光电工程, 2022, 49 (12): 220008, 网络出版: 2023-01-17
量子点微显示技术研究进展  下载: 513次
下载: 513次
Research progress of quantum dot micro display technology
摘要
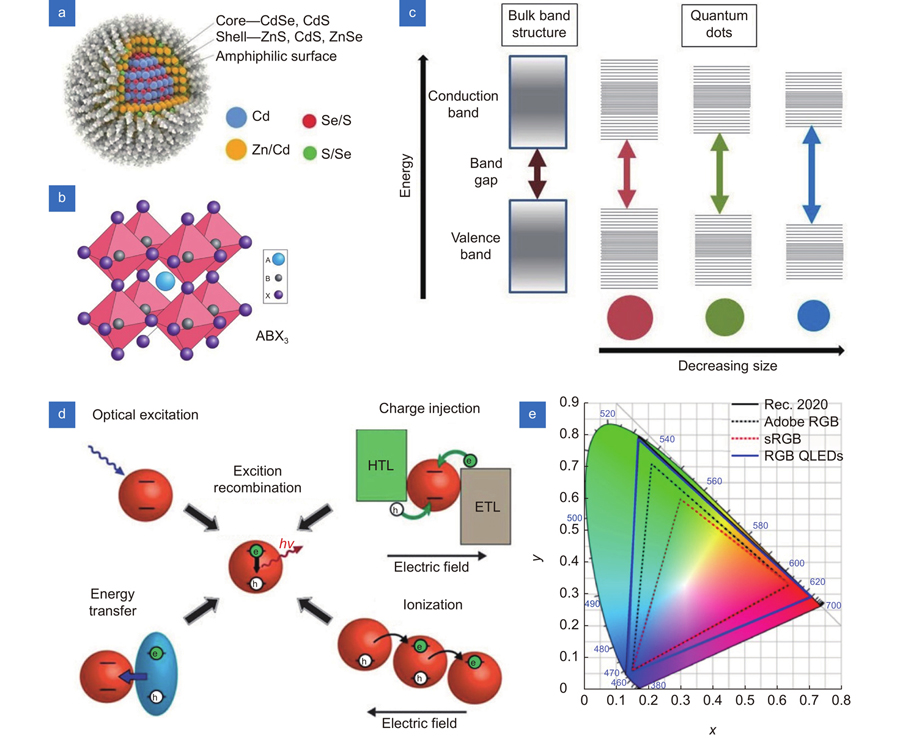
量子点是一种具有量子限域效应的半导体纳米晶,近年来,以其优异的光电特性得到了广泛关注。量子点具有发光效率高、发光波长可调、发光半峰宽窄、可溶液法低成本制备等优势,已被大量应用于显示领域,成为了新型显示的核心材料之一。微显示技术一般应用于有效显示区域对角线长度小于1 inch 的近眼显示场景中,近年来虚拟现实、增强现实等近眼显示场景的兴起,对高亮度、高像素密度、全彩色的微显示技术提出了更高的要求。本文将从量子点应用于高亮度、高像素密度的全彩微显示技术的角度出发,从光致发光和电致发光两条技术路线对现有的进展进行回顾和总结,最后对量子点应用于微显示技术面临的机遇和挑战进行展望。
Abstract
Overview: Quantum dot is a kind of semiconductor nanocrystal with a quantum confinement effect. Recently, quantum dots have been applied for display due to their advantages including high photoluminescent efficiency, tunable emission wavelength, narrow emission spectrum, and low-cost solution process. In this paper, we focus on the application of quantum dots in microdisplay. With the rising near-eye display demands such as AR/VR, the realization of full color, high efficiency, and high luminance microdisplay attracts many attentions. However, the realization of the target microdisplay is difficult due to the high-cost mass transfer technology in micro-LED and the insufficient luminance in micro-OLED. Here, the photoluminescent (PL) and electroluminescent (EL) quantum dots can provide new routes for microdisplay. For PL, quantum dots can work as color conversion material for micro-LED. The multiple-time mass transfer can be avoided with the combination of red and green quantum dots and blue micro-LED. Meanwhile, the color gamut can be improved due to the narrow FWHM of quantum dot emission. For EL, RGB quantum dots can work as an emission layer in QLED, and the RGB micro-QLED can be applied for microdisplay directly with a compact and high-efficiency system. Compared with OLED, the QLED can realize higher luminance due to the inherent stability of the inorganic quantum dot, which is more suitable for AR display requiring high luminance. The patterning of quantum dot layer is the first step for the application in microdisplay. For both PL and EL applications, a high pixel density, high pixel uniformity, high pixel consistency, and low-cost patterning method is required. For the quantum dot color conversion layer in PL application, a high optical density is required for the sufficient absorption of the blue light. For the quantum dot emission layer in EL application, the uniform and small roughness surface quantum dot layer is required with few damages to the quantum dots to ensure the good performance of QLED devices. There are several patterning methods have been reported for quantum dots including inkjet printing, photolithography, transfer printing, electrophoretic deposition, in situ fabrication, and optical micro cavity. However, it is still challenging to find a perfect patterning method for the quantum dot layer. For PL application, the stability of quantum dot under long time high-intensity blue light excitation is a big problem due to the photoinduced quenching and oxidation. For EL application, compared with red and green QLED, the peak luminance, efficiency, and lifetime of blue QLED needs to be further improved by optimizing the blue quantum dots and device structure to satisfy the requirement of the display application.The quantum dot is a kind of semiconductor nanocrystal with quantum confinement effect, which attracts a lot of attention due to the excellent optoelectronic properties and has been widely used in the display area. The quantum dot become one of the core materials of display with several advantages including the high luminance efficiency, tunable emission wavelength, narrow FWHM and low-cost solution fabrication. Micro display technology is applied in the near eye display scenario with small effective display area (diagonal < 1 inch). Recently, the rising of VR/AR application scenarios require micro display technology with higher luminance, higher pixel density, and full color display. In this paper, we review the current progress of the quantum dot in micro display from photoluminescence and electroluminescence technique routes. The chances and challenges of the quantum dot in micro display are also summarized.
叶泰康, 李德鹏, 孙小卫, 王恺. 量子点微显示技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(12): 220008. Taikang Ye, Depeng Li, Xiaowei Sun, Kai Wang. Research progress of quantum dot micro display technology[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2022, 49(12): 220008.