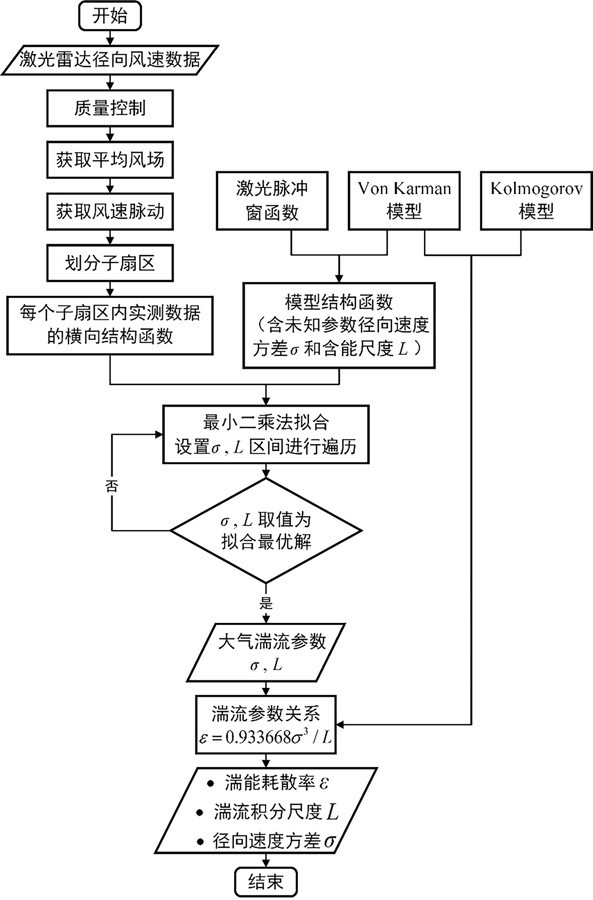
基于相干多普勒激光雷达的斜程湍流参数反演方法研究
陈晓敏, 张洪玮, 孙康闻, 吴松华. 基于相干多普勒激光雷达的斜程湍流参数反演方法研究[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2023, 18(1): 1.
Xiaomin CHEN, Hongwei ZHANG, Kangwen SUN, Songhua WU. Inversion methods of slant turbulence parameters based on coherent Doppler lidar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2023, 18(1): 1.
[1] International Civil Aviation Organization. Safety report [R]. 2020.
[2] 刘艳华, 李富余, 张宏升, 等. 超声风速仪与三轴风速仪测风的比较研究[J]. 气象水文海洋仪器, 2003, 20(3): 7-16.
Liu Y H, Li F Y, Zhang H S, et al. The comparison between sonic-anemometer and three-component propeller anemometer[J]. Meteorological Hydrological and Marine Instrument, 2003, 20(3): 7-16.
[3] 李柏, 古庆同, 李瑞义, 等. 新一代天气雷达灾害性天气监测能力分析及未来发展[J]. 气象, 2013, 39(3): 265-280.
Li B, Gu Q T, Li R Y, et al. Analyses on disastrous weather monitoring capability of CINRAD and future development[J]. Meteorological Monthly, 2013, 39(3): 265-280.
[4] Armijo L. A theory for the determination of wind and precipitation velocities with Doppler radars[J]. Journal of the Atmospheric Sciences, 1969, 26(3): 570-573.
[5] Frehlich R, Cornman L. Estimating spatial velocity statistics with coherent Doppler lidar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2002, 19(3): 355-366.
[6] Smalikho I, Köpp F, Rahm S. Measurement of atmospheric turbulence by 2-μm Doppler lidar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2005, 22(11): 1733-1747.
[7] Frehlich R, Meillier Y, Jensen M L, et al. Measurements of boundary layer profiles in an urban environment[J]. Journal of applied meteorology and climatology, 2006, 45(6): 821-837.
[8] Frehlich R. Doppler lidar measurements of winds and turbulence in the boundary layer[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2008, 1: 012017.
[9] Chan P W, Lee Y F. Application of short-range lidar in wind shear alerting[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, 2012, 29(2): 207-220.
[10] Smalikho I N, Banakh V A. Measurements of wind turbulence parameters by a conically scanning coherent Doppler lidar in the atmospheric boundary layer[J]. Atmospheric Measurement Techniques, 2017, 10(11): 4191-4208.
[11] Zhai X C, Wu S H, Liu B Y. Doppler lidar investigation of wind turbine wake characteristics and atmospheric turbulence under different surface roughness[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(12): A515-A529.
[12] 翟晓春. 相干多普勒激光雷达的湍流探测与ALADIN机载样机A2D风场反演方法研究 [D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2019.
ZhaiX C. Atmospheric Turbulence Detection Using Coherent Doppler Lidar and Wind Field Retrieval of ALADIN Airborne Demonstrator(A2D) [D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2019.
[13] KwongK M, ChanP W. LIDAR-based turbulence intensity calculation along glide paths [C]. 14th Coherent Laser Radar Conference, 2007.
[14] Chan P W. LIDAR-based turbulence intensity calculation using glide-path scans of the Doppler Light Detection And Ranging (LIDAR) systems at the Hong Kong International Airport and comparison with flight data and a turbulence alerting system[J]. Meteorologische Zeitschrift, 2010, 19(6): 549-563.
[15] Hon K K, Chan P W. Application of LIDAR-derived eddy dissipation rate profiles in low-level wind shear and turbulence alerts at Hong Kong International Airport[J]. Meteorological Applications, 2014, 21(1): 74-85.
[16] Kolmogorov A N. Dissipation of energy in the locally isotropic turbulence[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1991, 434(1890): 15-17.
[17] MoninA S, YaglomA M, LumleyJ L. Statistical Fluid Mechanics: Mechanics of Turbulence [M]. Array Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1971.
[18] Zhang H W, Wu S H, Wang Q C, et al. Airport low-level wind shear lidar observation at Beijing Capital International Airport[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2019, 96: 113-122.
[19] Zhang H W, Liu X Y, Wang Q C, et al. Low-level wind shear identification along the glide path at BCIA by the pulsed coherent Doppler lidar[J]. Atmosphere, 2021, 12(1): 50.
[20] 刘晓英, 吴松华, 张洪玮, 等. 基于相干多普勒测风激光雷达的不同成因类型的低空风切变观测[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2020, 39(4): 491-504.
陈晓敏, 张洪玮, 孙康闻, 吴松华. 基于相干多普勒激光雷达的斜程湍流参数反演方法研究[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2023, 18(1): 1. Xiaomin CHEN, Hongwei ZHANG, Kangwen SUN, Songhua WU. Inversion methods of slant turbulence parameters based on coherent Doppler lidar[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2023, 18(1): 1.