面向黏膜组织诊断的亚扩散域漫反射与荧光联合光谱测量系统  下载: 544次
下载: 544次
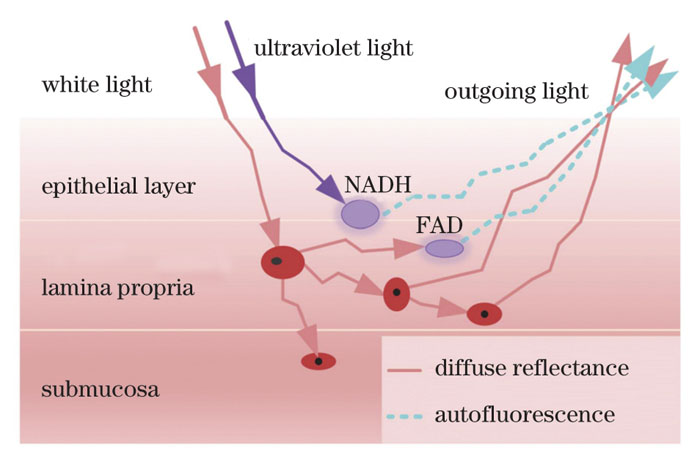
Early-stage detection and treatment of mucosal tissue lesions are effective means for curbing mucosal cancer. Histopathological examination is the gold standard for the clinical examination of mucosal tissue lesions. However, this method is invasive and easily affected by doctors' experience and is unsuitable for large-scale and rapid screening of precancerous lesions. Spectral technologies can detect the changes in optical properties caused by the morphological changes of mucosal tissue cells in a real-time, in vivo, and noninvasive way, and can objectively analyze them using reasonable algorithms, which provides low-cost and large-scale screening of mucosal tissue lesions. In this study, we develop a mucosal lesion diagnosis system using joint sub-diffusive domain diffuse reflectance and fluorescence spectroscopy to improve sensitivity and specificity. The system can efficiently collect diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence spectra of mucosal tissues at varying depths. Furthermore, it extracts the characteristics of spectral data to realize the rapid screening of mucosal lesions and the real-time diagnosis of malignant tumor grade.
In this study, the mucosal lesion diagnostic system is composed of a light source module, detection module, main control module, man-machine interface module, and an optical fiber probe to measure the joint spectrum signal and real-time analysis and display tissue lesion information. First, we evaluate the stability of the light source module of the system using phantom experiments. Next, the in vitro experiments are conducted to verify the ability of the system to distinguish different tissues, including chicken and pork tissues. In the spectral pretreatment, the spectral data are preprocessed by smoothing and normalization to eliminate the system and environmental noise. Furthermore, the first derivative, principal component analysis, kurtosis, skewness, mean, and variance are used as input information for subsequent tissue classification to extract spectral features and realize the feature extraction. Next, we employ the support vector machine to distinguish the spectral characteristics of different tissues due to its advantages in dealing with small sample pattern recognition. To further verify the effectiveness and recognition ability of the proposed system, we conduct in vivo experiments on the human oral mucosa. The diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence spectra of the lower lip and tongue mucosal tissues are collected for tissue spectrum comparison.
The results of the phantom experiments show that the proportion of the intensity standard deviation of the two LEDs in the overall intensity is below 1%, implying that the system has excellent measurement stability (Fig. 7). The in vitro tissue experiments show that the system has excellent classification ability (the classification accuracy of different tissues is above 98%; the classification accuracy of different parts in a specific tissue is above 74%) (Tables 1 and 2). The in vivo experiments preliminarily verify the application potential of the system in mucosal tissue diagnosis and classification (Fig. 10).
In this study, we develop a mucosal lesion diagnosis system using joint sub-diffusive domain diffuse reflectance and fluorescence spectroscopy, which is noninvasive, operates in real-time, and is cost effective. First, the phantom with stable diffuse reflectance verifies that the system meets the required steady-state measurement. Next, the classification results of different tissues by the diffuse reflectance and autofluorescence spectra verify that our proposed system can realize the classification of different in vitro tissues. Finally, the in vivo experiments on human oral mucosa preliminarily verify that the system has the ability of in vivo detection. In the future, the detection of diseased mucosal tissue will be performed to further explore the clinical potential of the developed system. These findings support the utility of the system. In conclusion, the system provides strong systematic support and is an important method of reference for low-cost, large-scale screening of precancerous lesions of mucosal tissue.
郑杰, 刘东远, 张琪, 张丽敏, 高峰. 面向黏膜组织诊断的亚扩散域漫反射与荧光联合光谱测量系统[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(24): 2407101. Jie Zheng, Dongyuan Liu, Qi Zhang, Limin Zhang, Feng Gao. Mucosal Lesion Diagnosis System Using Joint Sub-Diffusive Domain Diffuse Reflectance and Fluorescence Spectroscopy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(24): 2407101.