光子学报, 2023, 52 (10): 1052401, 网络出版: 2023-12-05
基于人工局域表面等离激元的高灵敏传感研究进展(特邀)
Progress in Highly Sensitive Sensing Based on Spoof Localized Surface Plasmons(Invited)
电磁谐振 人工局域表面等离激元 传感增强 传感灵敏度 传感系统 Electromagnetic resonances Spoof localized surface plasmons Sensing enhancements Sensing sensitivity Sensing systems
摘要
人工局域表面等离激元是一种基于表面等离激元超材料的电磁谐振模式,在微波、毫米波和太赫兹频段可实现深亚波长场束缚、高品质因子、高介电灵敏度等优异传感特性,并且与平面印刷电路工艺兼容,易于和信号检测电路、无线通信电路集成,因此在小型化便携式的物联传感领域展现出广阔的应用前景。本文重点介绍人工局域表面等离激元传感的新原理、相关技术及典型应用。在传感新原理方面,讨论了新型人工局域表面等离激元的谐振结构、电磁模式、以及涡旋波传感原理;在传感指标提升技术方面,探讨了模式间耦合和有源放大两种传感增强方法;在应用探索方面,回顾了人工局域表面等离激元在溶液浓度传感、细胞传感和力学量传感等方向的代表性工作,介绍了小型化人工局域表面等离激元传感系统的最新进展。最后,对人工局域表面等离激元传感的发展趋势进行了讨论和展望。
Abstract
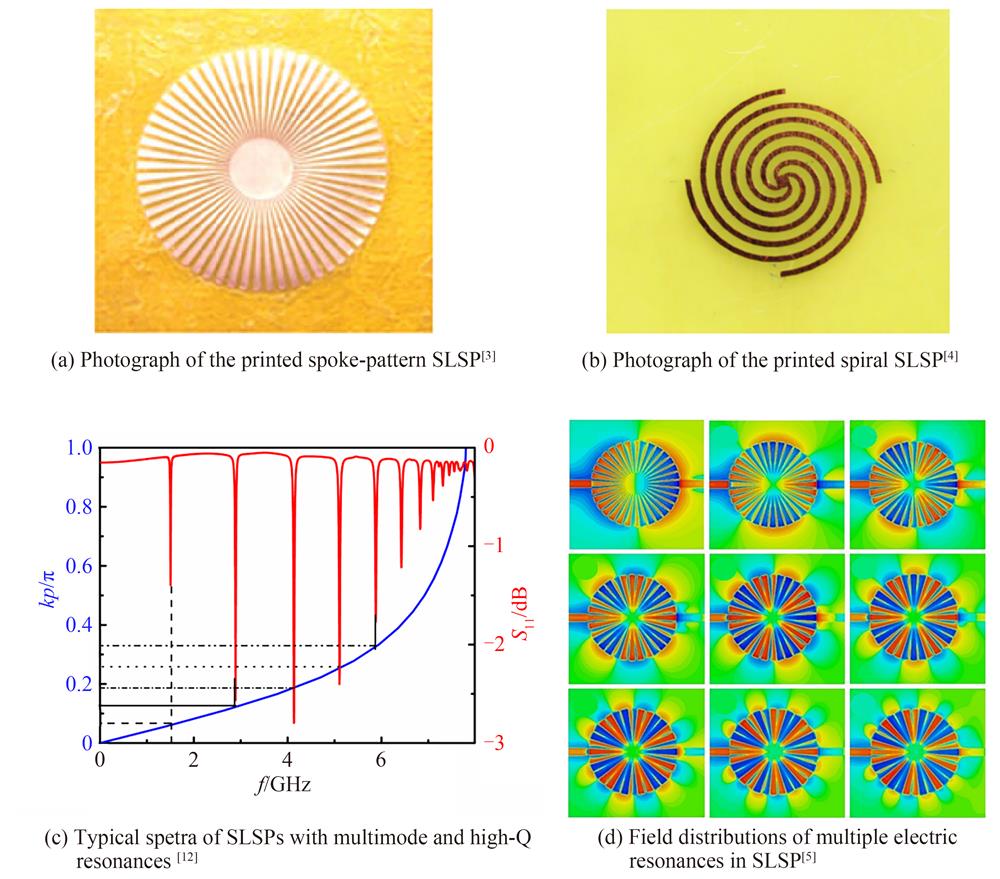
Spoof Localized Surface Plasmons (SLSPs) are electromagnetic resonance modes in the microwave, millimeter-wave, and terahertz frequency bands, which can mimic the modal profiles and physical properties of optical localized surface plasmons based on plasmonic metamaterials. Due to the lower metal loss in these frequencies and the flexibilities in metamaterial designs, SLSPs can achieve excellent sensing characteristics such as deep-subwavelength field confinements, high quality factors, and high dielectric sensitivity. The SLSP concept was theoretically proposed by Pendry and Garcia-Vidal et al in 2012. In 2014, Cui et al proved that SLSPs can be sustained by ultrathin metal patterns on printed circuit boards, and envisioned SLSPs' applications in both the printed circuits and the integrated circuits. Meanwhile, the SLSPs can be integrated with passive and active lumped devices, and exhibit high flexibilities in integration with the signal detection circuits and the wireless communication circuits. Therefore, SLSPs present promising application potentials in compact and portable sensing systems for the internet of things.This paper reviews the representative progress in recent years in the SLSP sensing area. In the first section, some novel resonance modes and resonance structures are introduced, with discussions on their promotions in the sensing indices. Hot topics such as plasmonic skyrmions, exceptional points, quasi-bound states in the continuum, and vortex mode are discussed here. Those novel SLSP electromagnetic modes provide new ideas for sensing. The spiral phase wavefronts of vortex waves can provide rich information and result in a high ability to detect multiple physical quantities. Novel resonance structures including fan-shaped ones, the three-dimensional ones based on origami metamaterials are introduced too, which provide new ideas and methods for SLSP sensor design. The resonance characteristics of SLSP in the terahertz band and its applications are also overviewed. Besides the widely studied array structures under space-wave excitation, it is an irresistible trend to develop terahertz sensing in semiconductor integrated circuits. SLSP sensors pioneers the way for the development of on-chip terahertz biosensing systems. In the second section, the sensing enhancement techniques based on mode coupling and active amplifiers are discussed. Hot spot structures where electromagnetic energy converges can be constructed based on mode coupling inside SLSPs, and can result in highly sensitive hybridization modes. Loading active amplifiers can effectively compensate for the losses in the sensing structure and can improve the quality factor and the excitation efficiency. These techniques supply reliable solutions for the improvements of SLSP sensing indices. Then, typical application scenarios of SLSP sensing are introduced, ranging from solution concentration sensing, bacteria and cancer cell sensing, and mechanical sensing based on flexible SLSP circuits. SLSP can compress the microwave electromagnetic resonances into a deep sub-wavelength scale, greatly enhance the sensing sensitivity to tiny biomedical targets, and break the bottleneck of microwave resonance sensing limited by long wavelengths. Finally, we introduce a recently reported SLSP sensing system, which integrates the SLSP sensor with its signal detection circuits and the Bluetooth module into an ultra-compact size of 1.8 cm×1.2 cm. The signal-noise ratio of this ultracompact sensing system can reach a high value of 69 dB and the system is validated by explosive acetone vapor sensing.The review paper ends with prospective discussions of the SLSP sensing development. Novel principles and phenomena still emerge continuously in the SLSP area, while ultra-compact sensing systems have been constructed yet. We believe that it is good timing now to land the SLSP concept on practical applications. In the following research, there is still a large space for both scientific research and application explorations of SLSP sensing. The mutual promotion of scientific and engineering investigations will surely stimulate the continuous development of SLSP sensing.
白天硕, 王莞竹, 张龙飞, 张璇如, 崔铁军. 基于人工局域表面等离激元的高灵敏传感研究进展(特邀)[J]. 光子学报, 2023, 52(10): 1052401. Tianshuo BAI, Wanzhu WANG, Longfei ZHANG, Xuanru ZHANG, Tiejun CUI. Progress in Highly Sensitive Sensing Based on Spoof Localized Surface Plasmons(Invited)[J]. ACTA PHOTONICA SINICA, 2023, 52(10): 1052401.