太赫兹多维复用与折射率传感集成器件封面文章【增强内容出版】
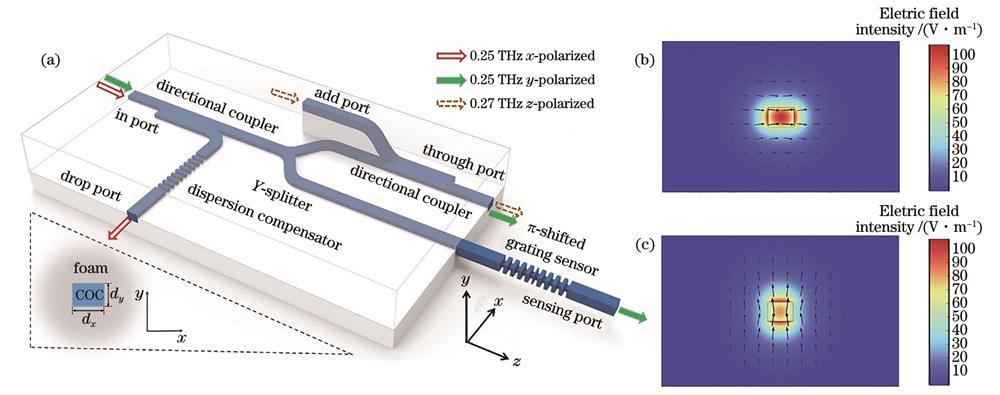
Terahertz waves featuring broad bandwidths play an increasingly important role in next-generation communication systems. For both terahertz wired and wireless communications, terahertz waveguide integrated devices providing“on-line”signal processing functionalities are in vital demand. In the next-generation communication system, the multiplexing technology around the electromagnetic wave physical parameters such as terahertz radiation polarization, frequency, and phase is an effective solution to enhancing spectrum efficiency. Additionally, the future Internet of Everything information system should have a real-time monitoring function of communication environmental parameters (temperature, humidity, etc.). Given the above technical requirements of multidimensional multiplexing and environmental sensing, novel terahertz functional integrated devices for high-speed information transmission-manipulation-perception fusion should be studied urgently. Several terahertz silicon-based waveguide devices have been demonstrated, but the planar structure restricts the spatial degree of freedom for the devices, which means the devices can only be integrated in a 2D plane. Terahertz fiber-based devices are substrate-free to provide terahertz wave routing abilities along any spatial direction. Nevertheless, most of the reported terahertz fiber devices offer a single functionality, remaining a significant scope of multiple device integration. Thus, we propose a polarization-maintaining subwavelength fiber-based multidimensional multiplexing and sensing integrated device which is composed of fiber bends, a 50/50 Y-splitter, directional couplers, and Bragg gratings. The proposed fiber device provides (de)multiplexing in an additional direction that is orthogonal to the 2D space in contrast to the planar devices. Meanwhile, the device integrates multiple functionalities, including frequency- and polarization-(de)multiplexing, dispersion compensation, and surrounding refractive index sensing. In a nutshell, the integrated device provides exciting perspectives for boosting transmission capacity and developing communication-sensing integration of the next-generation communication systems.
The finite element analysis method and finite-difference time-domain model are employed in our study. First, the finite element analysis method is adopted to calculate the transmission parameters (fractional power in the core, loss, group velocity dispersion, etc.) of terahertz subwavelength fibers with different cross-sectional parameters to design polarization-maintaining fibers supporting low-loss and low-dispersion transmission. Then, S-shaped and 90° bending fibers are designed using Bessel curves. Furthermore, the finite-difference time-domain model is utilized to analyze the transmission characteristics of S-shaped and 90° bending fibers. Then, two S-shaped bending fibers with the same bending radius are utilized to form a Y-splitter. In the next step, we leverage the supermode theory as a theoretical guide and the finite element analysis method as a tool to calculate the required coupling length of the directional couplers. Additionally, the finite element analysis method is employed to investigate the effects of grating cell cross-section parameters, thickness, and number of cycles on grating performance (e.g., transmission and dispersion compensation), and thus accomplish the structural design of uniform gratings. Finally, the performance of the proposed terahertz devices including directional couplers, Y-splitter, uniform grating, and phase-shifted grating is simulated and analyzed using the time-domain finite difference method.
We present terahertz subwavelength rectangular fibers, bending fibers, Y-splitter, directional couplers, uniform grating, phase-shift grating, and multidimensional-multiplexing and refractive-index-sensing integrated devices. First, the subwavelength fiber supports low-loss (below 0.051 dB/mm) and high-birefringent (beyond 0.03) transmissions at a target bandwidth over 0.24-0.28 THz as shown in Fig. 2. Second, the transmission of S-shaped bending fibers with a bending radius of 10 mm is slightly higher than that of 90° bending fibers in the frequency range of 0.24-0.28 THz, whose transmission is higher than -1 dB at the operating frequency of 0.25 THz [Fig. 4(d)]. Thanks to the high transmission of x-bent S-shaped bends, a 50/50 Y-splitter can be readily designed using two bends with the same radius of 10 mm. Third, for the x-placed x-bent directional coupler, high transmission (above -3 dB) and high ER (above 7 dB) are obtained for both x-polarization and y-polarization modes when coupling lengths are in the range of 11.8-12.3 mm. Finally, the integrated device achieves simultaneously polarization and frequency (de)multiplexing, with high transmissions [drop port: -5.94 dB for 0.25 THz x-polarization with dispersion compensation; through port: -7.20 dB for 0.25 THz y-polarization, -2.02 dB for 0.27 THz x-polarization] and high ER (drop port: 15.16 dB; through port: 8.06 dB). Additionally, the device integrates fiber Bragg gratings, allowing both zero-GVD dispersion compensation and refractive-index sensing (sensitivity of 0.181 THz/RIU) abilities (Figs. 17 and 18).
We propose and analyze a terahertz multidimensional-multiplexing and sensing integrated device based on subwavelength birefringent fibers, composed of fiber bends, 50/50 Y-splitter, directional couplers, and Bragg gratings. First, a directional coupler with high transmission and high extinction ratio is designed by introducing a bent fiber to achieve polarization and frequency (de)multiplexing functions. Second, the uniform grating and phase-shift grating in the integrated device enable dispersion compensation and environmental refractive index sensing respectively. Terahertz subwavelength fiber devices feature dense integration in 3D space and efficient transmission, which provides novel design solutions for the integrated terahertz wave transmission-manipulation-sensing information system. Meanwhile, we also envision that many more components such as modulators and imaging devices will be further integrated on the terahertz fiber platform.
揭璐, 李海粟, 刘亚静, 王建帅, 任国斌, 裴丽. 太赫兹多维复用与折射率传感集成器件[J]. 光学学报, 2024, 44(8): 0823001. Lu Jie, Haisu Li, Yajing Liu, Jianshuai Wang, Guobin Ren, Li Pei. Terahertz Multidimensional-Multiplexing and Refractive-Index-Sensing Integrated Device[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2024, 44(8): 0823001.