光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42 (5): 1529, 网络出版: 2022-11-10
红外光谱和热重分析法评估三种加固剂对“小白礁Ⅰ号”考古木材微力学性能的影响
Effects of Three Kinds of Consolidants on the Micromechanical Properties of Archaeological Wood From “Xiaobaijiao Ⅰ” Shipwreck by Infrared Spectroscopy and Thermogravimetric Analysis
饱水考古木材 微力学 红外光谱 热重分析 “小白礁Ⅰ号”沉船 Waterlogged archaeological wood Micromechanical property Infrared spectroscopy Thermogravimetric analysis Xiaobaijiao Ⅰ shipwreck
摘要
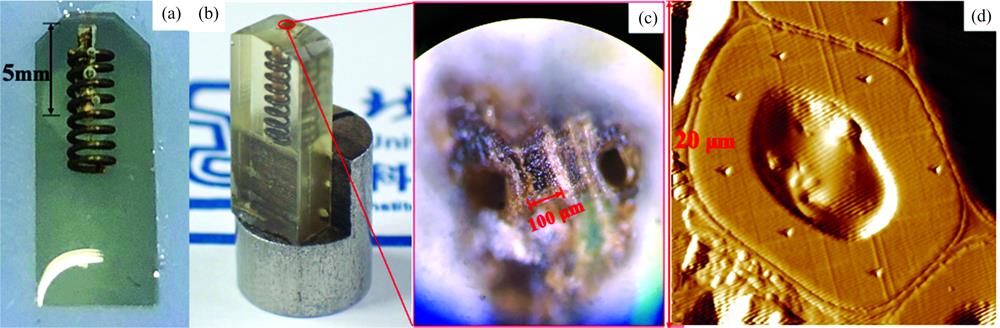
随着社会对木质文物重视程度的提高和现代考古技术的进步, 饱水木质文物得到不断发掘和保护。 饱水木质文物木材的细胞形态和化学结构普遍发生非均匀降解或变化, 成为了不同于健康木材的“新材料”。 PEG法和糖法作为国际通用的脱水加固方法可避免饱水木质文物干燥过程中收缩变形。 本研究选用“小白礁Ⅰ号”沉船主要用材树种柚木(Tectona sp.)为试验对象, 分别使用PEG、 三氯蔗糖和海藻糖加固, 并在开发的适用于脆弱木质文物的非包埋式纳米压痕样品制备方法的基础上, 通过纳米压痕力学技术(NI)评估了三种饱水木质文物常用加固处理方法对考古木材微力学性能的影响; 同时, 结合红外光谱法(FTIR)和热重分析(TGA)方法, 进一步揭示了加固剂种类影响考古木材微力学性能的原因。 研究结果表明: 使用非包埋法制备的纳米压痕样品, 可准确获取加固处理后考古木材细胞壁的纵向弹性模量和硬度; PEG法、 三氯蔗糖法和海藻糖法均可显著提高考古木材木纤维细胞壁的纵向弹性模量和硬度, 三种方法加固处理后的木材的弹性模量比未处理样品分别增加了6.9%, 25.4%和29.1%, 硬度比未处理样品分别增加了9.3%, 25.9%和13.6%。 红外光谱试验结果表明PEG、 三氯蔗糖和海藻糖均进入了考古木材细胞腔等内部组织结构, 热重分析结果证实部分加固剂进入了木材细胞壁, 是细胞壁强度提高的主要原因。 总之, 三氯蔗糖和海藻糖较适用于饱水考古木材的脱水加固, 加固效果优于PEG, 其中三氯蔗糖的加固效果最佳。 研究结果为饱水木质文物加固性能的准确评估提供了方法参考, 为沉船等饱水木质文物的加固与保护提供了科学依据。
Abstract
Waterlogged wooden cultural relics have been constantly excavated and preserved, driven by increasing public interest and upgrading archaeological technologies. Wood cells' morphology and chemical structure from waterlogged wooden relics normally undergo non-uniform degradation or changes, presenting a different “new material” from sound woods. PEG and sugars have been widely applied for consolidation. This study selected teak (Tectona sp.), the main timber species of the “Xiaobaijiao Ⅰ” shipwreck, as the research object. Based on the developed sample preparation method of nonembedded nanoindentation suitable for wooden cultural relics. The PEG, sucralose and trehalose treated samples were evaluated by Nanoindentation technology (NI) and studied by infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The results showed that samples prepared by the nonembedded method could accurately measure the longitudinal elastic modulus and hardness of wood cell wall, and the PEG, sucralose and trehalose were able to significantly improve the elastic modulus of fiber cell wall respectively, by 6.9%, 25.4% and 29.1% compared to untreated samples, and increase its hardness by 9.3%, 25.9% and 13.6%. Infrared spectroscopy showed that PEG, sucralose and trehalose penetrated the wood, and thermogravimetric analysis confirmed that partial consolidants could enter the wood cell wall, which was the main reason for the improvement of cell wall strength. In general, sucralose and trehalose were more suitable than PEG for consolidating the waterlogged archaeological wood, with sucralose being the most effective consolidant in this research. This research provided a proven method for the accurate performance evaluation of consolidates for waterlogged wooden cultural relics such as shipwrecks and could provide a scientific basis for their consolidation and conservation.
韩刘杨, 韩向娜, 田兴玲, 周海宾, 殷亚方, 郭娟. 红外光谱和热重分析法评估三种加固剂对“小白礁Ⅰ号”考古木材微力学性能的影响[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2022, 42(5): 1529. Liu-yang HAN, Xiang-na HAN, Xing-ling TIAN, Hai-bin ZHOU, Ya-fang YIN, Juan GUO. Effects of Three Kinds of Consolidants on the Micromechanical Properties of Archaeological Wood From “Xiaobaijiao Ⅰ” Shipwreck by Infrared Spectroscopy and Thermogravimetric Analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2022, 42(5): 1529.