1 中北大学仪器与电子学院,山西 太原 030051
2 中北大学山西省光电信息与仪器工程技术研究中心,山西 太原 030051
3 中北大学前沿交叉科学研究院,山西 太原 030051
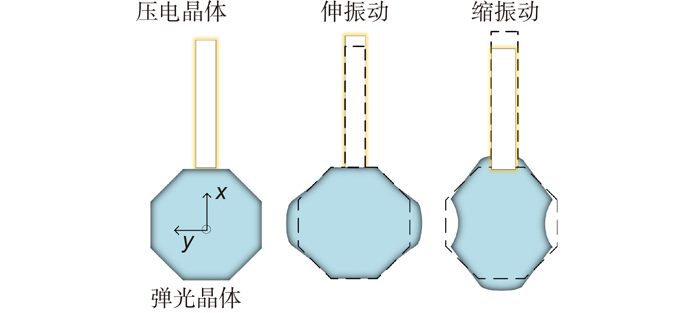
Overview: Overview: Photoelastic modulator, a high-quality thermo-mechanical coupling device composed of isotropic elastic optical crystal and piezoelectric crystal, is widely used in polarization measurement, spectral measurement, and many other fields. A high-voltage resonant circuit is adopted to generate the periodically changing high voltage amplitude, which is applied to both ends of the piezoelectric crystal to drive the photoelastic modulator to perform forced telescopic vibration, thus generating periodic birefringence. Although the quality factor of the photoelastic modulator is as high as 103, the photoelastic crystal in the photoelastic modulator will vibrate in length under the action of the piezoelectric crystal when driven by the high voltage. In addition, there will be thermal dissipation caused by dielectric loss and mechanical loss, some of which exchange heat with the environment, and the rest will raise the temperature of the photoelastic modulator itself. When the heat exchange between the photoelastic modulator and the external environment is happened before the heat balance, the resonant frequency will be changed, which will lead to the reduction of the modulator driving efficiency and the instability of the modulation amplitude. Standing from the perspective of mechanical point, the system can be equivalent to the vibration model of a damped spring-mass system. The system is an underdamped second-order system, and the modulator can also be equivalent to a RLC series resonant circuit from the electrical perspective. Therefore, when the temperature of the modulator changes, its electrical parameters and resonat will also vary. Therefore, this paper first analyzes the resonant frequency characteristics of the photoelastic modulator from the perspective of electricity, and establishes the equivalent circuit model of the photoelastic modulator and the composite resonant network model with the high-voltage resonant drive circuit. Meanwhile, the resonant network is analyzed, and the results show that when the phoyoelastic is in the resonant state, the modulator impedance and the inductance voltage amplitude of the high-voltage resonant circuit are both the smallest. Therefore, this paper designs a control and test system based on field programmable gate array (FPGA) by combining the above mentioned characteristic and applying the amplitude and frequency characteristics of the resonant network. FPGA completes the measurement of the inductance voltage amplitude and the demodulation of the photoelastic modulation signal through the digital phase-locked amplifier. After obtaining the inductance voltage amplitude, the real-time tracking of the minimum value of the inductance voltage amplitude can be obtained by FPGA, so that the tracking of the resonant frequency of the photoelastic modulator can be realized. By demodulating the modulated signal, the calibration optical path system of the photoelastic modulator is also capable of measuring the modulation amplitude of the modulator. Finally, this paper successfully builds the test system, and conducts the frequency sweep test to verify the feasibility of the resonance tracking system. The resonance tracking tests on the modulator are implemented at room temperature - 20℃ & 80℃ respectively. The results show that the test meets the requirements, and the maximum standard deviation of modulation amplitude is lower than 0.83% rad.
弹光调制器 频率跟踪 相位调制幅度 幅频特性 photoelastic modulator frequency tracking phase modulation amplitude amplitude-frequency characteristics 臧晓阳 1,2,3李克武 2,3王志斌 1,2,3,*李坤钰 1,2,3[ ... ]刘坤 1,2,3
1 中北大学仪器与电子学院,山西 太原 030051
2 中北大学前沿交叉科学研究院,山西 太原 030051
3 山西省光电信息与仪器工程技术研究中心,山西 太原 030051
快轴可调弹光调制器(FaaPEM)不仅具有调制频率高、通光孔径大、抗震性能好等优势,同时还弥补了传统弹光调制器相位延迟量和快轴方位角无法灵活调节的不足,在偏振调制以及偏振测量中发挥着重要的作用,FaaPEM是由两个压电驱动器和弹光晶体构成的谐振型光机电器件,在高压谐振状态下,因其自身的温度升高会导致弹光晶体谐振频率与驱动电压的频率不匹配,极大地影响了对于入射光的调制效率。为了确保FaaPEM在工作时的调制能力和稳定性达到最优效果,开展了FaaPEM的稳定闭环控制研究,提出了基于调制信号跟踪和相位调节的闭环驱动控制方法,并对FaaPEM稳定性进行了测试。测试结果表明:该系统加载反馈控制后,半波状态下稳定度达到4.18%,四分之一波状态下稳定度达到3.43%。
物理光学 快轴可调弹光调制器 频率温漂 数字锁相技术 反馈控制 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(7): 0726003
1 中北大学 仪器与电子学院, 山西 太原 030051
2 中北大学 前沿交叉科学研究院, 山西 太原 030051
3 中北大学 山西省光电信息与仪器工程技术研究中心, 山西 太原 030051
针对高精度、快速实时的偏振测量需求, 提出了一种双弹光差频调制的偏振参量测量方法。对偏振测量原理进行了详细分析, 针对双弹光调制器工作控制及信号解调需求, 设计了基于数字可编程逻辑门阵列(FPGA)的多通道数字锁相数据处理方案。FPGA提供一定频率占空比的脉冲宽度调制波(PWM), 经高压谐振电路输出正弦高压驱动弹光调制器工作, 与此同时, 探测器探测到的调制光信号经模数转换器(ADC)采集后进入FPGA中。FPGA提供本地参考信号完成多个频率信号的同时解调, 进而单次测量便可得到4个斯托克斯分量。搭建了实验系统进行了实验验证, 利用旋转1/4波片法建立了偏振产生装置, 实现了对线偏振光、圆偏振光、椭圆偏振光的测量。实验结果表明, 系统测量的相对误差小于0.8%, 重复性标准差小于0.2%, 单次测量时间小于200ms,实现了高精度、重复性好、实时的偏振测量。
弹光调制 偏振测量 斯托克斯矢量 数字锁相 photoelastic modulation polarization measurement stokes vector digital lock-in amplifier
刘梓良 1,2,3,4,*王志斌 2,3,4李克武 2,3,4李晋华 2,3,4[ ... ]李坤钰 2,3,4
1 中北大学 理学院, 山西 太原 030051
2 中北大学 前沿交叉科学研究院, 山西 太原 030051
3 中北大学 南通智能光机电研究院, 江苏 南通 26000
4 山西省光电信息与仪器工程技术研究中心, 山西 太原030051
弹光调制器利用各向同性晶体受迫振动后产生的双折射效应, 对入射的偏振光进行相位调制, 在偏振调制及测量方面具有重要应用。弹光调制器的相位延迟是其关键指标参数, 实际应用时需对驱动电压与相位延迟进行标定。但传统的弹光调制器定标系统中的元件体积较大, 且在使用前完成标定, 误差大。为了使弹光调制系统能够实现实时定标, 达到精确定标的目的, 同时提高使用的便捷性, 提出一种弹光调制器精确定标微系统设计, 通过缩小定标系统元件的尺寸, 集成固定在弹光调制器通光孔径边缘, 实现相位延迟实时标定。经实验验证, 弹光调制器定标微系统的能够在不影响中心光路情况下, 实时精确标定弹光调制器的相位延迟, 实验测试了1h相位延迟定标, 定标结果表明相位延迟偏差小于1%。
光学测量 弹光调制器 精确定标 相位调制 数字锁相技术 optical measurement photoelastic modulator precise calibration phase modulation digital phase-locked technique





