光子学报, 2024, 53 (2): 0206004, 网络出版: 2024-03-28
空间碎片干扰下的卫星光网络路由算法研究
Research on Routing Algorithms for Satellite Optical Networks under Space Debris Interference
激光通信 卫星路由 链路状态路由算法 空间碎片 Laser communications Satellite routing Link-state routing algorithms Space debris
摘要
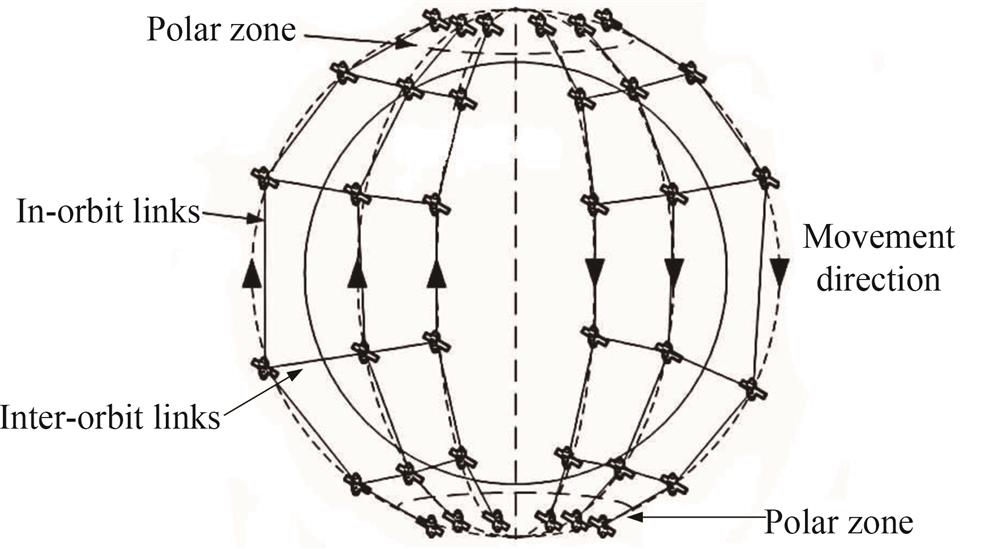
针对低轨卫星激光通信中空间碎片可能造成的星间链路中断问题,提出一种方向增强的链路状态路由算法。首先搭建了卫星通信的网络拓扑结构,对空间碎片的运动模型和卫星的运动模型进行联合建模仿真,得到卫星与碎片的相对位置并进行星间可见性分析,提出了方向影响因子和方向增强指数,结合星间链路距离及传输时延综合考虑链路代价,从而选择合适的传输路径方向,依次在每个卫星节点对间进行最小路径选择,并以路由跳数为评价指标。仿真结果表明,在有空间碎片存在的环境中,所提算法能够在不牺牲通信质量的前提下,实现路由跳数相比Dijkstra算法降低14%,传输时延相比Dijkstra算法减少17%。
Abstract
With the advancement of the construction of space, space and ground integrated information networks, satellite communication systems nowhave a higher requirements for information transmission rate, satellite node storage capacity, satellite coverage and security. Traditional microwave communication methods are limited by bandwidth, speed, geographical location, spectrum, etc., and will be difficult to meet the ultra-high speed and ultra-large capacity communication requirements of multimedia broadband services for satellite networks. At the same time, laser communications are gradually becoming an important technical means for satellite communications due to its advantages of high transmission rate, high security and reliability, strong confidentiality, small terminal equipment, light weight and low power consumption. To achieve all-round coverage of communication signals, laser networking based on dynamic satellites and the establishment of high-speed, low-latency, high-reliability and large-capacity satellite communication systems will become the future development trend of satellite communication. In the future, space will inevitably gather a large number of products of human space activities, including rockets, satellites, and rocket ejections. As humans develop space, the increase in these space debris will also bring a series of hazards. Existing space debris research mainly focuses on how to avoid collisions with satellites and spacecraft in orbit. In addition, these space debris move randomly in space, which will block point-to-point laser communications. Therefore, more effective research on the reliability of satellite laser communication systems is needed.In order to solve the problem of inter-satellite link interruption that may be caused by space debris in low-orbit satellite laser communications, this paper proposes a Direction-enhanced Link State (DE-LS) routing algorithm. Firstly, the network topology of satellite communication is built. The polar orbit constellation model is selected. According to the orbital plane and the number of satellites, an initial and constant address is set for each satellite in the polar orbit constellation. Based on the changes in the satellite node addresses of the starting and ending points in different transmission tasks, the Direction Influencing Factor (DIF) is introduced. Then, based on the celestial motion patterns of satellites and space debris in polar orbit constellations. A joint simulation model of space debris and satellites is constructed to obtain the relative positions of satellites and debris at a given moment and to perform inter-satellite visibility analysis.. Based on the inter-satellite visibility data, a Direction Enhancement Index (DEI) is proposed corresponding to the four directions of each node. The direction impact factor and direction enhancement index are combined with the inter-satellite link distance and transmission delay to comprehensively represent the link cost. The cost is used as a measure to select the shortest path, and the shortest path is selected between each pair of satellite nodes in turn, and the number of routing hops is used as the evaluation index. The simulation experiment is carried out in the Walker constellation. Space debris and satellites are jointly modeled and simulated first. Then, in this environment, two situations are selected: the theoretical minimum number of hops in the same orbit is 4 hops and the theoretical minimum number in different orbits is 7 hops. Taking satellite communications No. 21 and No. 25 and satellite No. 21 and No. 55 as examples for routing selection, routing hop count and transmission delay are used as evaluation indicators, and compared with the Dijkstra routing algorithm, which also solves the shortest path. The simulation results show that the DE-LS algorithm can maintain the theoretical minimum number of hops when the link is interrupted. At the same time, it saves 14% of the hops and reduces the transmission delay by 17% compared with the Dijkstra algorithm, which reflects the effectiveness of DE-LS algorithm in avoiding faulty links.
曹阳, 邢雯珺, 彭小峰, 包朝园. 空间碎片干扰下的卫星光网络路由算法研究[J]. 光子学报, 2024, 53(2): 0206004. Yang CAO, Wenjun XING, Xiaofeng PENG, Chaoyuan BAO. Research on Routing Algorithms for Satellite Optical Networks under Space Debris Interference[J]. ACTA PHOTONICA SINICA, 2024, 53(2): 0206004.