辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 2023, 41 (1): 010402, 网络出版: 2023-03-06
γ 射线辐照及粒径对芦苇秸秆酶解发酵的影响
Effects of γ-ray irradiation and particle size on enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of reed straws
摘要
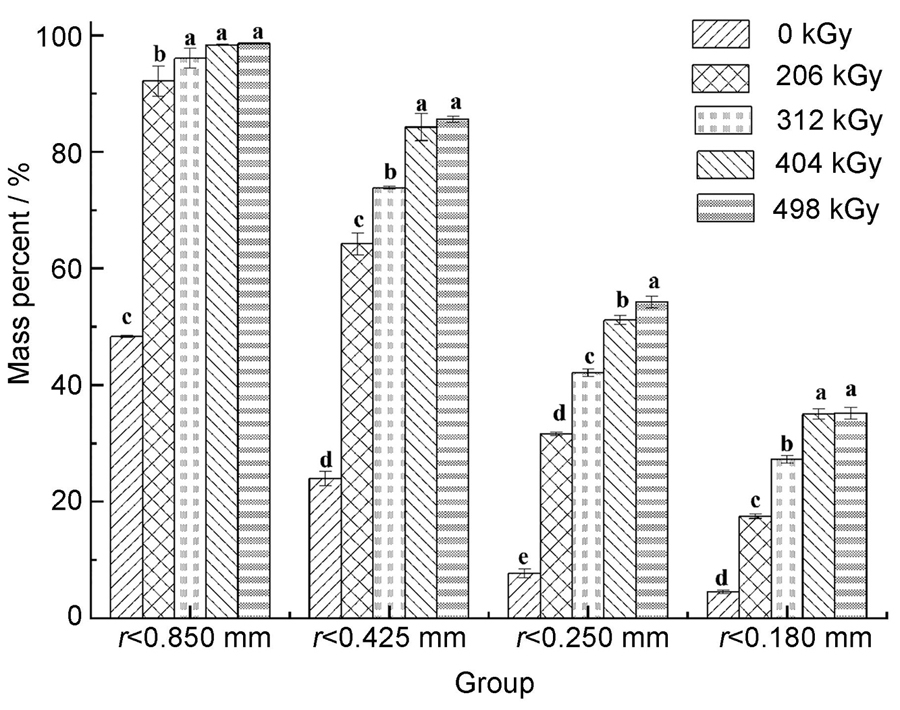
以经过不同吸收剂量(0?500 kGy)的γ射线辐照处理后的芦苇秸秆为研究对象,机械粉碎后过筛,研究吸收剂量、过筛孔径对其粒径分布、粉碎能耗、主要组分含量、纤维素酶解转化率、纤维素乙醇转化率的影响。研究结果显示:随着过筛孔径的减小,所获得的芦苇秸秆样品质量显著减少,且与吸收剂量负相关;芦苇的粉碎能耗随吸收剂量的升高而降低,获得相同质量的过筛样品,粉碎能耗又随过筛孔径的减小而显著增加;相同吸收剂量处理的芦苇秸秆,其纤维素酶解转化率和纤维素乙醇转化率均随过筛孔径的减小而增大,其中吸收剂量为分别0 kGy、206 kGy、404 kGy,粒径范围在r?0.180 mm的芦苇秸秆样品其纤维素酶解转化率较r?0.850 mm样品分别提高129.20%、85.98%、106.63%,纤维素乙醇转化率分别提高136.04%、21.75%、4.39%。综合比较粉碎能耗与纤维素酶解转化率和纤维素乙醇转化率的增加比率,最终确定未辐照(0 kGy)芦苇秸秆样品的最佳过筛孔径为0.850 mm;吸收剂量为206 kGy、404 kGy的芦苇秸秆样品最佳过筛孔径为0.425 mm。
Abstract
To explore the effects of absorbed dose and particle size on enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of reed straws (Phragmites australias), the straws were irradiated with γ-ray irradiation at different doses (0-500 kGy) and then passed through different aperture sieves after mechanical grinding. The effects of absorbed doses and sieving aperture size on particle size distribution, comminution energy, main component content, enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rate, and ethanol conversion rate of cellulose were examined, and the optimal respective sieving aperture for reed straws with different absorbed doses were determined. The results showed that with decreasing sieve aperture size, reed straw quality decreased significantly and was negatively correlated with the absorbed dose; the comminution energy of reed straws decreased with increasing absorbed doses. With respect to consistent quality of sieved reed straws, the comminution energy increased significantly with decreasing sieving particle size. In reed straws with the same absorbed dose, the enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rate and ethanol conversion rate of cellulose increased with decreasing sieving aperture size. Compared with reed straws with particle size r ? 0.850 mm, the cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rates in reed straws with particle size r ? 0.180 mm increased by 129.20%, 85.98%, and 106.63% at absorbed doses of 0 kGy, 206 kGy, and 404 kGy, respectively, and cellulose ethanol conversion increased by 136.04%, 21.75%, and 4.39%, respectively. By compre- hensively comparing the increased ratios of comminution energy, cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis conversion rate, and cellulose ethanol conversion rate, the optimal sieving aperture of non-irradiated (0 kGy) reed straws was deter-mined to be 0.850 mm, and that of reed straws irradiated with 206 kGy or 404 kGy was determined to be 0.425 mm.
齐慧, 陈亮, 武小芬, 刘安, 王丹阳, 张勇, 邓明, 王克勤.