光子学报, 2023, 52 (4): 0406001, 网络出版: 2023-06-21
基于拉丝塔光纤光栅的准分布式温盐传感器
Quasi-distributed Temperature and Salt Sensor Based on Drawing Tower Grating
盐度测量 温度补偿 拉丝塔光纤光栅 聚酰亚胺 准分布式 Salinity measurement Temperature compensation Drawing-tower gratings Polyimide Quasi-distributed
摘要
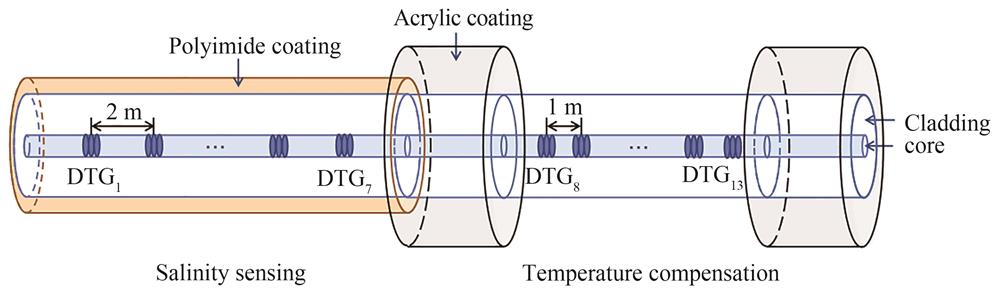
提出了一种基于拉丝塔光纤光栅(DTG)的准分布式温盐传感器,可以同时测量海水的温度和盐度。该传感器由多个聚酰亚胺(PI)涂敷DTG和无涂敷DTG串联构成,PI涂敷DTG作为盐度传感组件,盐度的变化会导致聚酰亚胺涂层吸收或释放水而产生膨胀或收缩作用,进而引起光纤光栅中心波长的漂移。温度串扰可以通过使用无涂敷光纤光栅中心波长的变化来补偿。实验结果表明,该传感器能实现温度和盐度的实时测量,对温度和盐度的变化表现出线性响应,且具有良好的重复性。其中,盐度灵敏度平均为-5.58 pm/(mol/L),温度灵敏度平均为10.02 pm/℃。由于拉丝塔光纤光栅的超弱反射特性,该方法可以实现大规模海水温度和盐度的准分布式测量,在海洋工程中有一定的应用前景。
Abstract
Seawater temperature and salinity are the most critical and fundamental physical parameters necessary for all oceanographic disciplines, which have important theoretical value and practical significance for studying ocean climate change, monitoring marine ecological environment, exploiting and utilizing marine resources, and ensuring military security, etc. The development of high-performance sensors for seawater parameter measurement has become one of the research hotspots. In recent years, optical fiber sensing methods have provided a new solution for high precision measurement of physical parameters with the advantages of anti-electromagnetic interference, corrosion resistance, small size, and real-time distributed measurement. At present, the widely studied optical fiber temperature and salt sensors mainly include optical fiber interference type sensors and fiber optic grating type sensors. Researchers at home and abroad have realized the design of optical fiber interference type temperature and salt sensors by micromachining the optical fiber, such as taper pulling, reverse taper pulling, side polishing, dislocation welding and core diameter mismatch welding, and achieved some research results. However, there are generally problems such as great fabrication difficulty and poor structural stability, which are difficult to meet the application requirements of marine engineering. In contrast, optical fiber grating type temperature and salinity sensor are mainly designed based on Fiber Bragg Grating (FBG), and a single FBG can form a sensor, which is simpler to manufacture, more stable in structure and more adaptable to the environment. However, the current fiber grating temperature and salinity sensors mostly adopt FBG with high reflectivity, which can only perform discrete point measurements and cannot realize distributed sensing. Besides, previous reports mostly used spectrometer demodulation, which cannot observe the real-time response of temperature and salinity. Therefore, a quasi-distributed temperature and salt sensor based on Drawing Tower Grating (DTG) is proposed in this paper. The sensor uses DTG coated with Polyimide(PI) as the salinity sensing element. The PI coating expands or contracts linearly in volume when in contact with solutions of varying salinity. The expansion or contraction response caused by the change in salinity is converted into an axial strain loaded on the PI-coated DTG, and the salinity can be measured by monitoring the drift of its central wavelength. During the experiment, the central wavelength of the fiber grating is demodulated in real time by the fiber grating array demodulator, and its data is collected and recorded by the computer in real time. In the temperature compensation coefficient measurement experiment, the optical fiber sensor was placed in the circulating temperature field from 25 ℃ to 30 ℃ and then back to 25 ℃. Compared with the electronic temperature sensor used for calibration, it can be found that both PI coated DTG and uncoated DTG can accurately measure the ambient temperature, and have good consistency and repeatability. Their temperature sensitivities are 10.24 pm/℃ and 10.02 pm/℃ respectively. In the experiment of simultaneous temperature and salt measurement, the fiber optic sensor was placed into a high concentration NaCl solution of 5 mol/L to make the PI coating lose water and shrink sufficiently. Then deionized water or low concentration NaCl solution was added to gradually dilute it to 4 mol/L, 3 mol/L, 2 mol/L, 1 mol/L, and 0.6 mol/L to observe its salinity response. In order to simulate the actual working environment of the sensor, the whole system was in a room temperature environment without temperature control operation, and the sensor was still able to measure the temperature of the solution accurately, and the average salinity sensitivity obtained after compensation was -5.58 pm/(mol/L). The experimental results show that the sensor can simultaneously measure the temperature and salinity of seawater in real-time and quasi-distributed, and also has the advantages of wide measurement range, high measurement accuracy and easy fabrication, which has certain prospects for application in marine engineering.
王宇琦, 潘震, 戢雅典, 范典, 周次明. 基于拉丝塔光纤光栅的准分布式温盐传感器[J]. 光子学报, 2023, 52(4): 0406001. Yuqi WANG, Zhen PAN, Yadian JI, Dian FAN, Ciming ZHOU. Quasi-distributed Temperature and Salt Sensor Based on Drawing Tower Grating[J]. ACTA PHOTONICA SINICA, 2023, 52(4): 0406001.