenon at present, resulting in a lack of theoretical guidance for solving this problem.
To analyze the influence of stray light on the surface of a 100-μm-diameter micro-cylindrical lens caused by lathe machining, a model of the periodic texture structure is constructed, and the influence of the surface periodic texture structure on diffractive stray light is analyzed. The theoretical diffraction model of the structure is established by using Fourier optical theory, and the intensity distribution rules of the diffracted light field at different depths are calculated. The theoretical rules obtained are basically consistent with the physical optics simulation and experimental test results of the commercial optical software VirtualLab, and the theoretical model is verified theoretically and experimentally.
Based on the model of the periodic texture structure, the light spots of the ideal lens are compared with those of the lens with the periodic texture structure. As shown in Fig.5, compared with those of the ideal lens, the light spots of the lens with the periodic texture structure produce obvious diffractive stray light along the fast axis direction. In view of this phenomenon, the beam intensity distributions are calculated and simulated at different depths of the periodic texture structure on the surface of the micro-cylindrical lens, as shown in Fig.6. It can be seen that, the deeper the periodic structure, the stronger the diffractive stray light generated. When the surface texture depth of the cylindrical lens is greater than 16.2 nm, the diffracted stray light is more significant, which has a significant impact on the optical performance of the device. This is basically consistent with the experimental result. Finally, according to the research results, a method is proposed to control the depth of the periodic structure and destroy the periodic characteristics of the surface to weaken the diffractive stray light.
In this study, the relationship between the periodic texture of the micro-cylindrical lens and the diffracted stray light of the beam is studied, an analysis model of the periodic texture structure of the micro-cylindrical lens is established, and theoretical calculation and simulation analysis methods for analyzing the relationship between the periodic structure and the intensity of the diffracted stray light are given. This research provides a theoretical analysis method for solving the problem of diffractive stray light caused by periodic knife grain in the machining process of micro-cylindrical lens.
孙昊, 唐乐, 王春艳, 张为国, 杜春雷, 夏良平. 微柱镜面周期性纹理结构衍射杂散光研究[J]. 中国激光, 2024, 51(5): 0513001. Hao Sun, Le Tang, Chunyan Wang, Weiguo Zhang, Chunlei Du, Liangping Xia. Diffractive Stray Light of Periodic Texture of Micro‑cylindrical Lens[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2024, 51(5): 0513001.